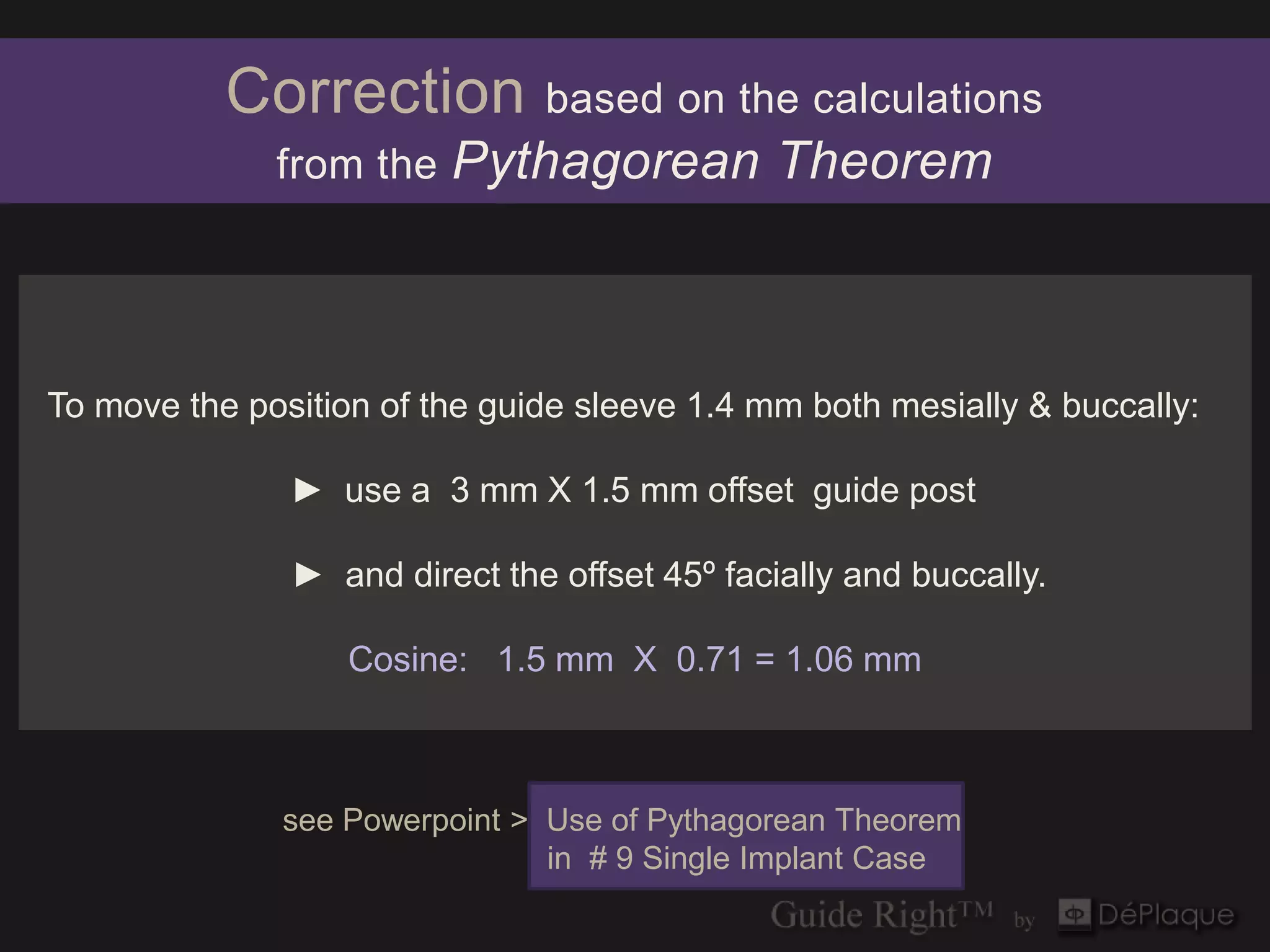
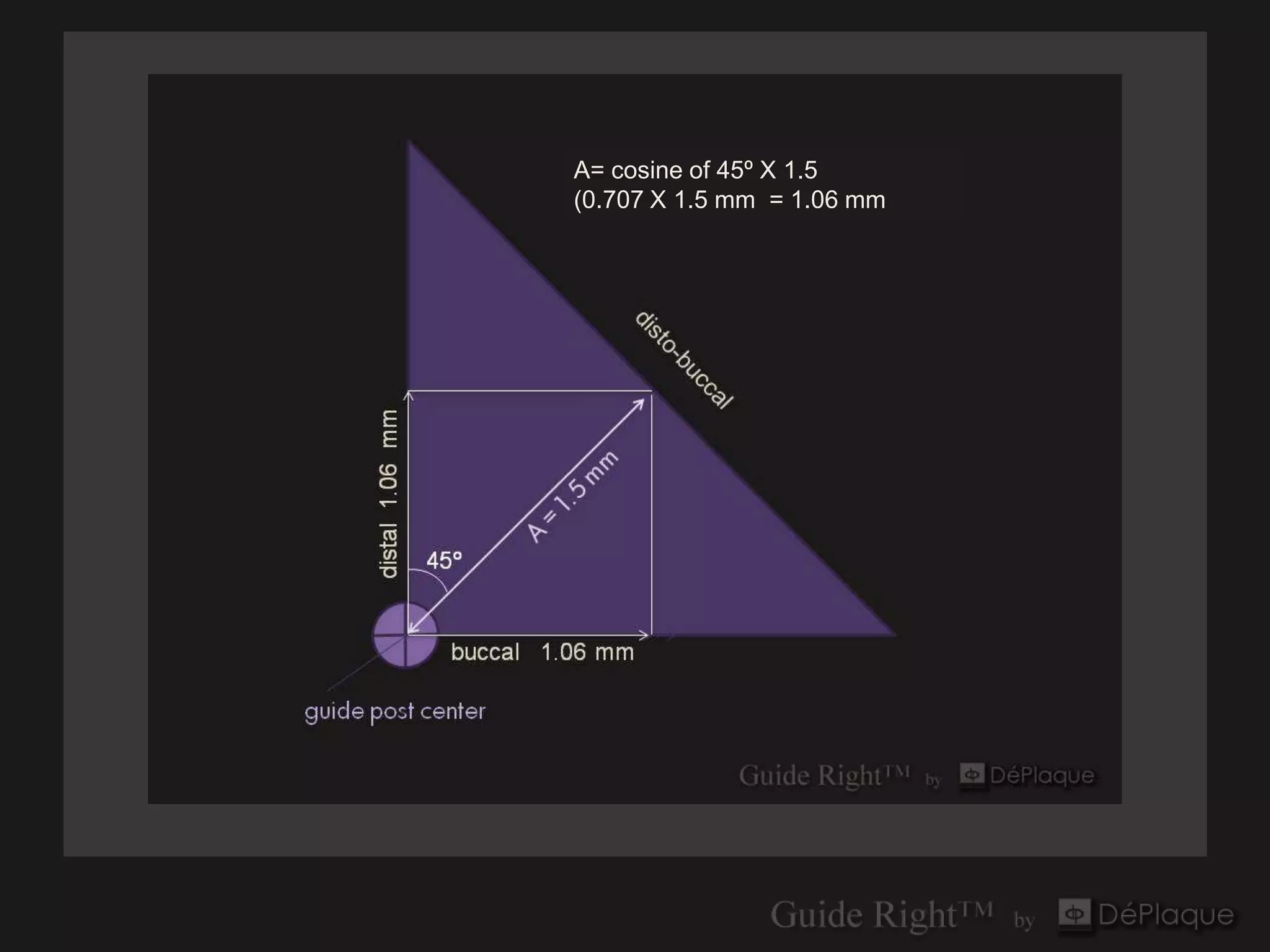
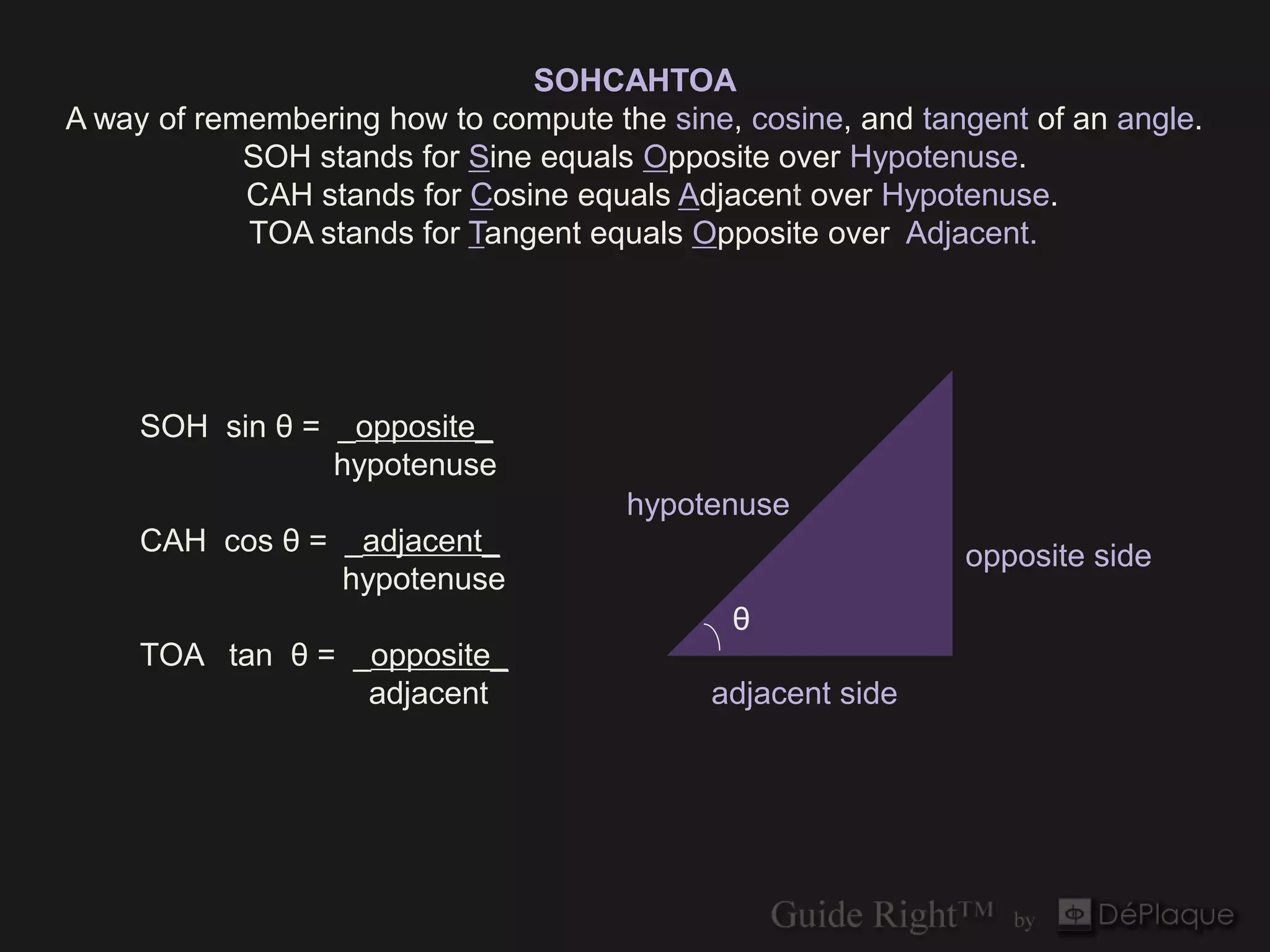
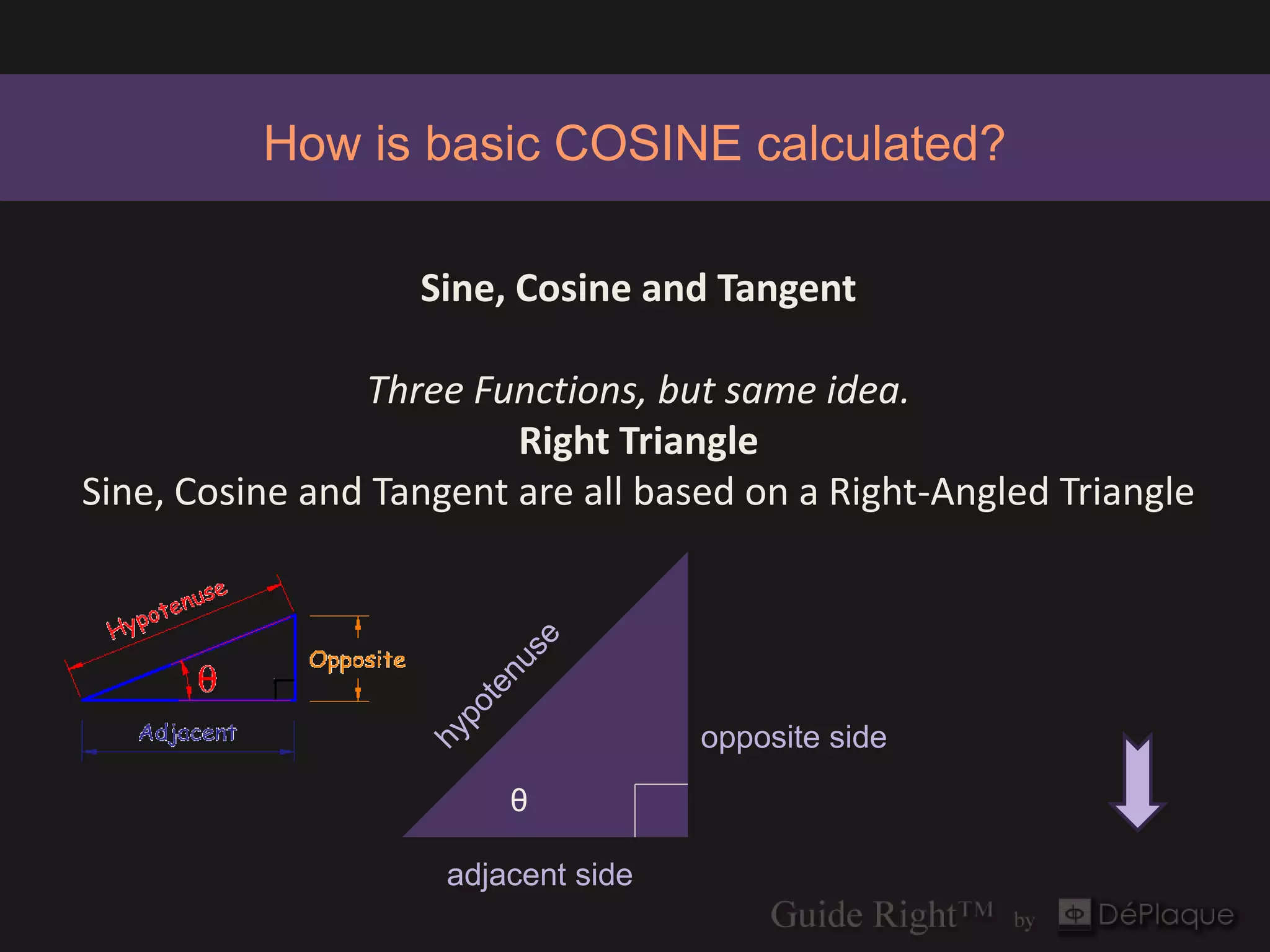
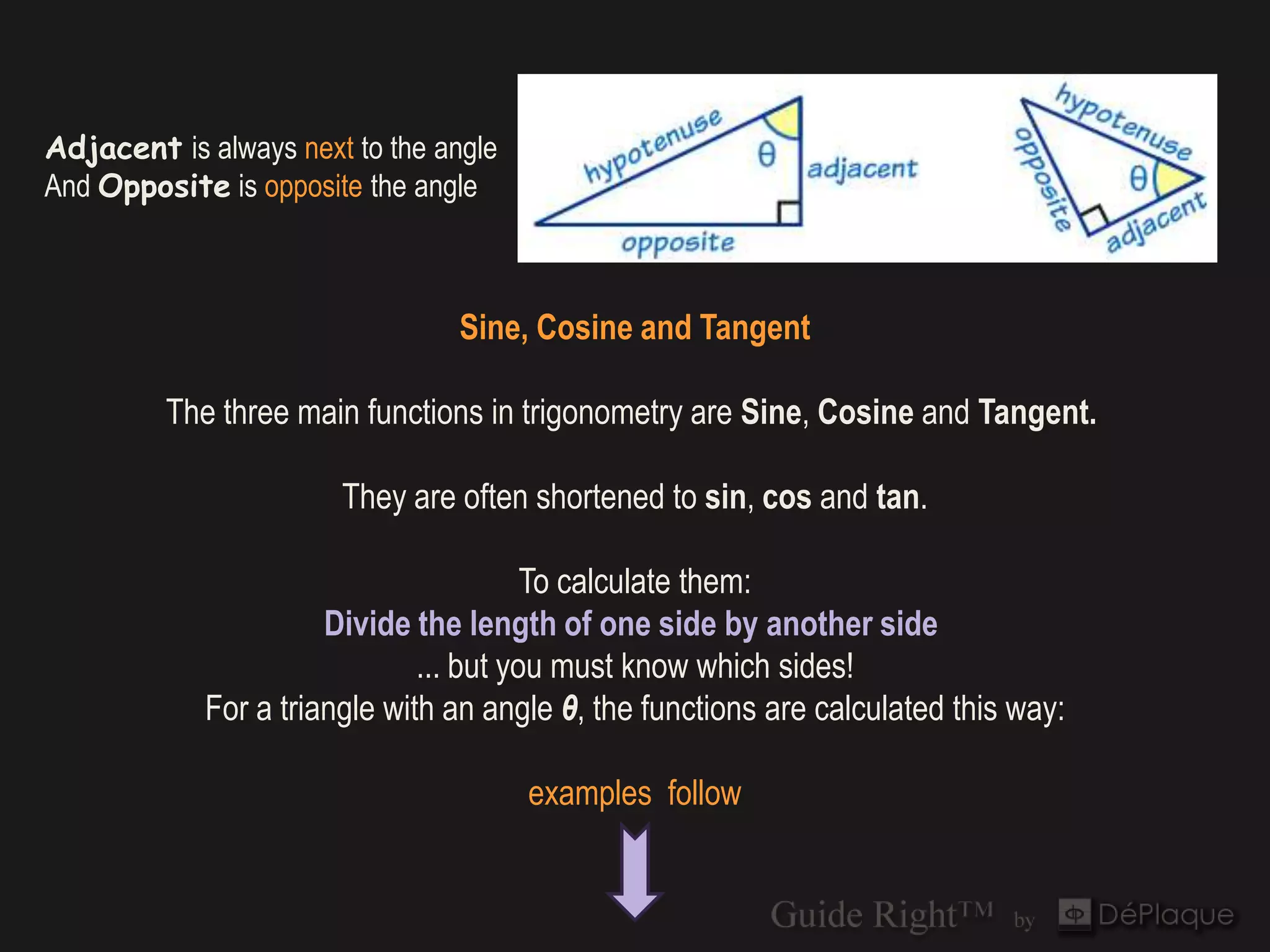
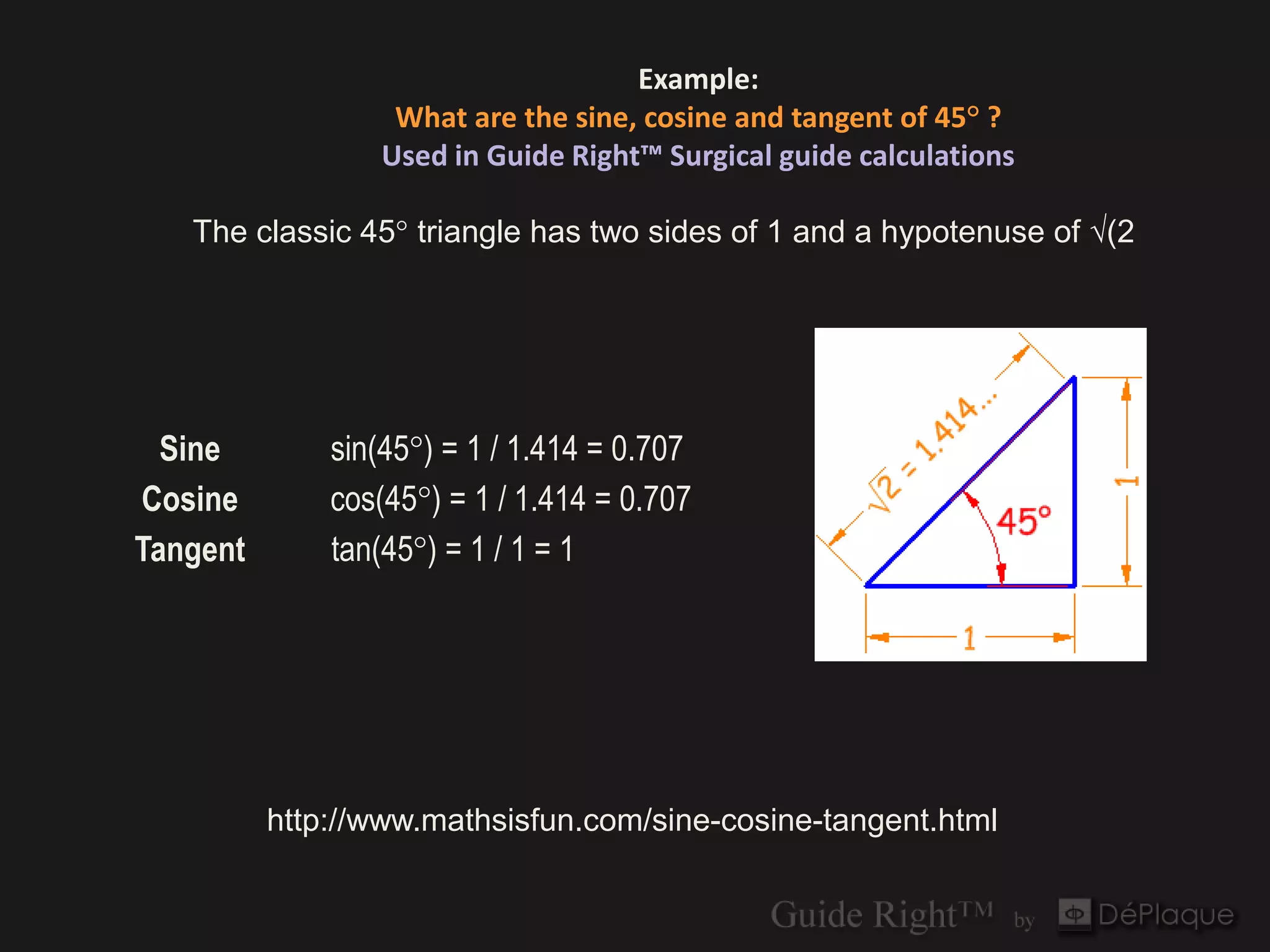
The document discusses the application of the Pythagorean theorem and cosine calculations in surgical guide design, particularly for guide right corrections at a 45° angle. It provides formulas for calculating sine, cosine, and tangent functions in relation to right triangles, using various examples to illustrate these concepts. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of correctly identifying triangle sides when performing these calculations.