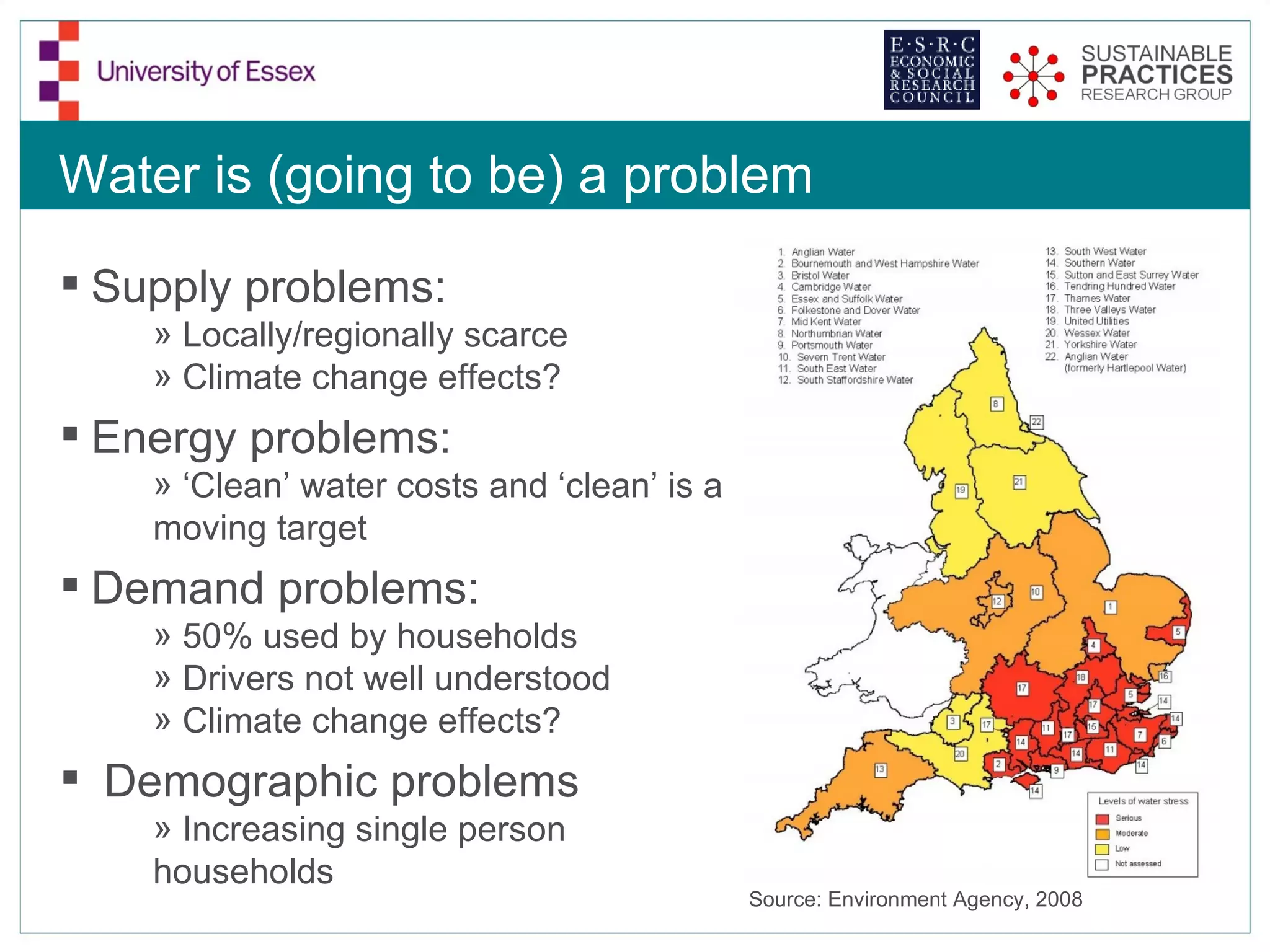
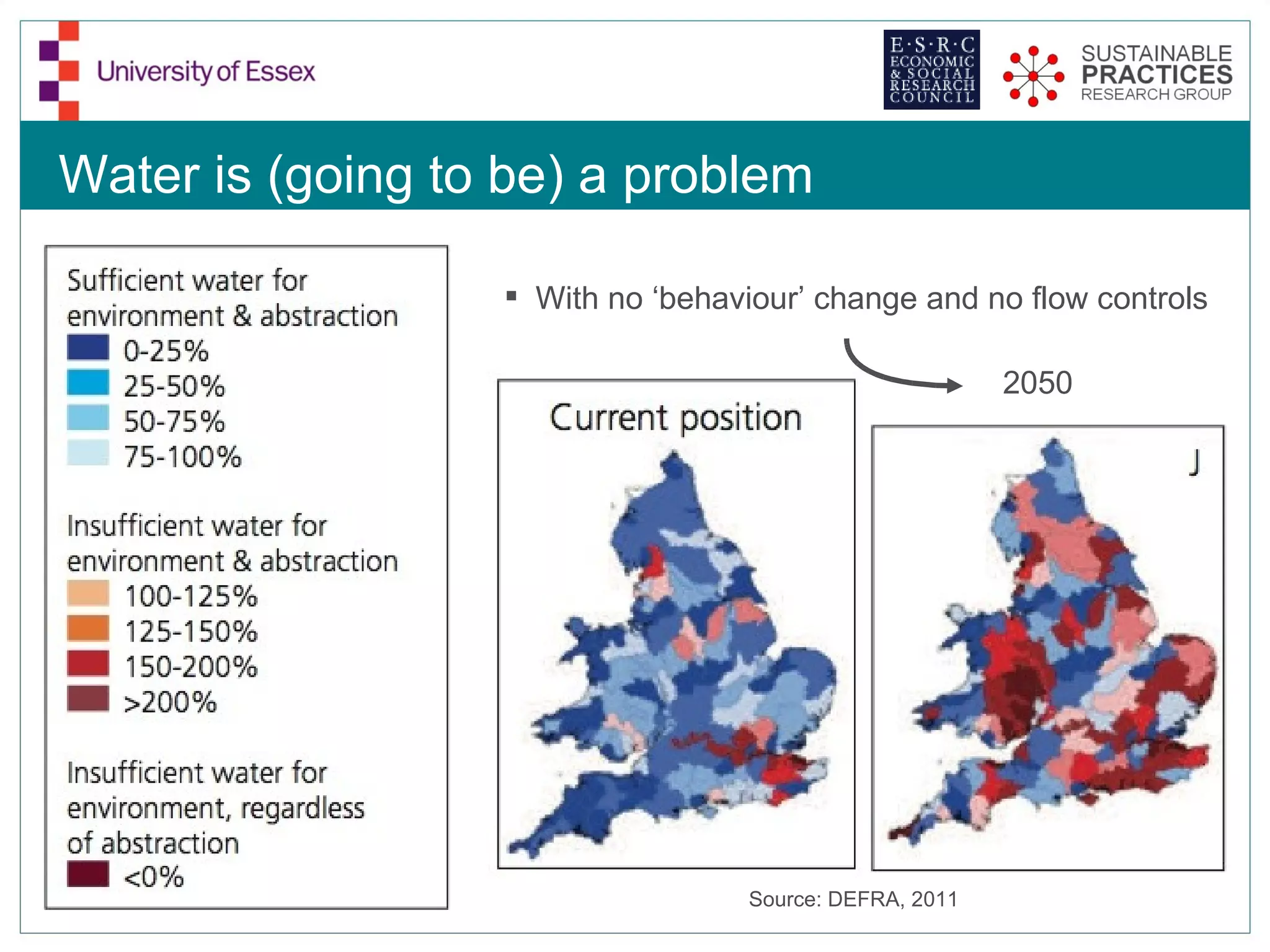
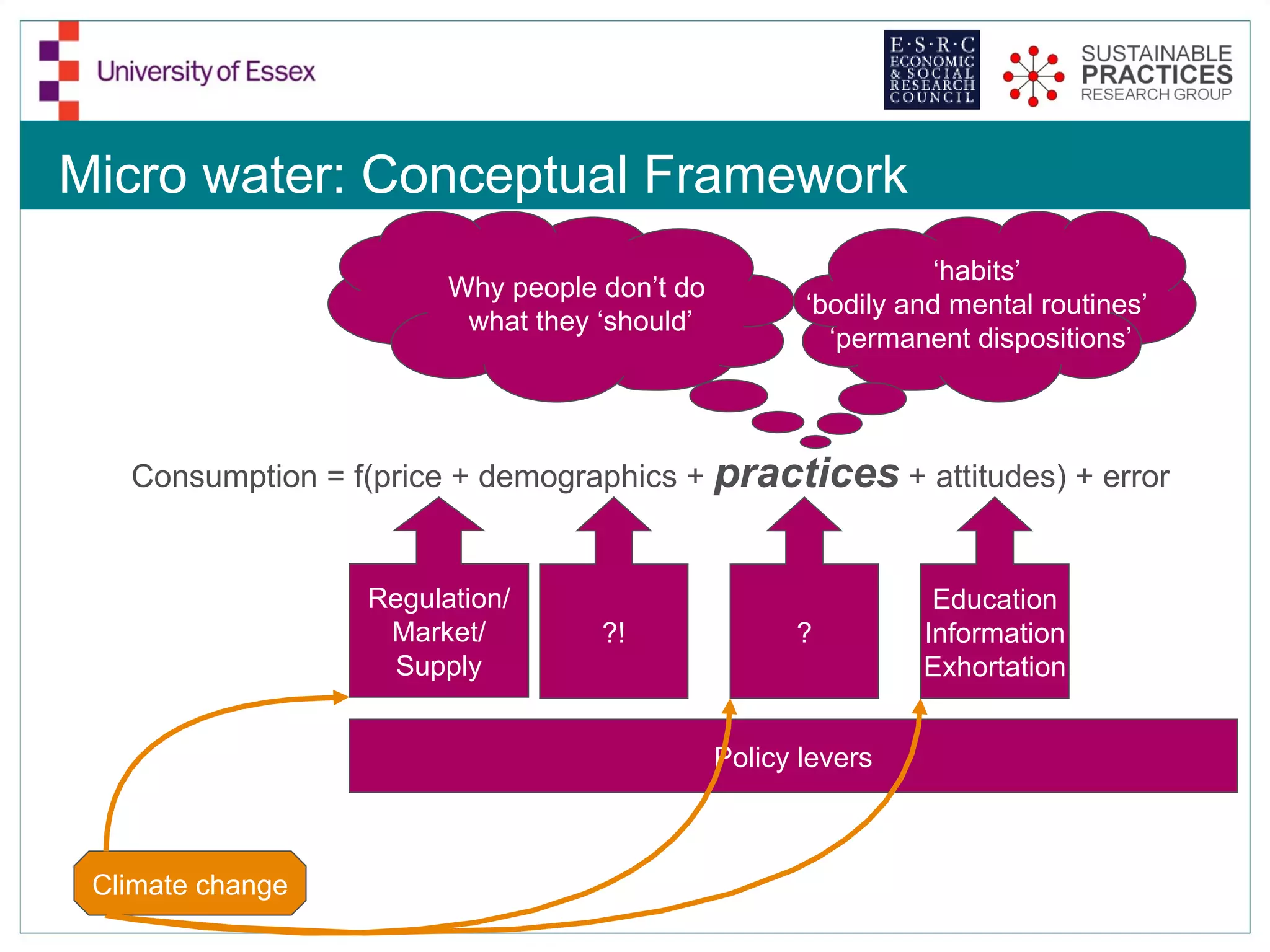
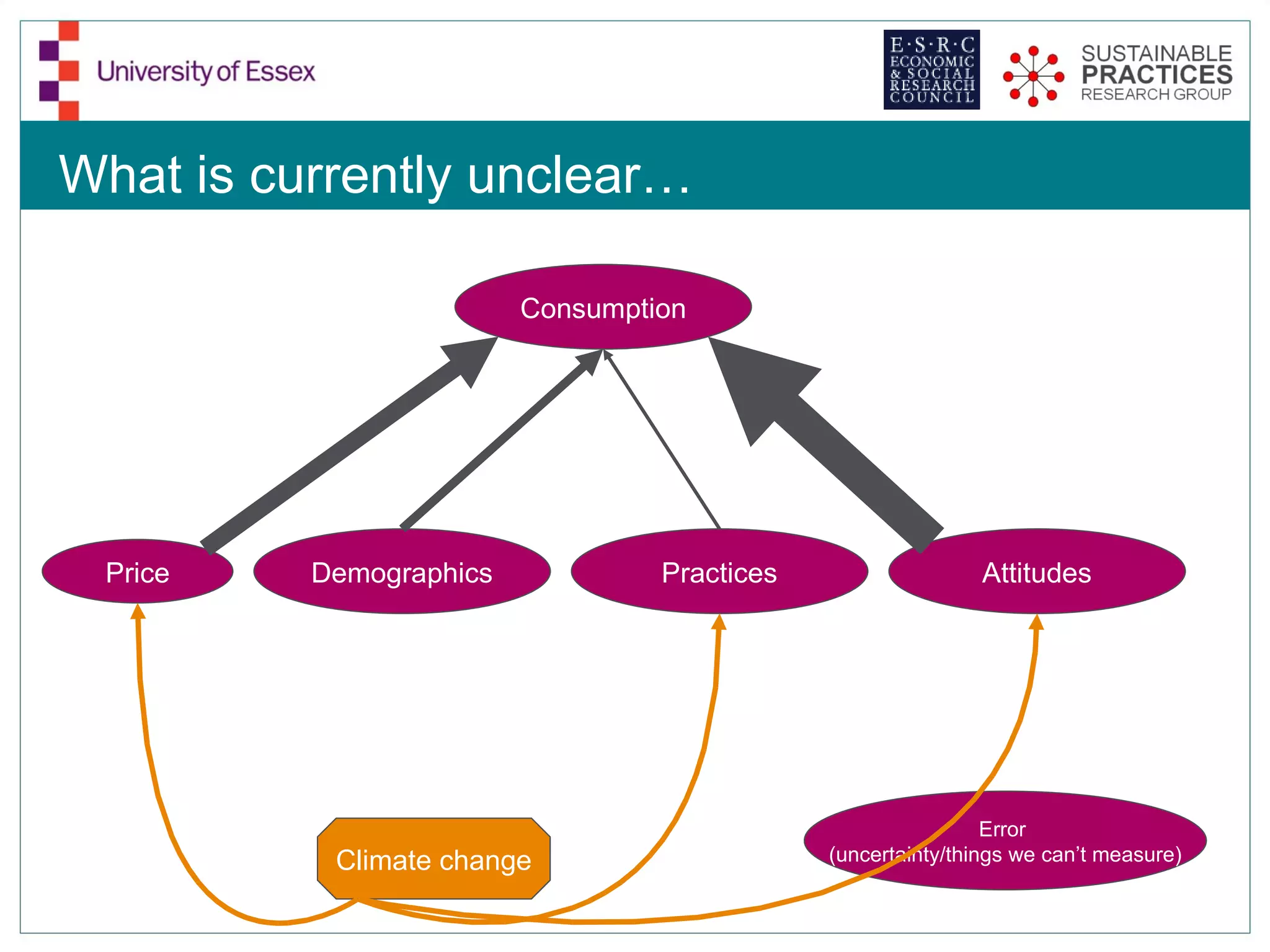
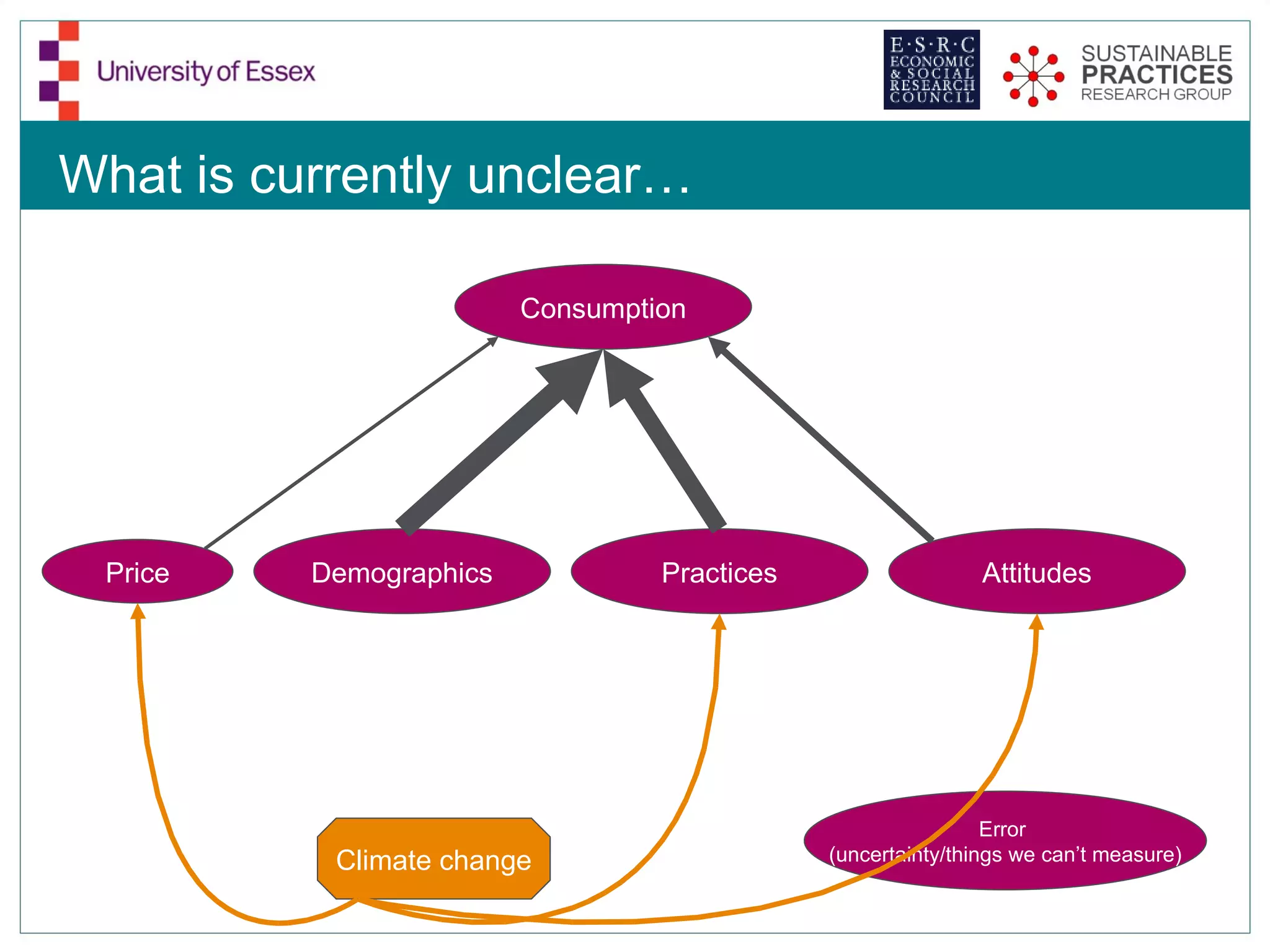
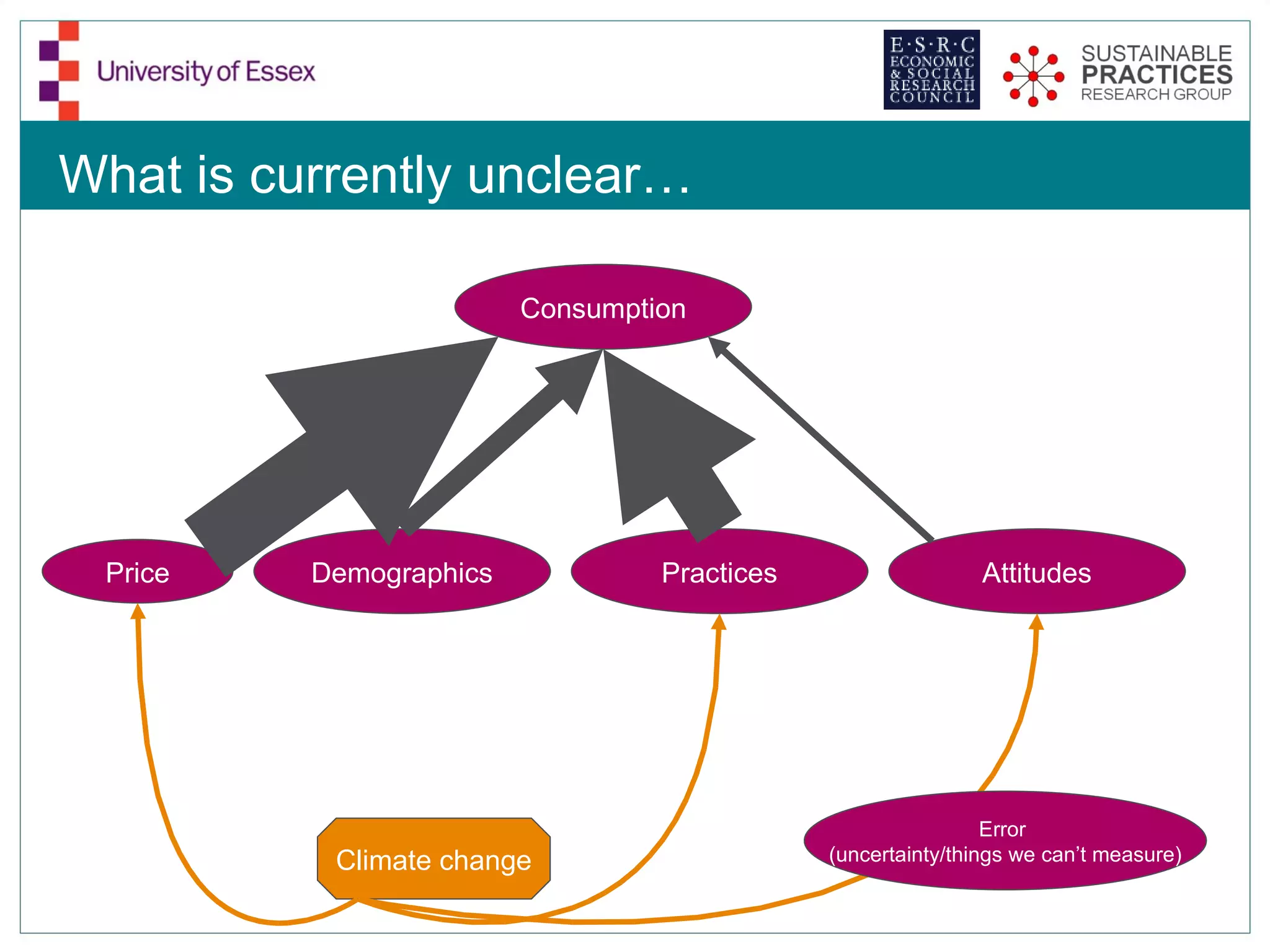
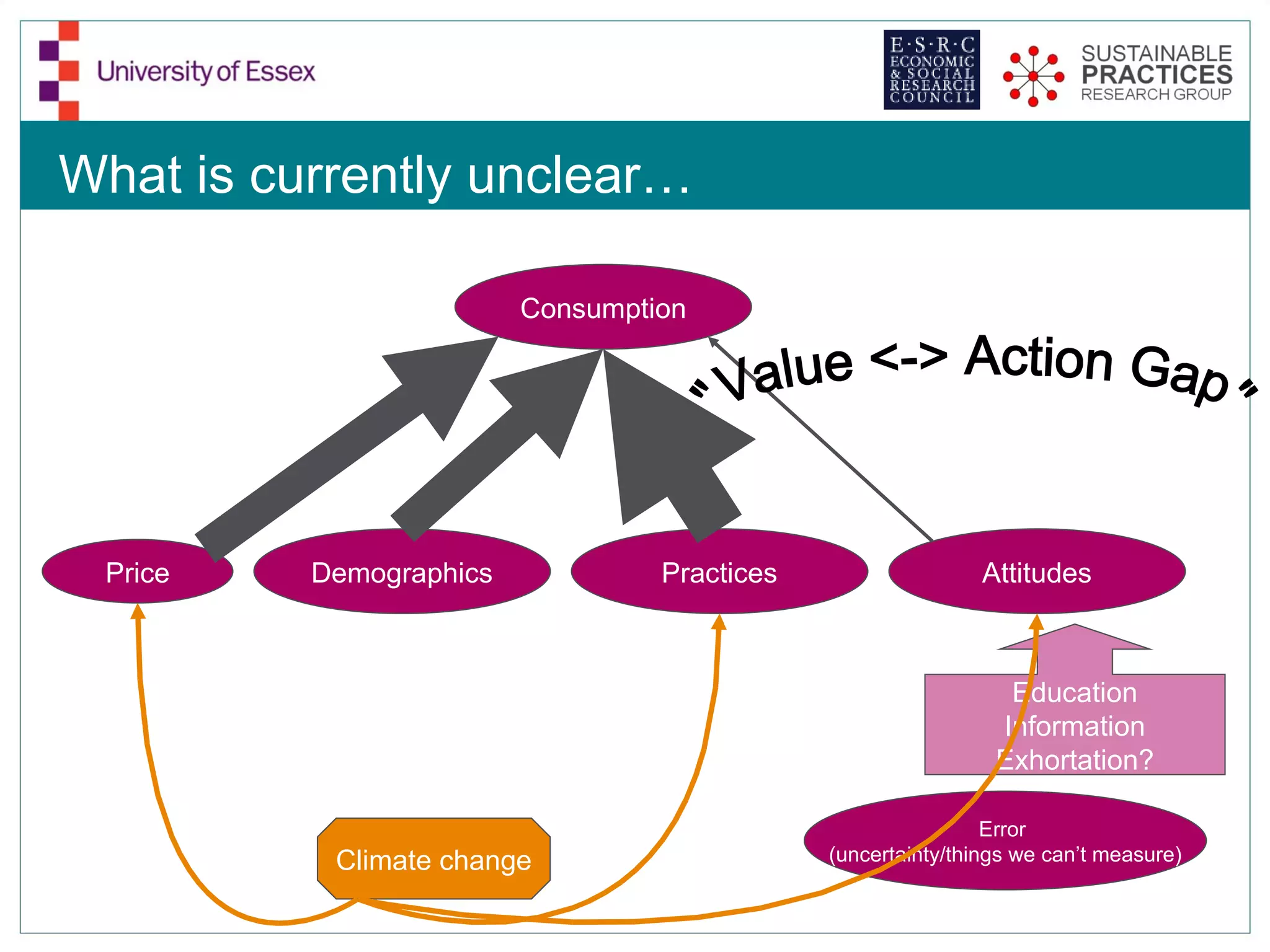
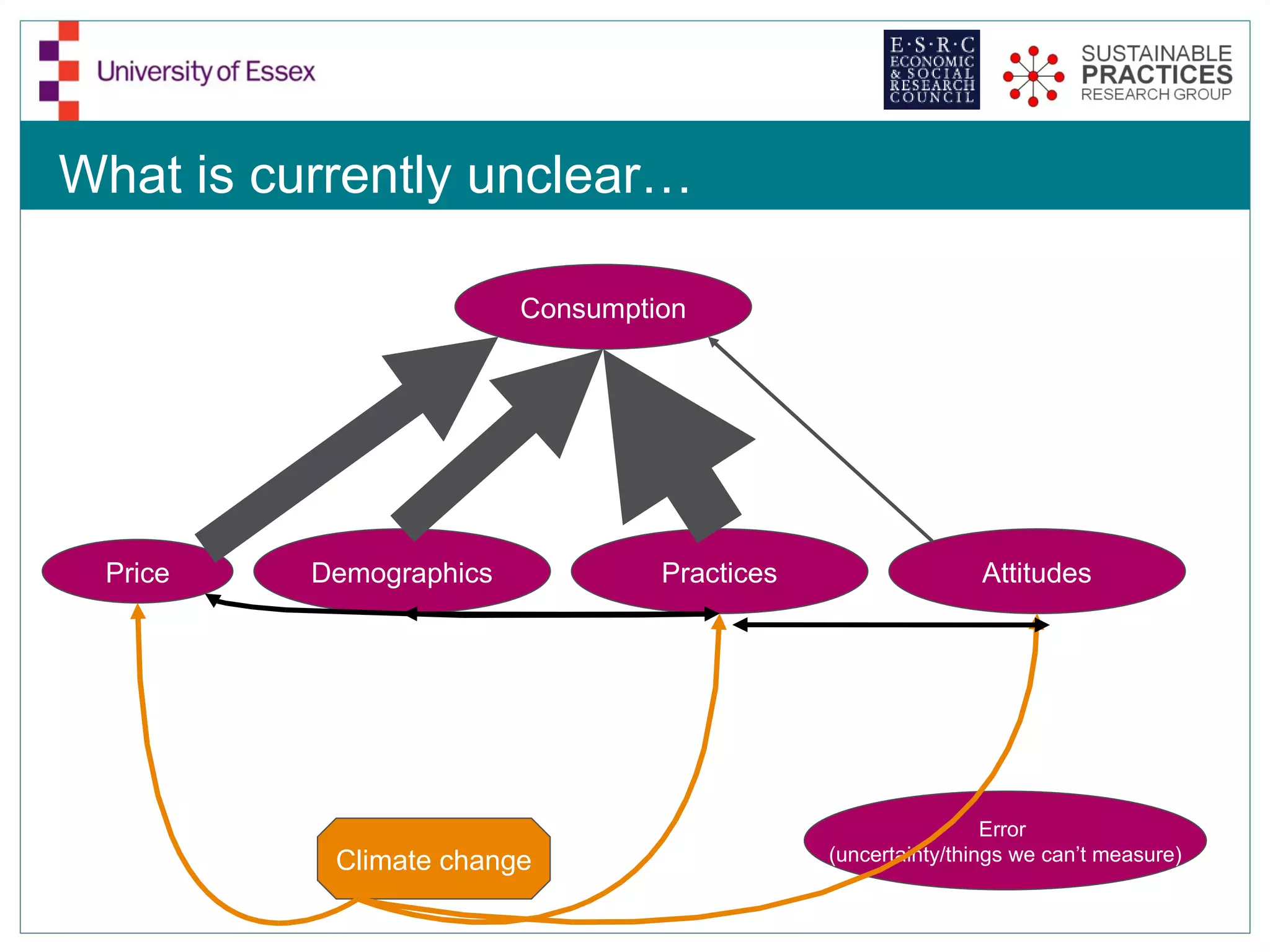
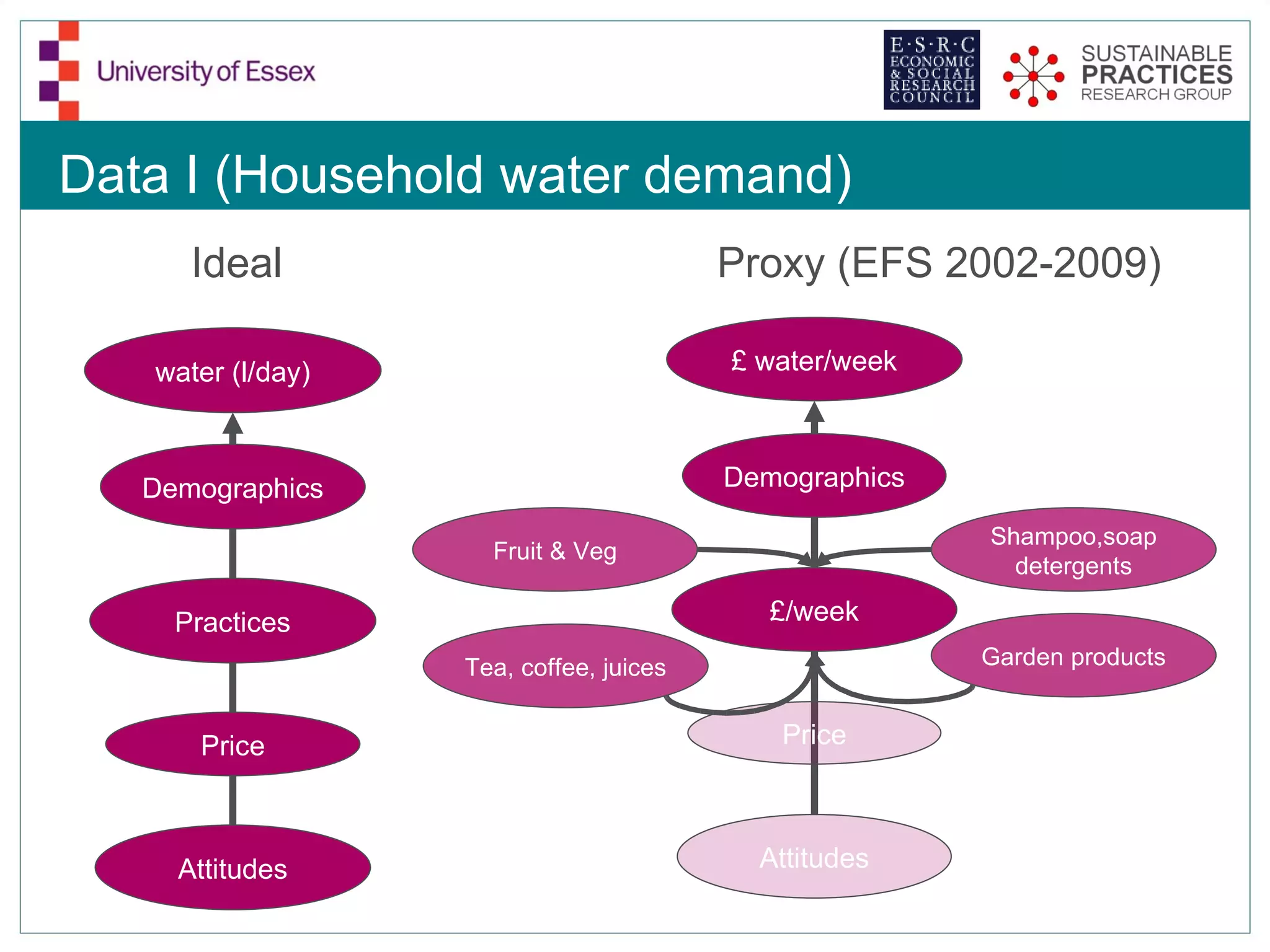
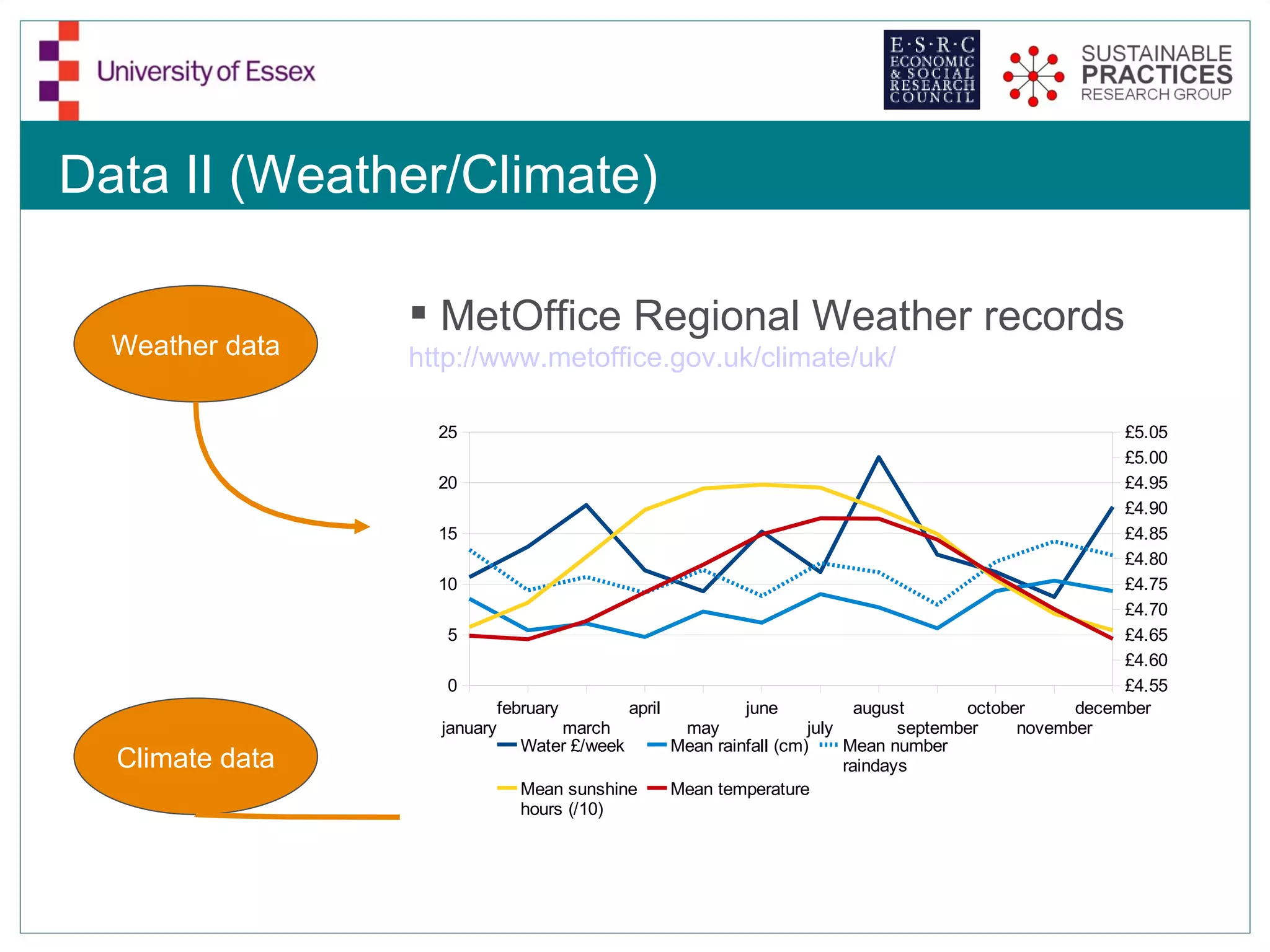
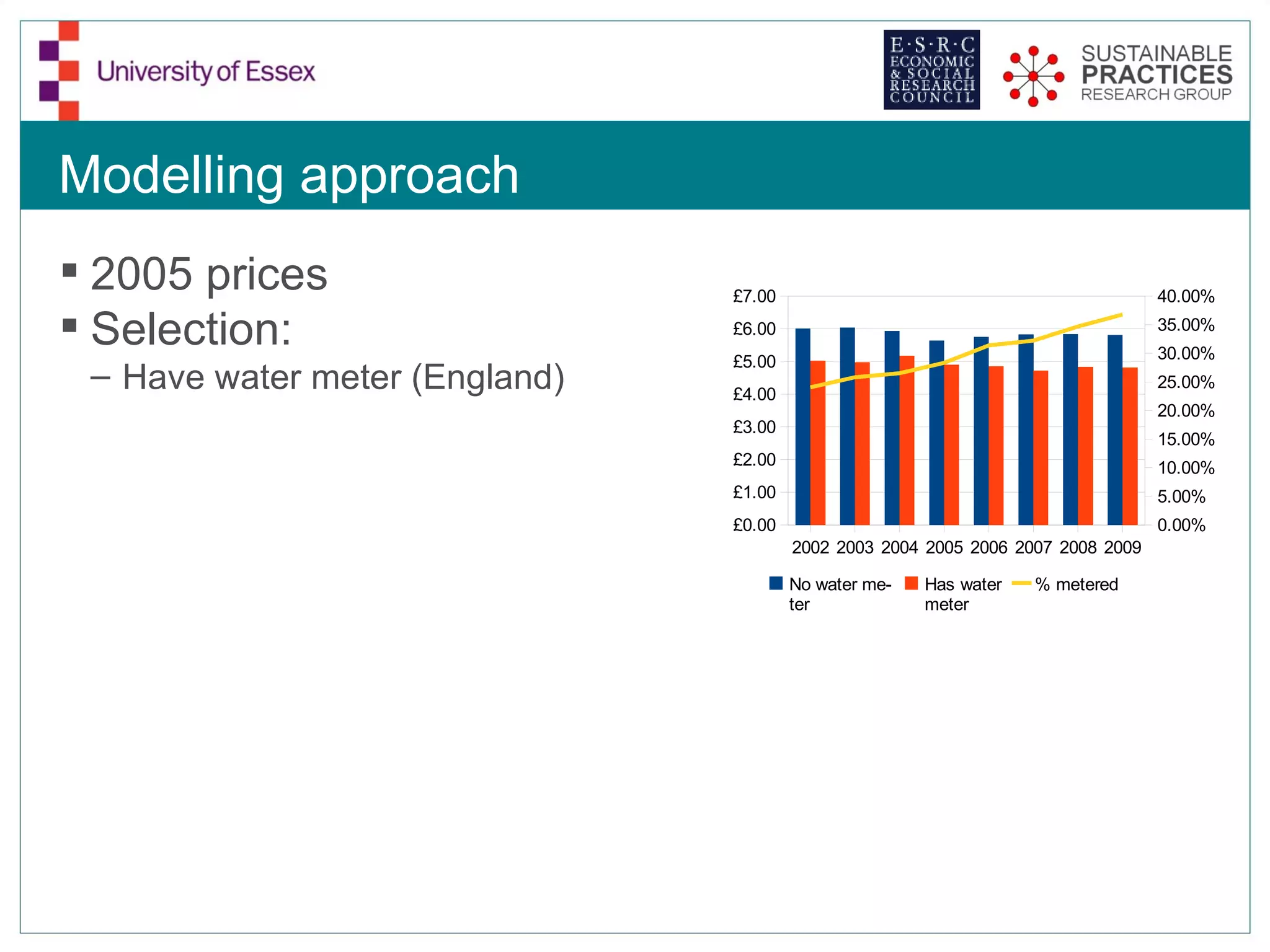
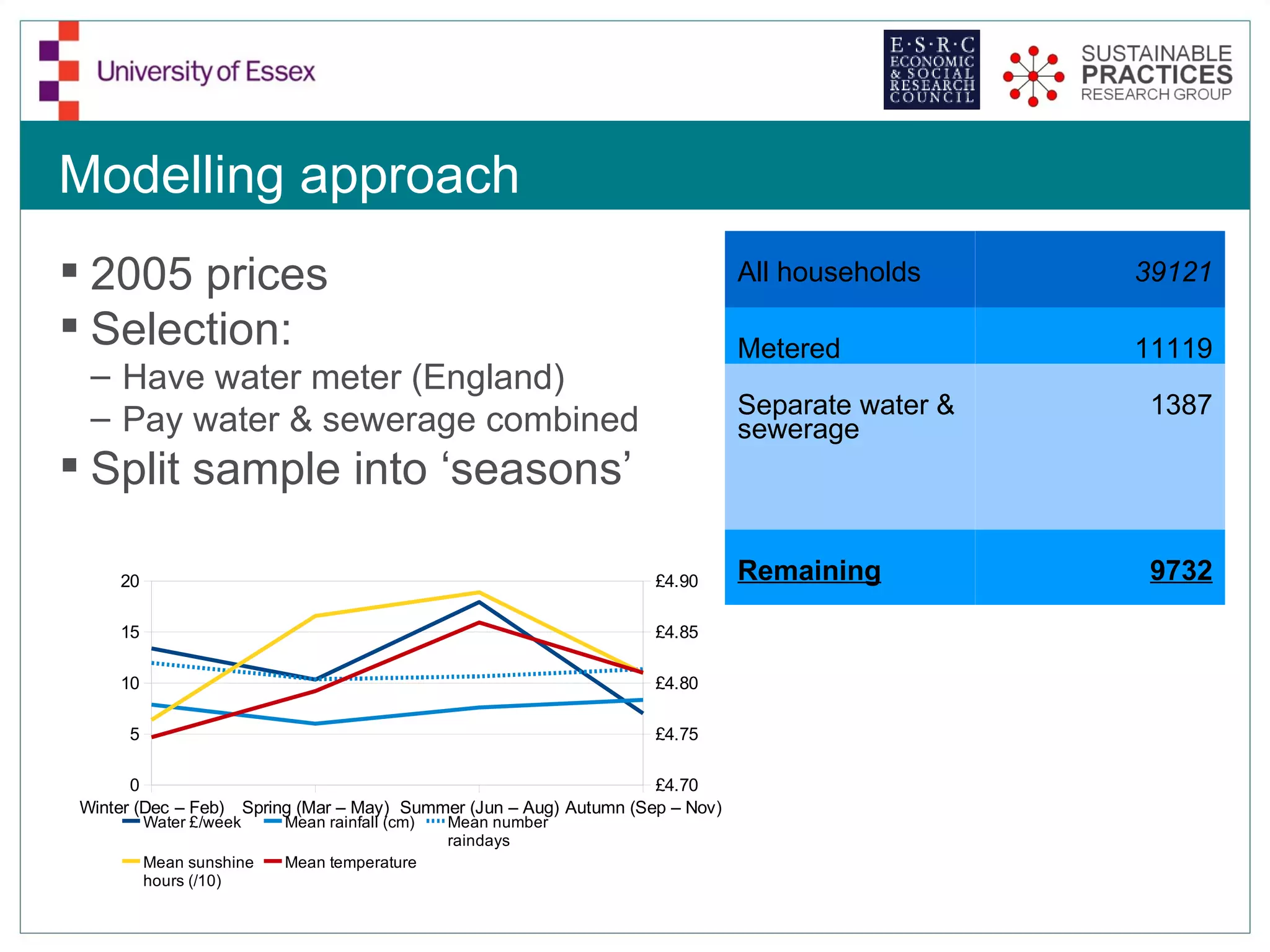
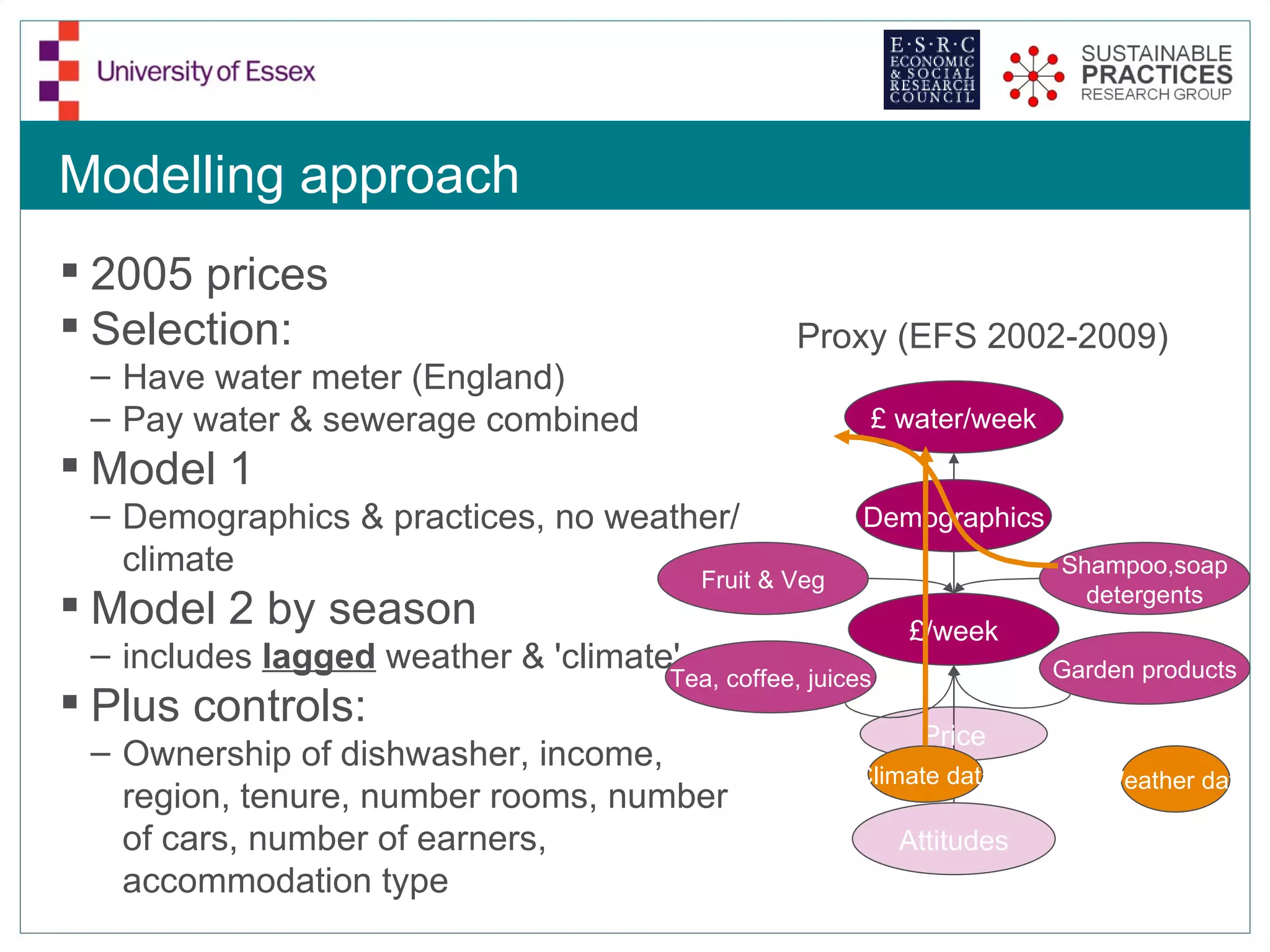
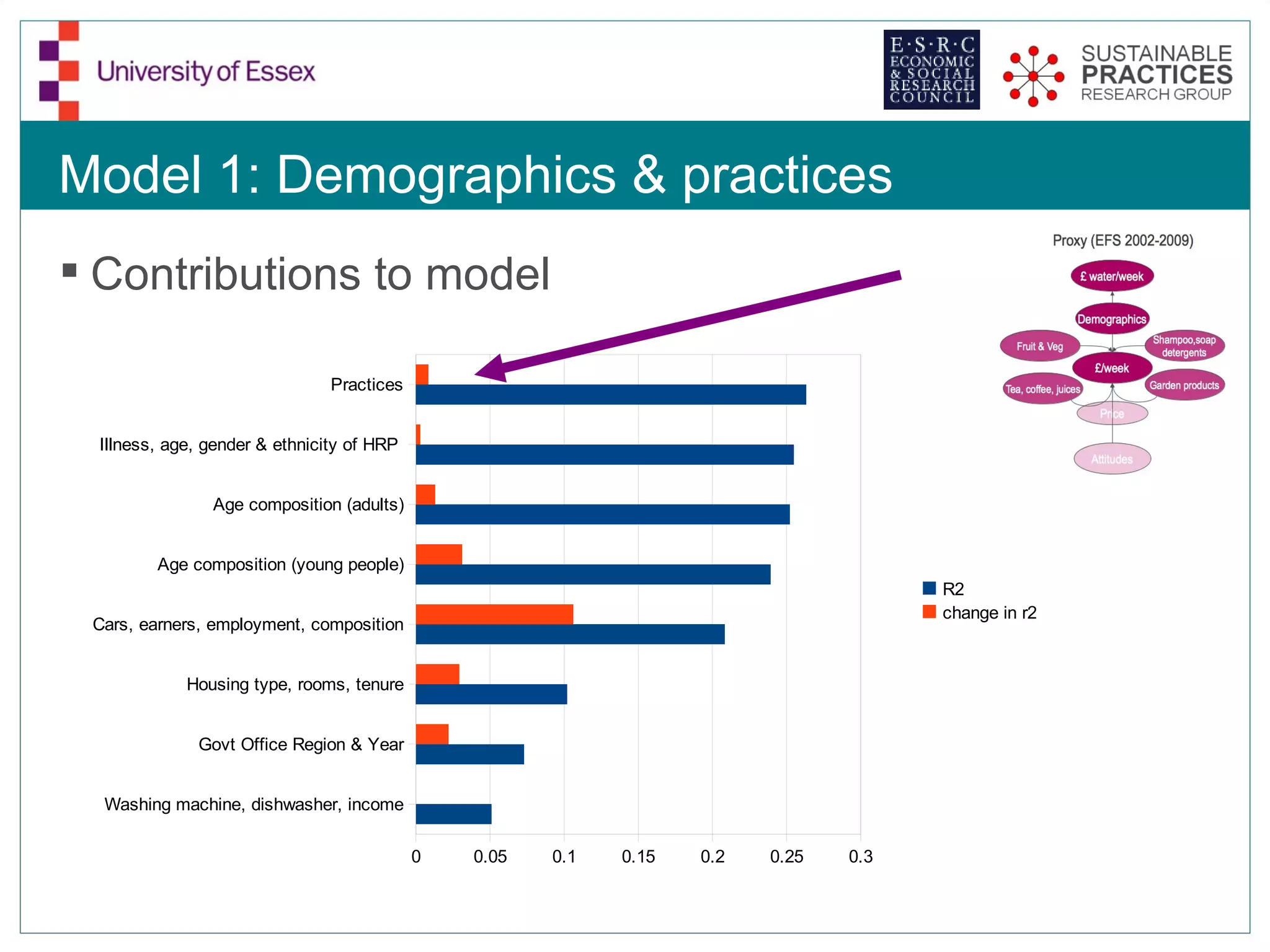
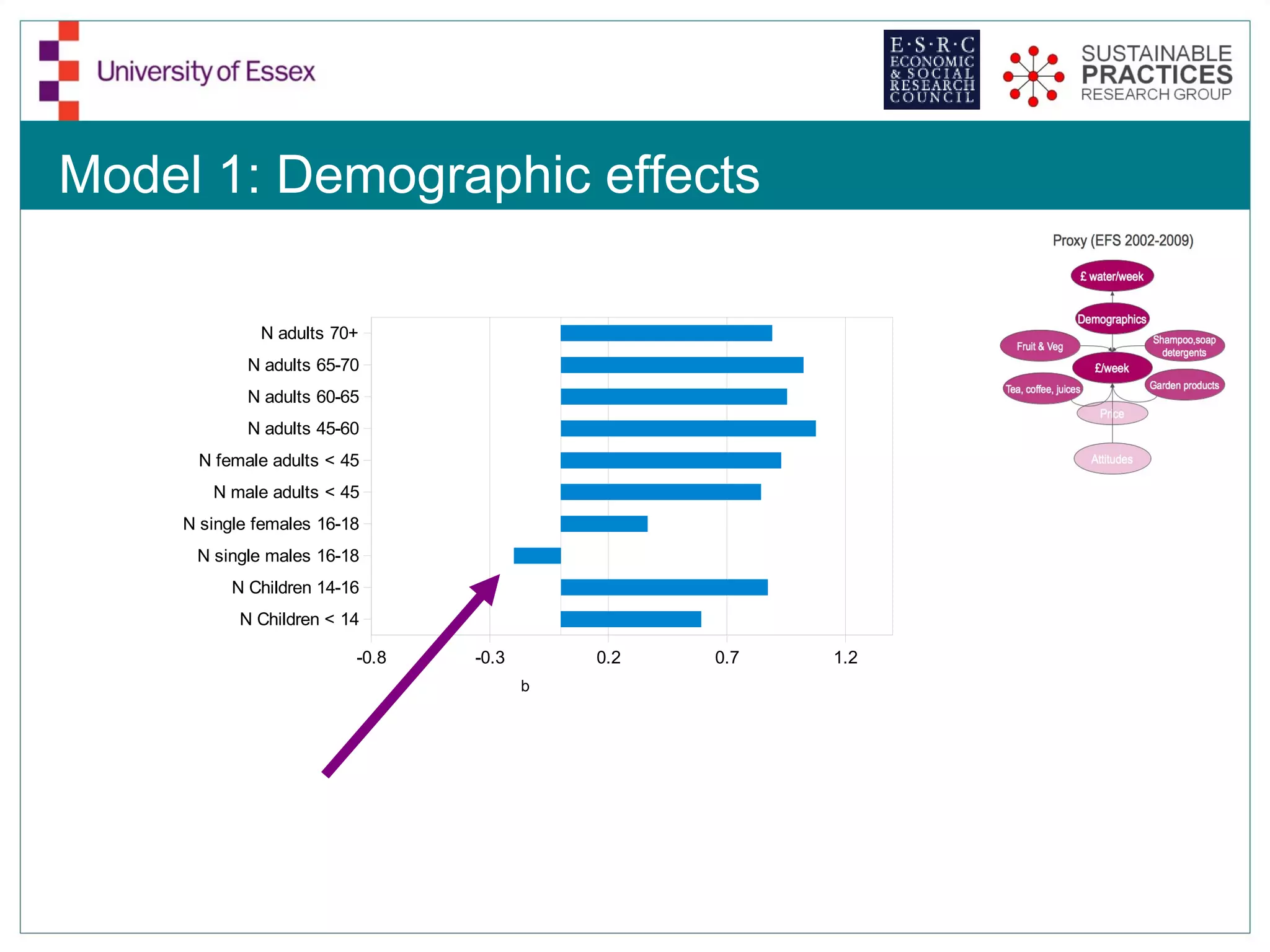
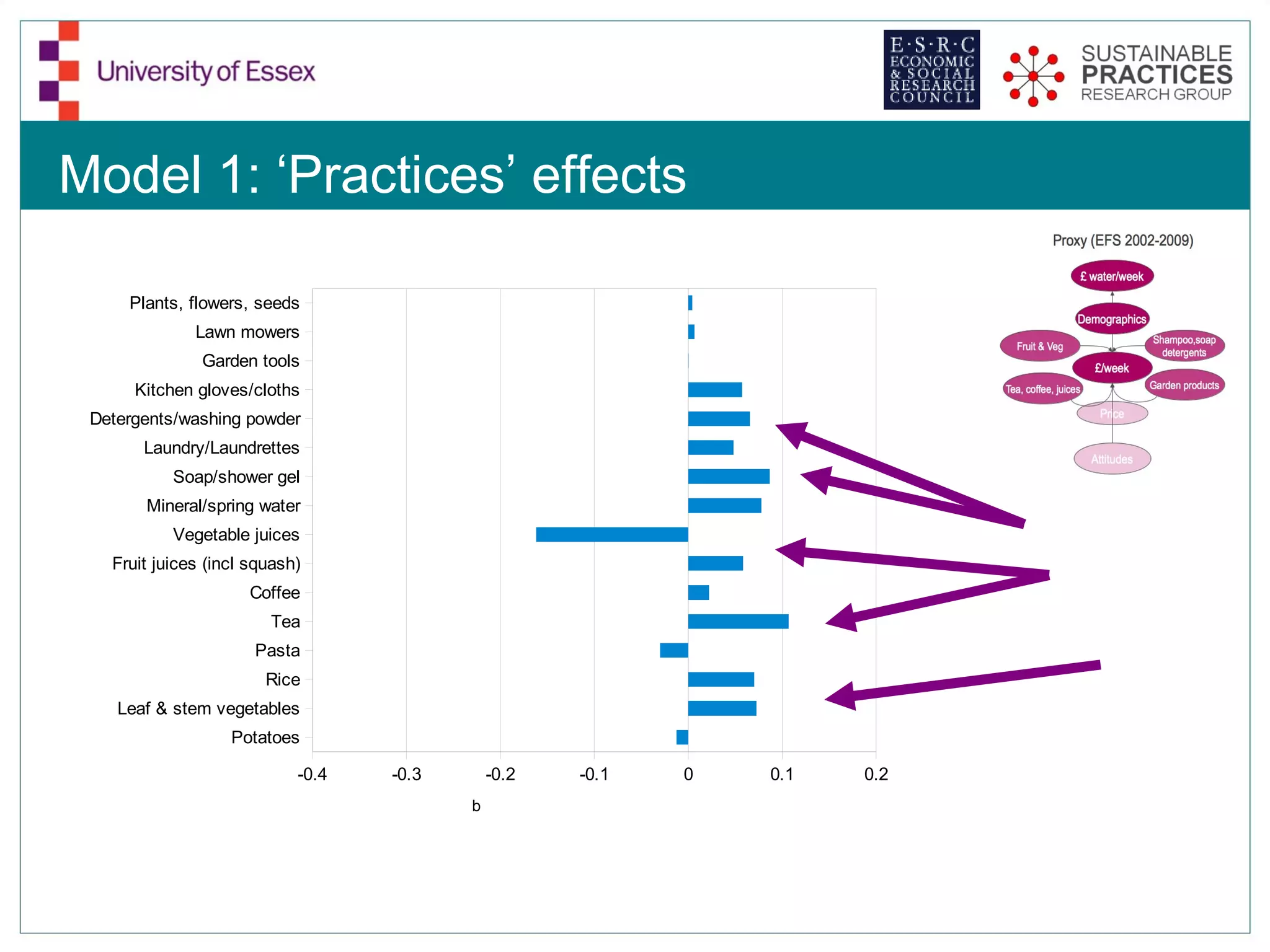
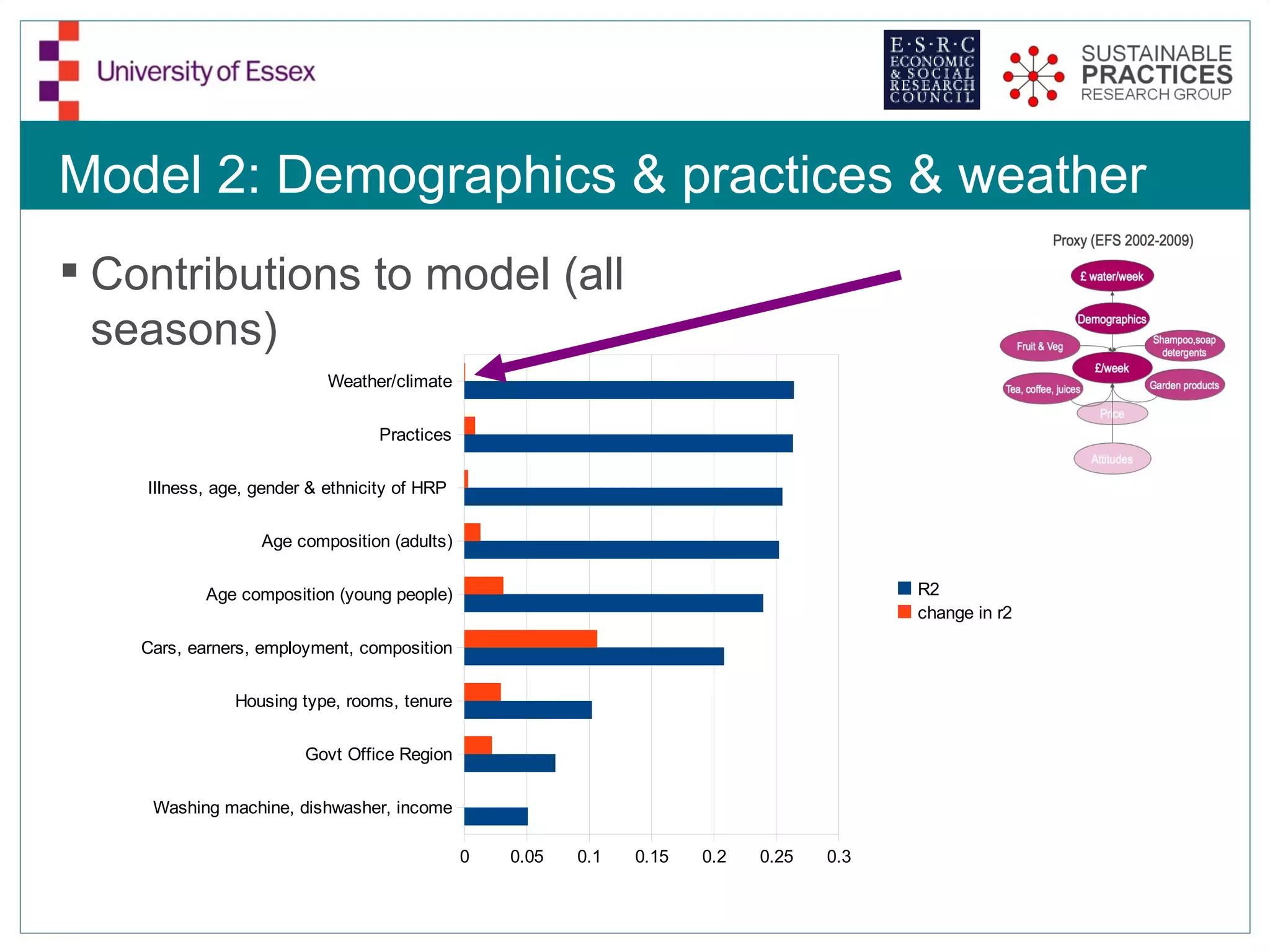
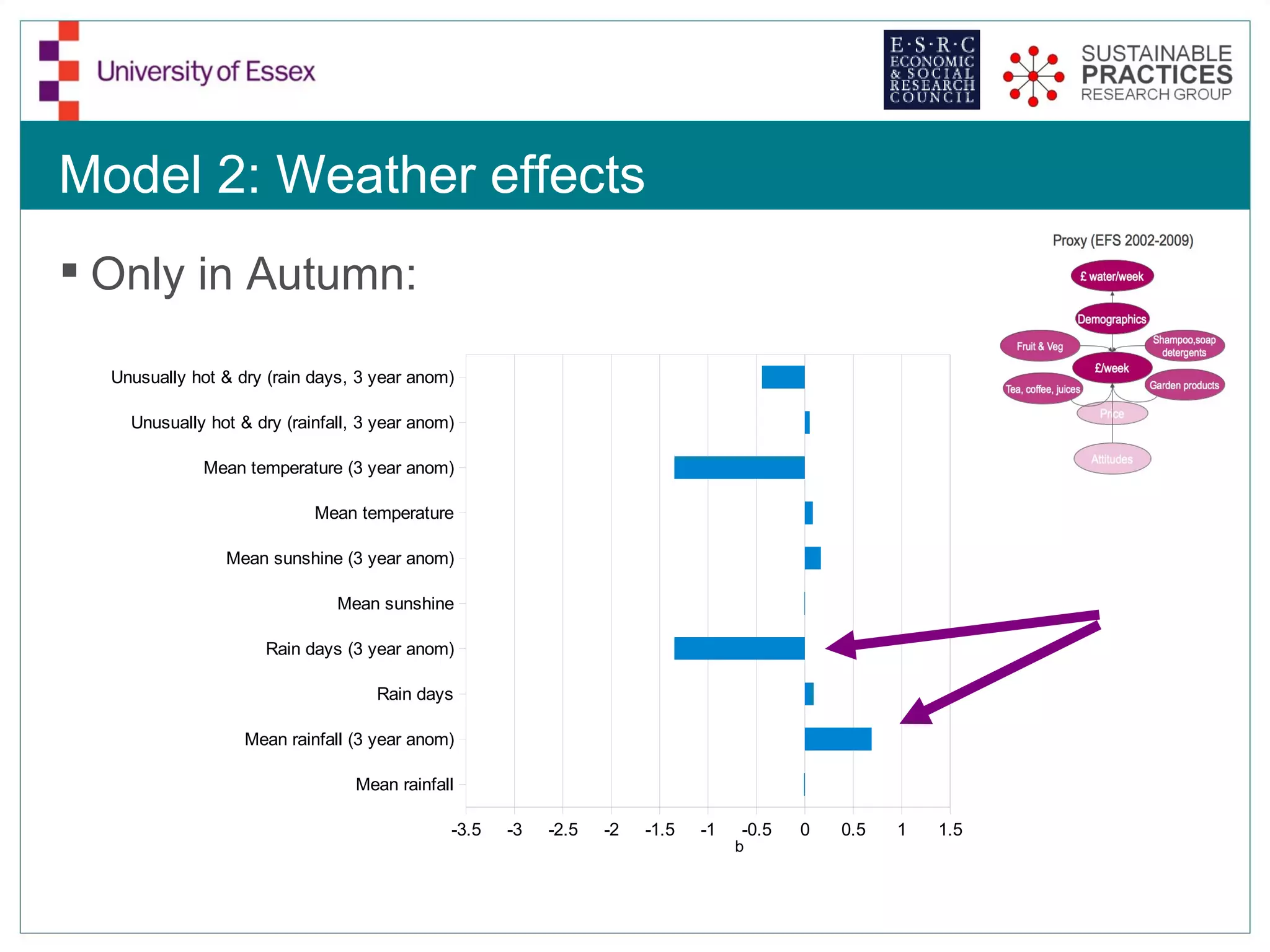
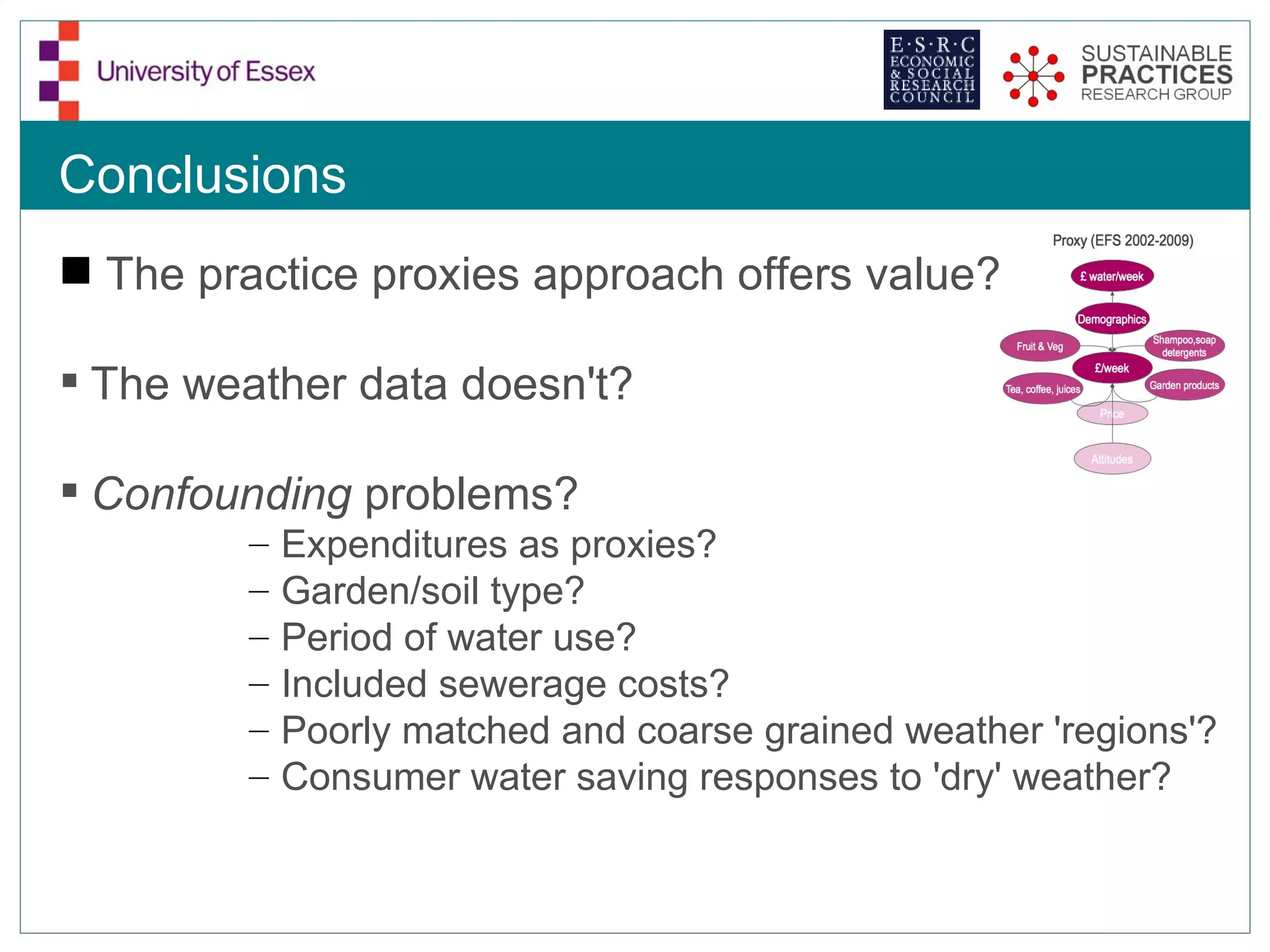
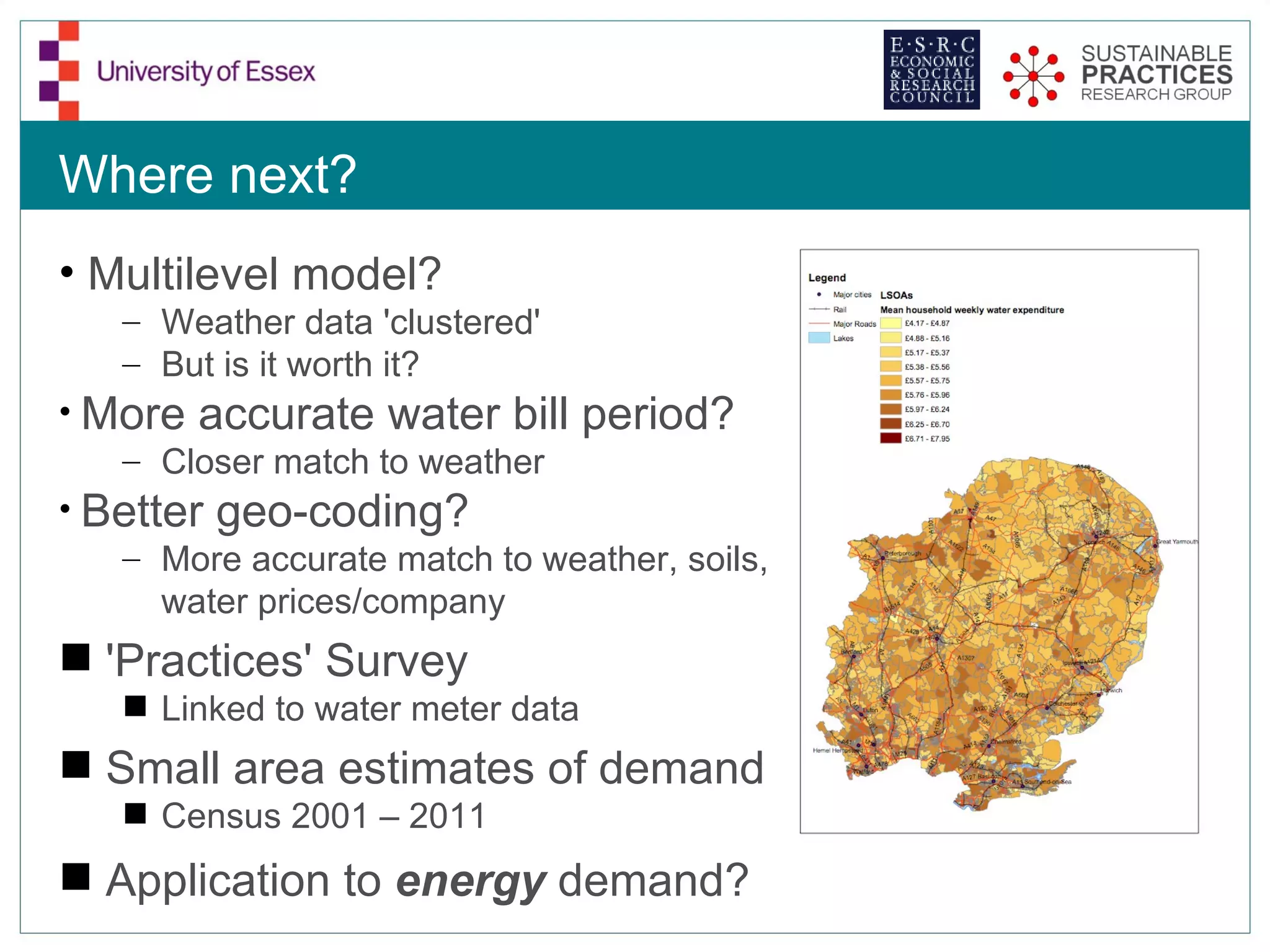
The document discusses the emerging challenges related to water supply, consumption, and potential impacts of climate change on water demand. It emphasizes the complexities concerning demographics, practices, and policy interventions necessary for addressing water scarcity issues by 2050. The document also outlines modeling approaches and future research directions to improve understanding and management of water consumption patterns.