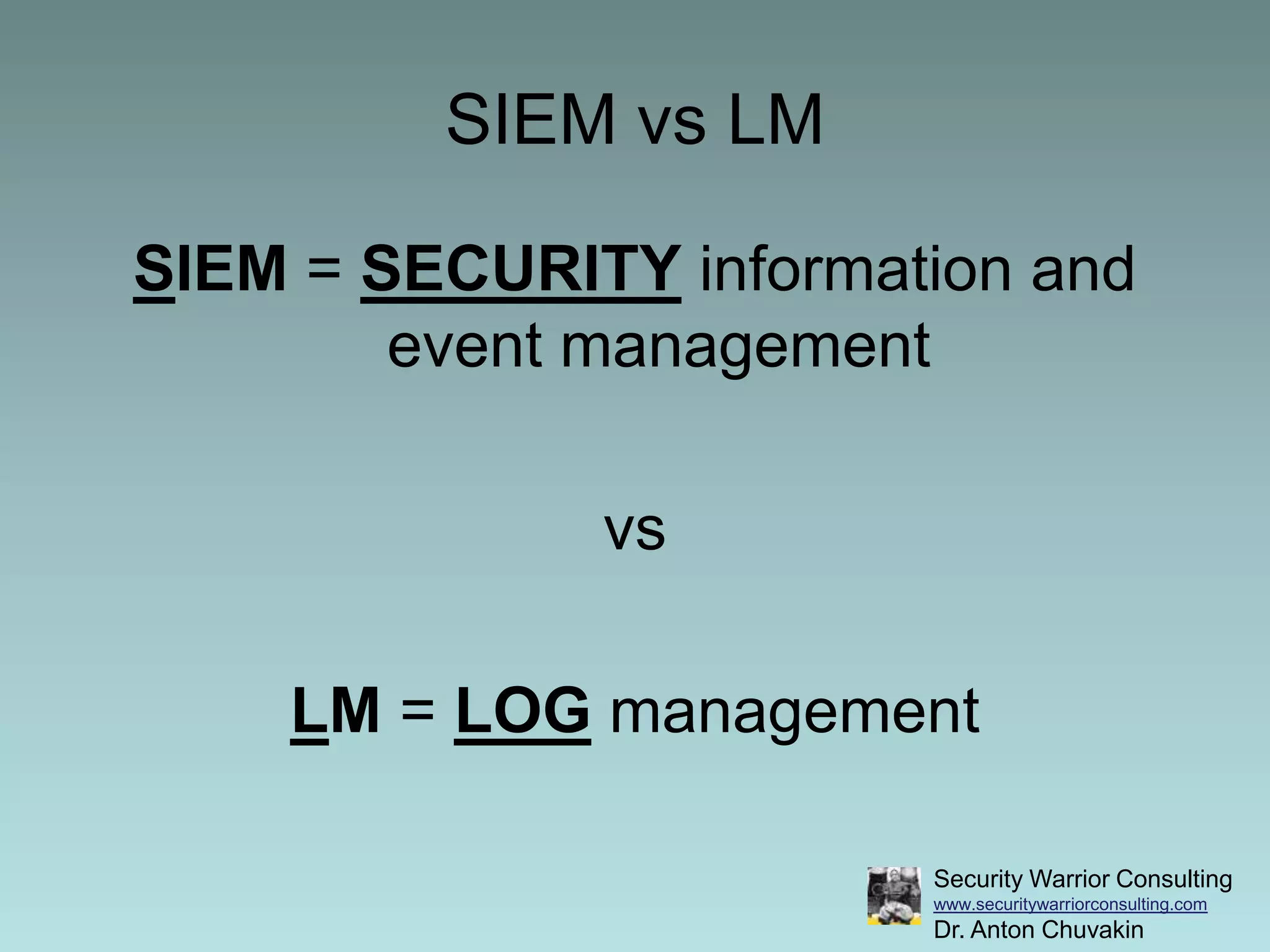
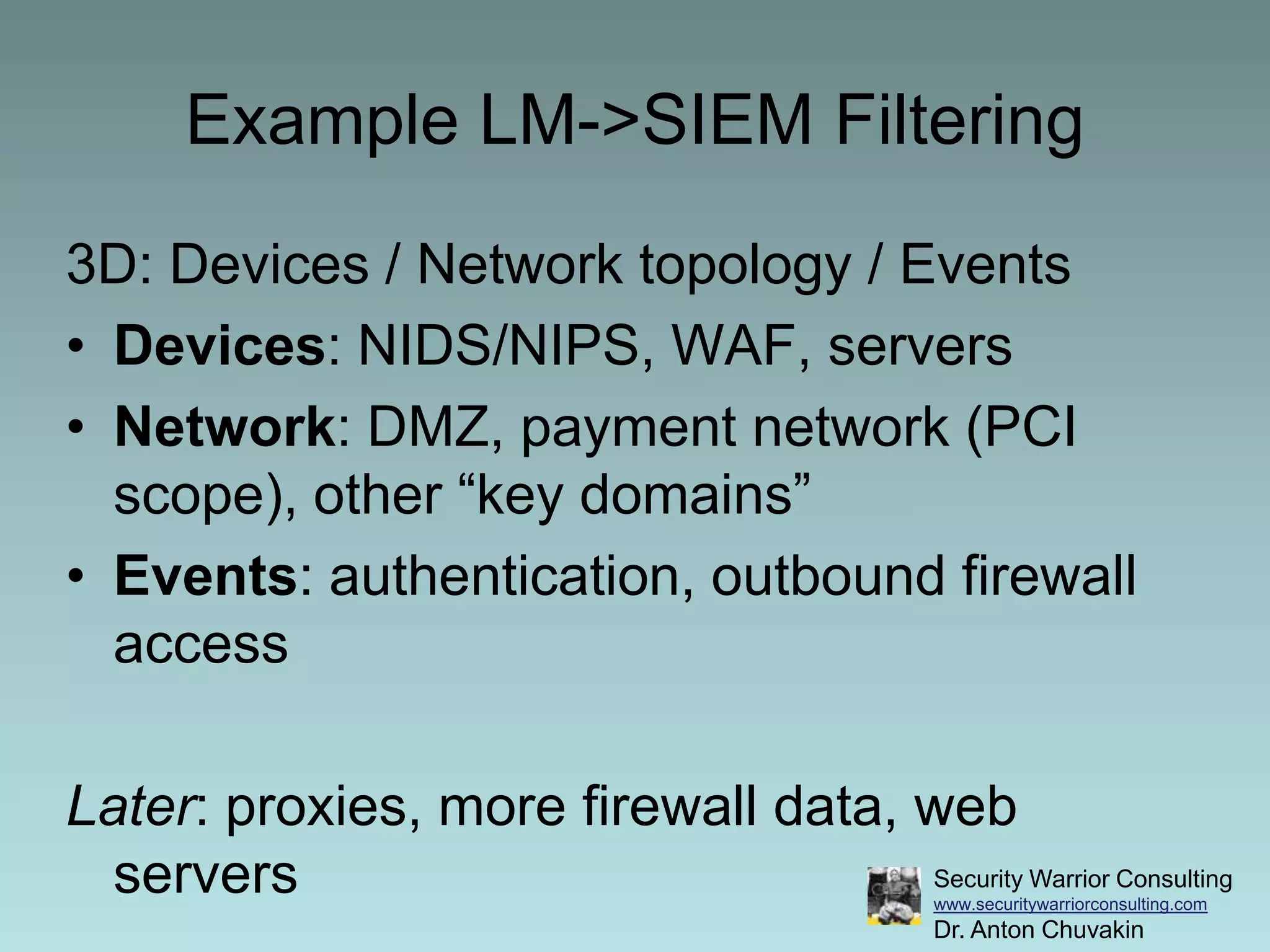
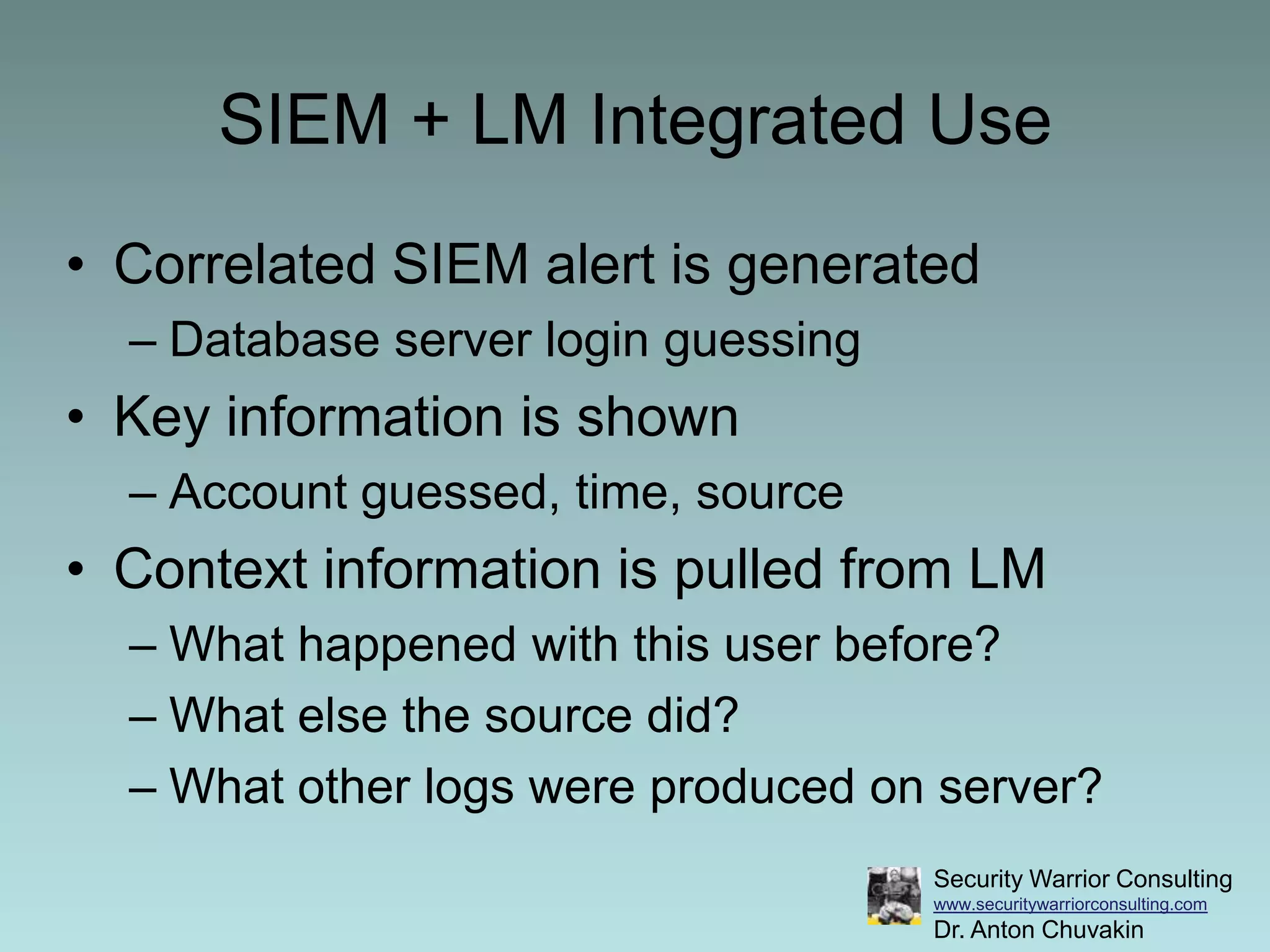
This document discusses the differences between security information and event management (SIEM) and log management (LM), and provides best practices for using SIEM and LM together. It recommends deploying LM before SIEM to collect and manage log data. Then organizations can decide when to implement SIEM to automate monitoring and correlation. The document provides examples of gradually evolving from solely using LM to integrating it with SIEM for increased monitoring and analytics capabilities.