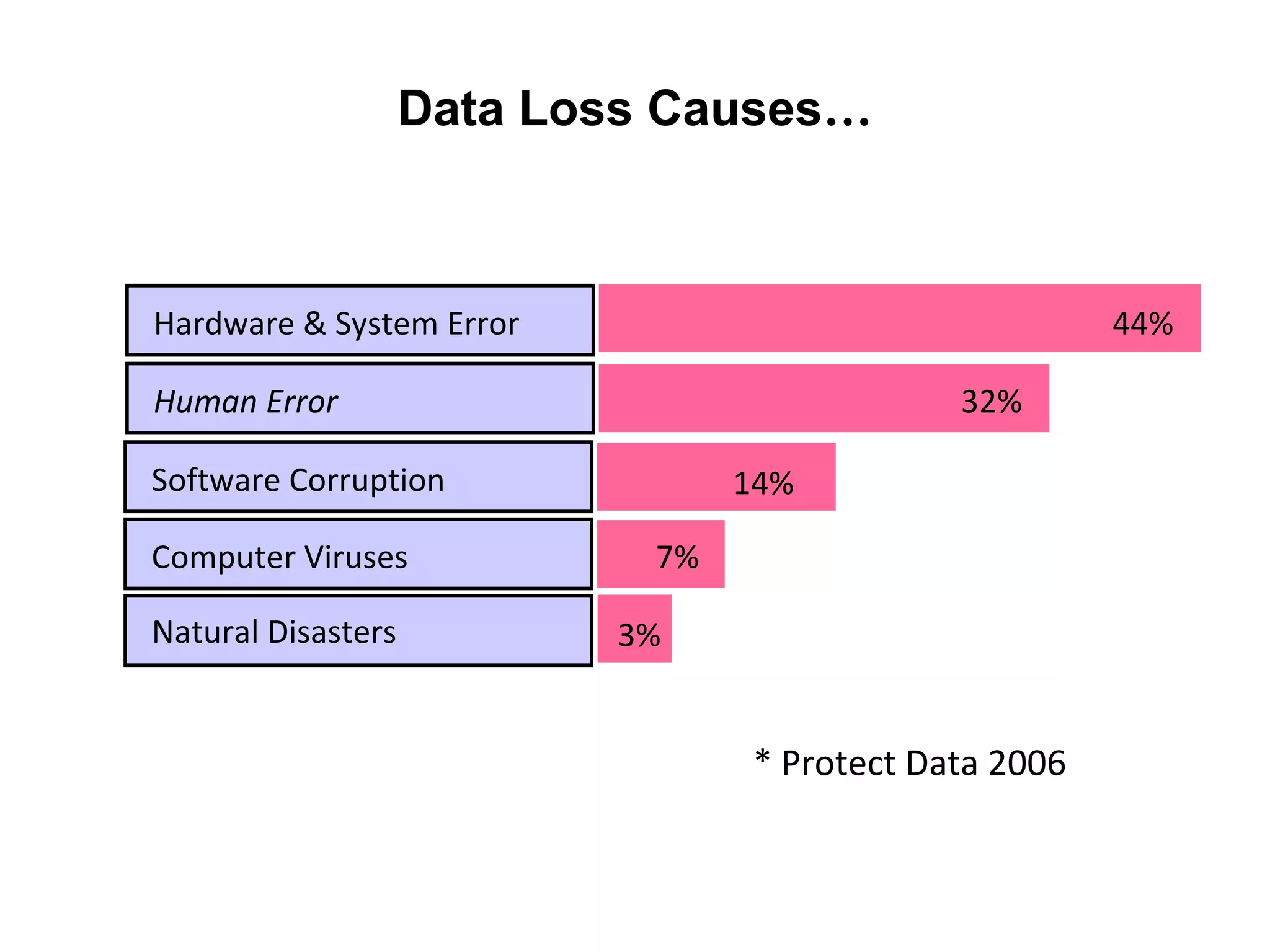
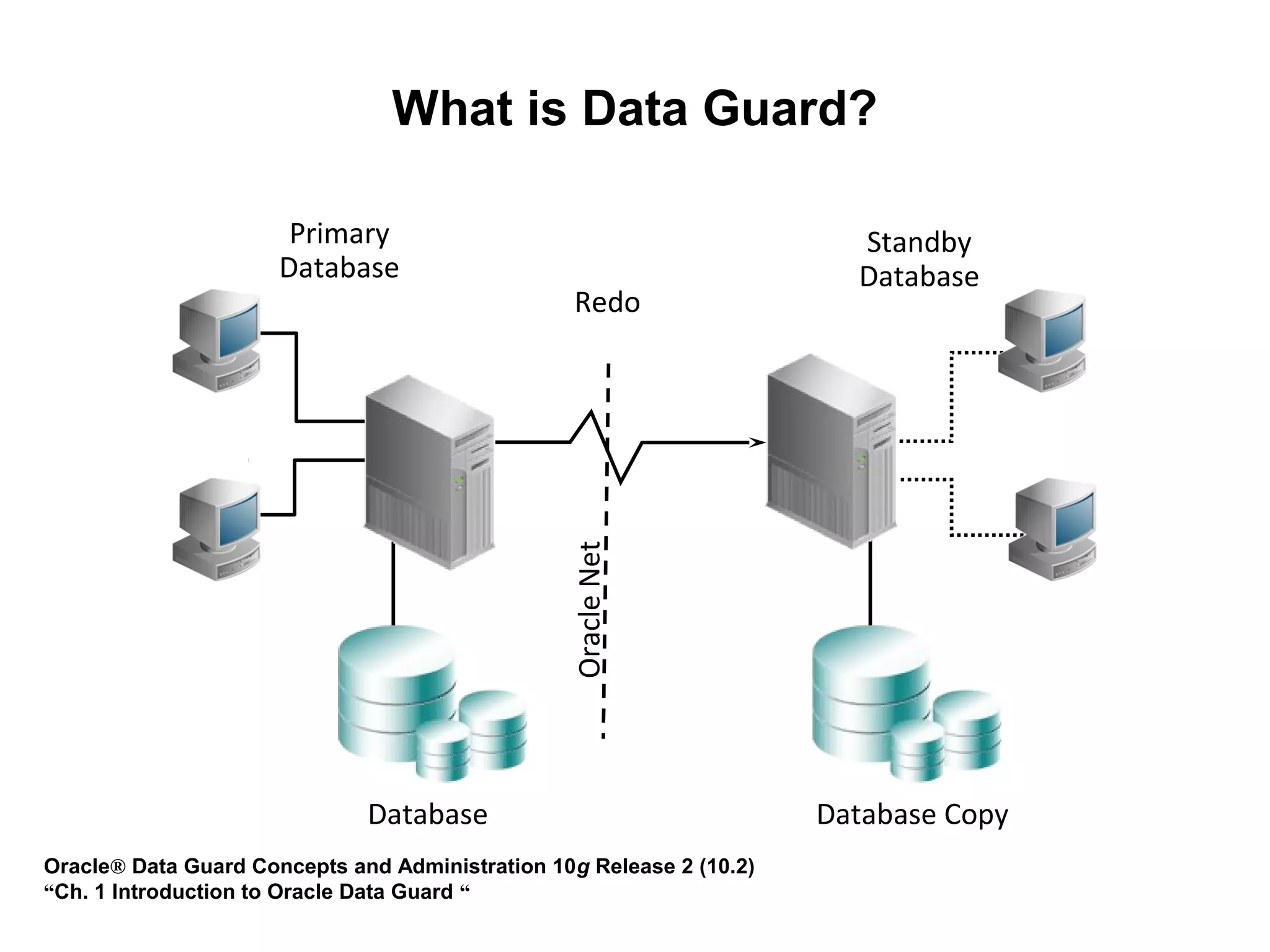
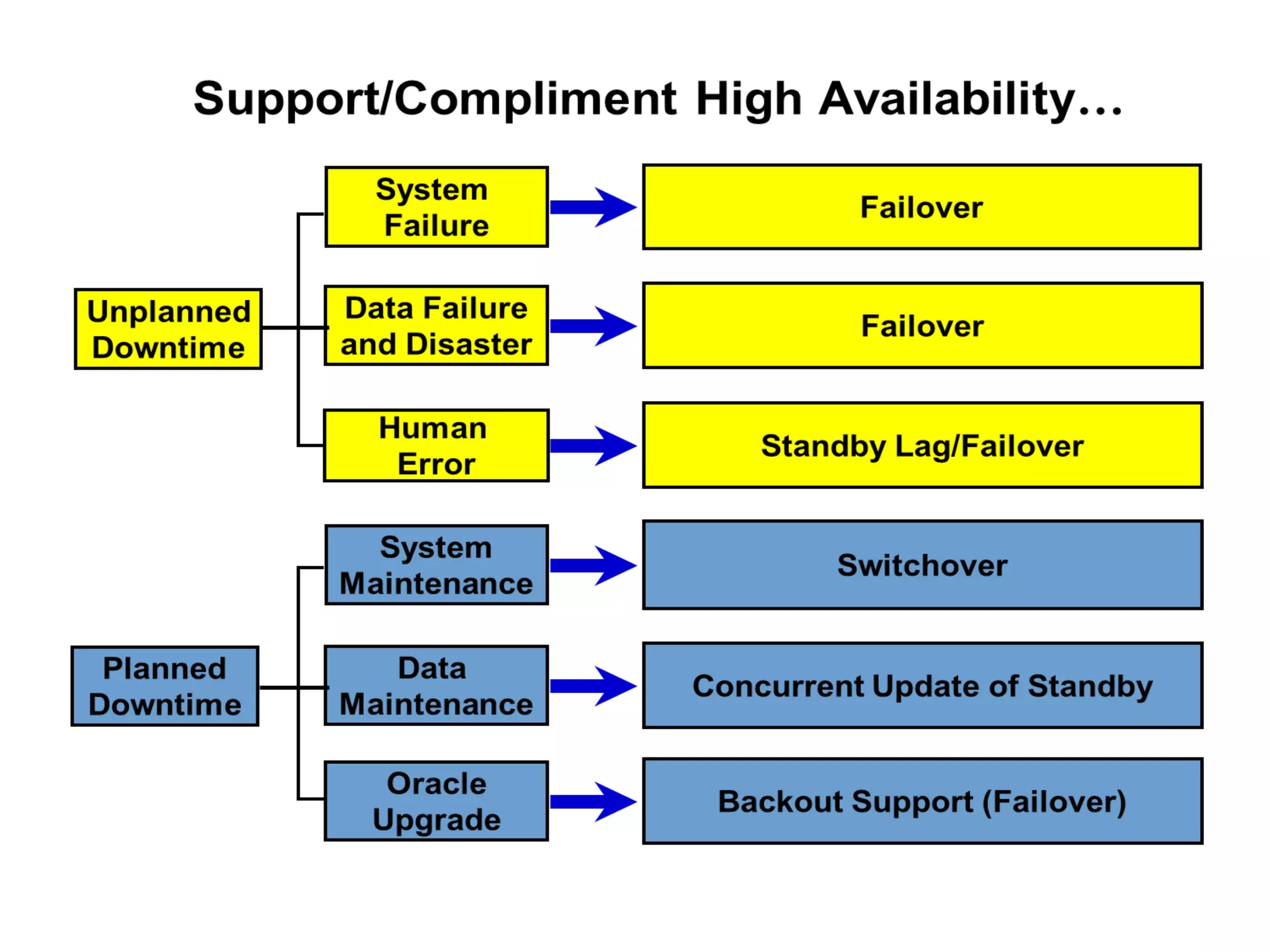
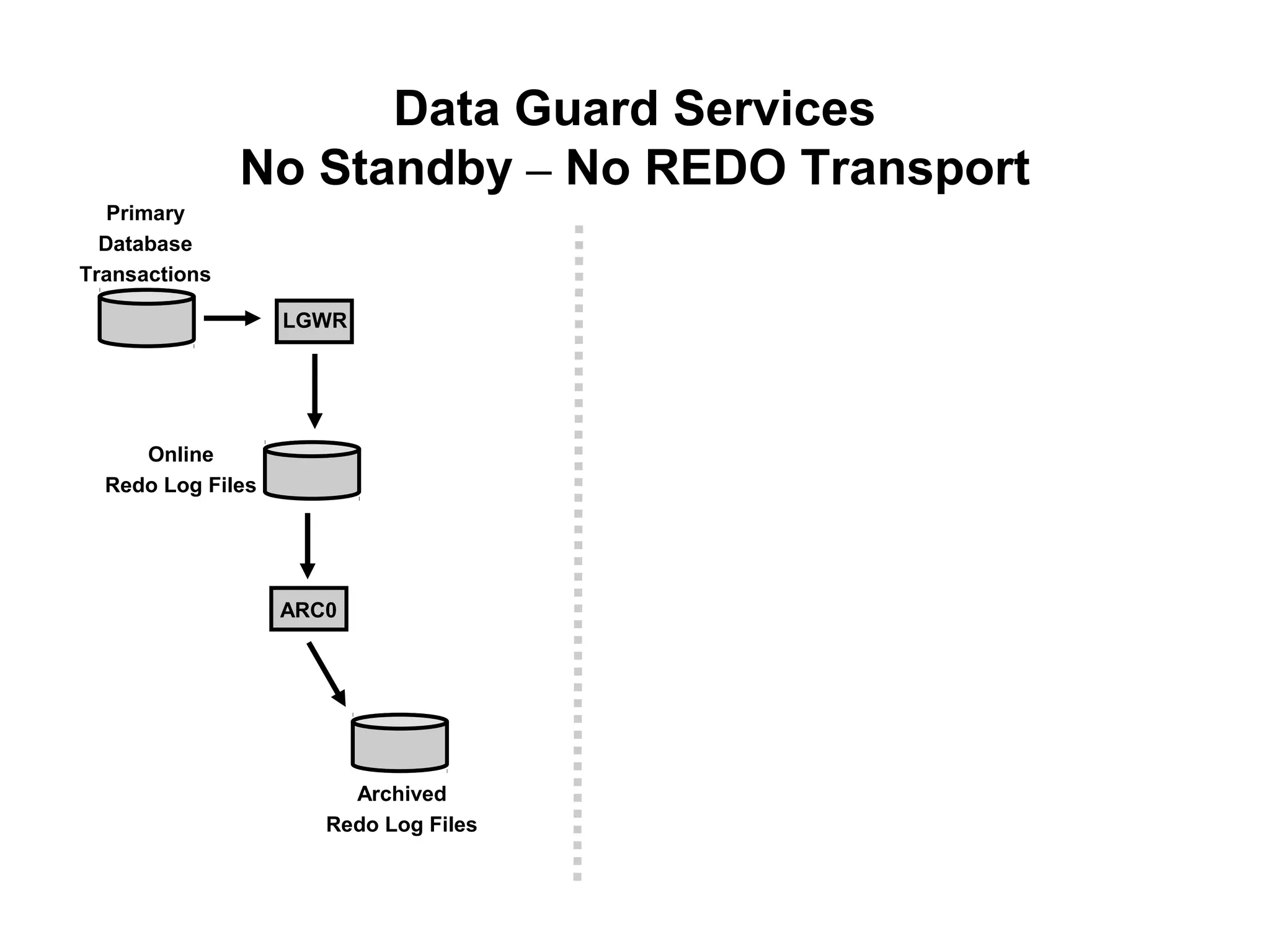
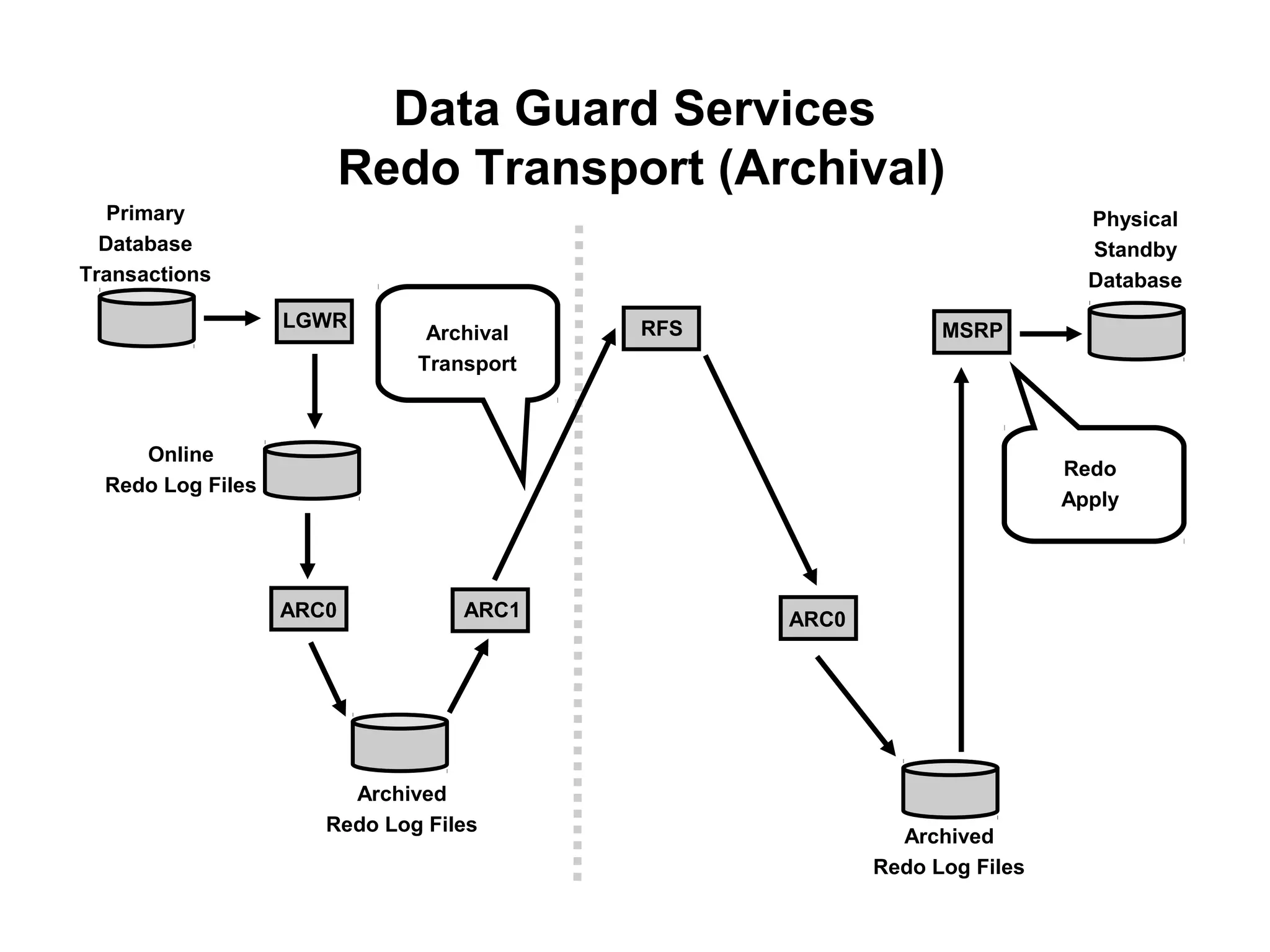
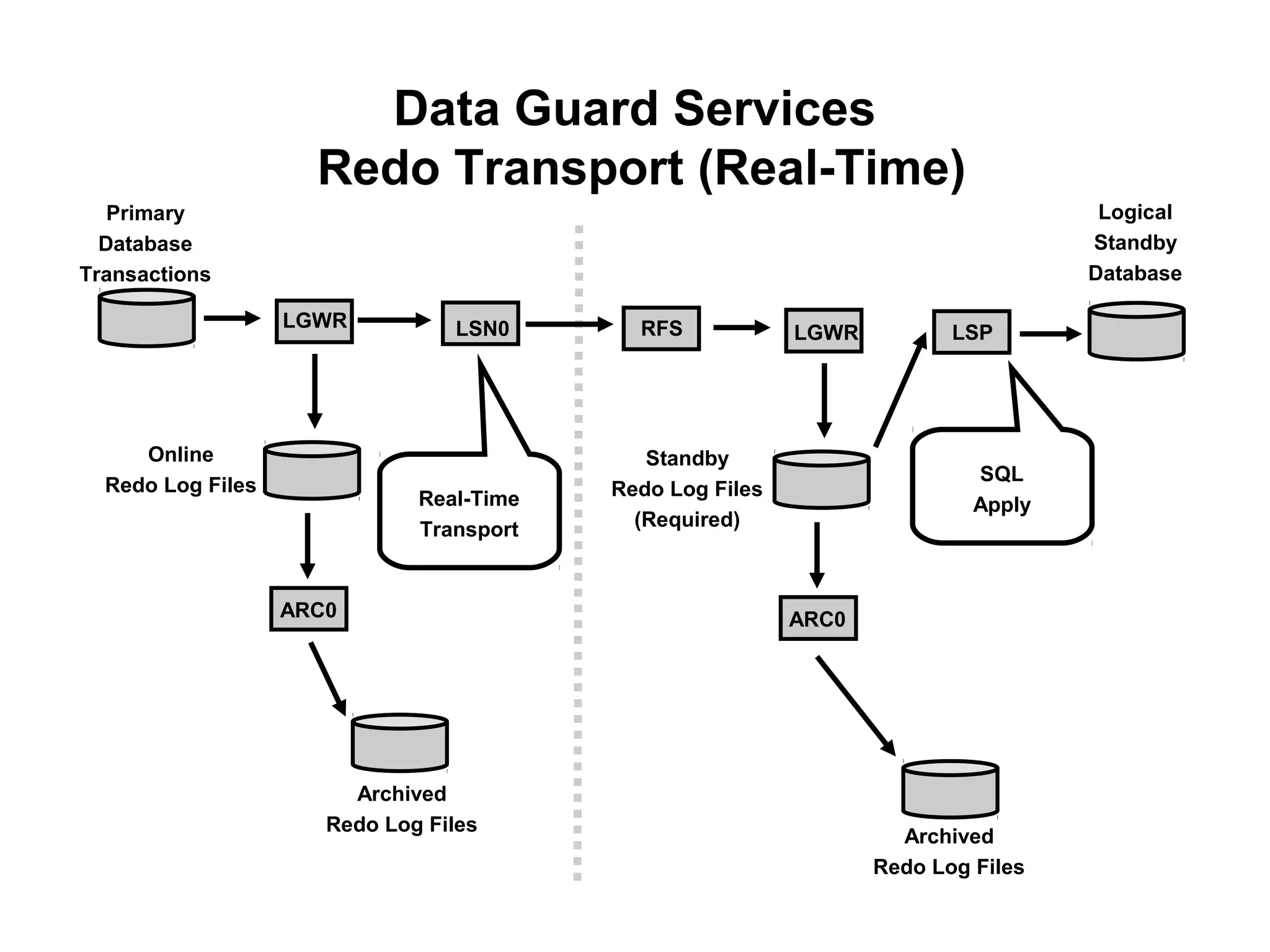
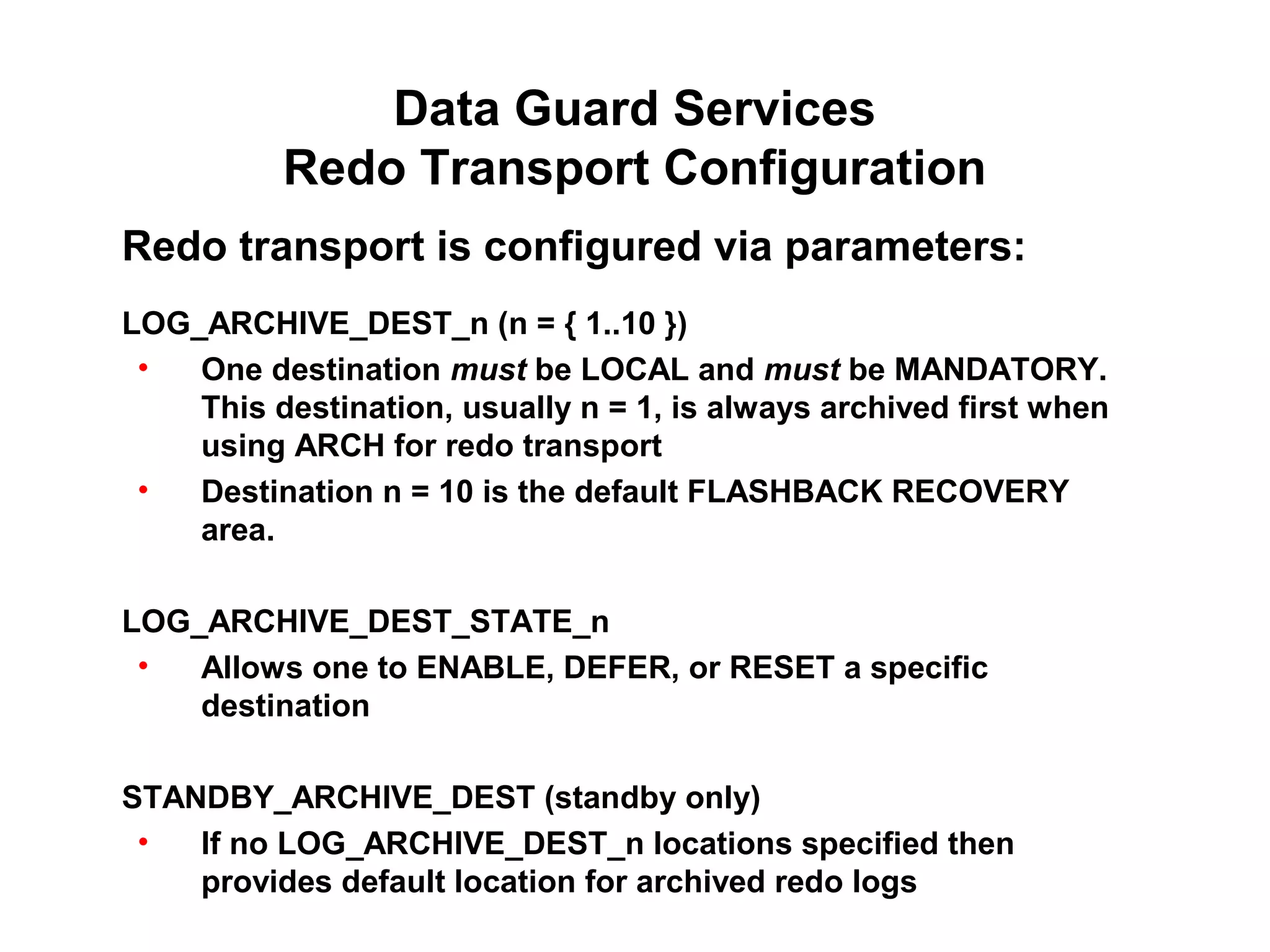
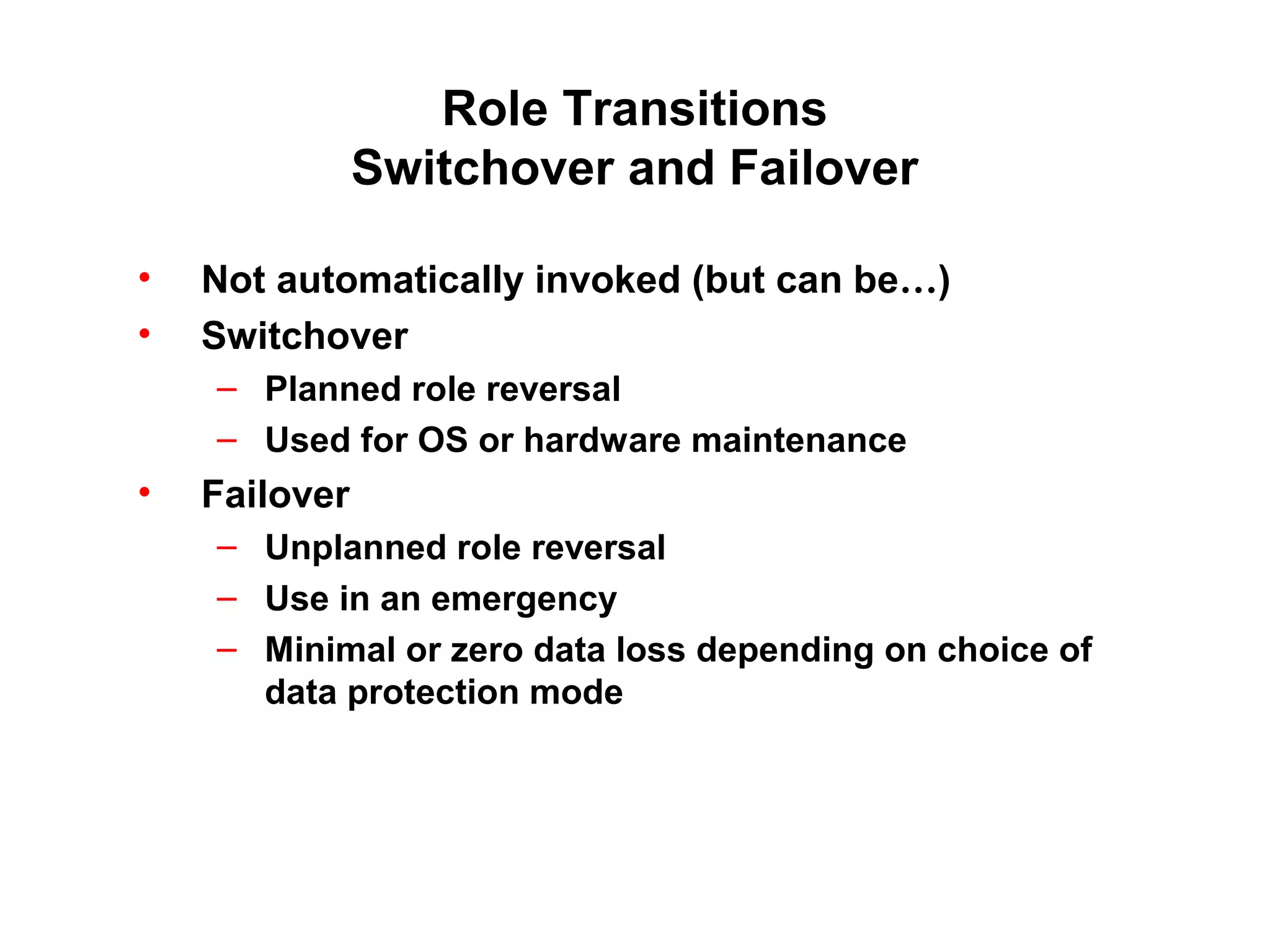
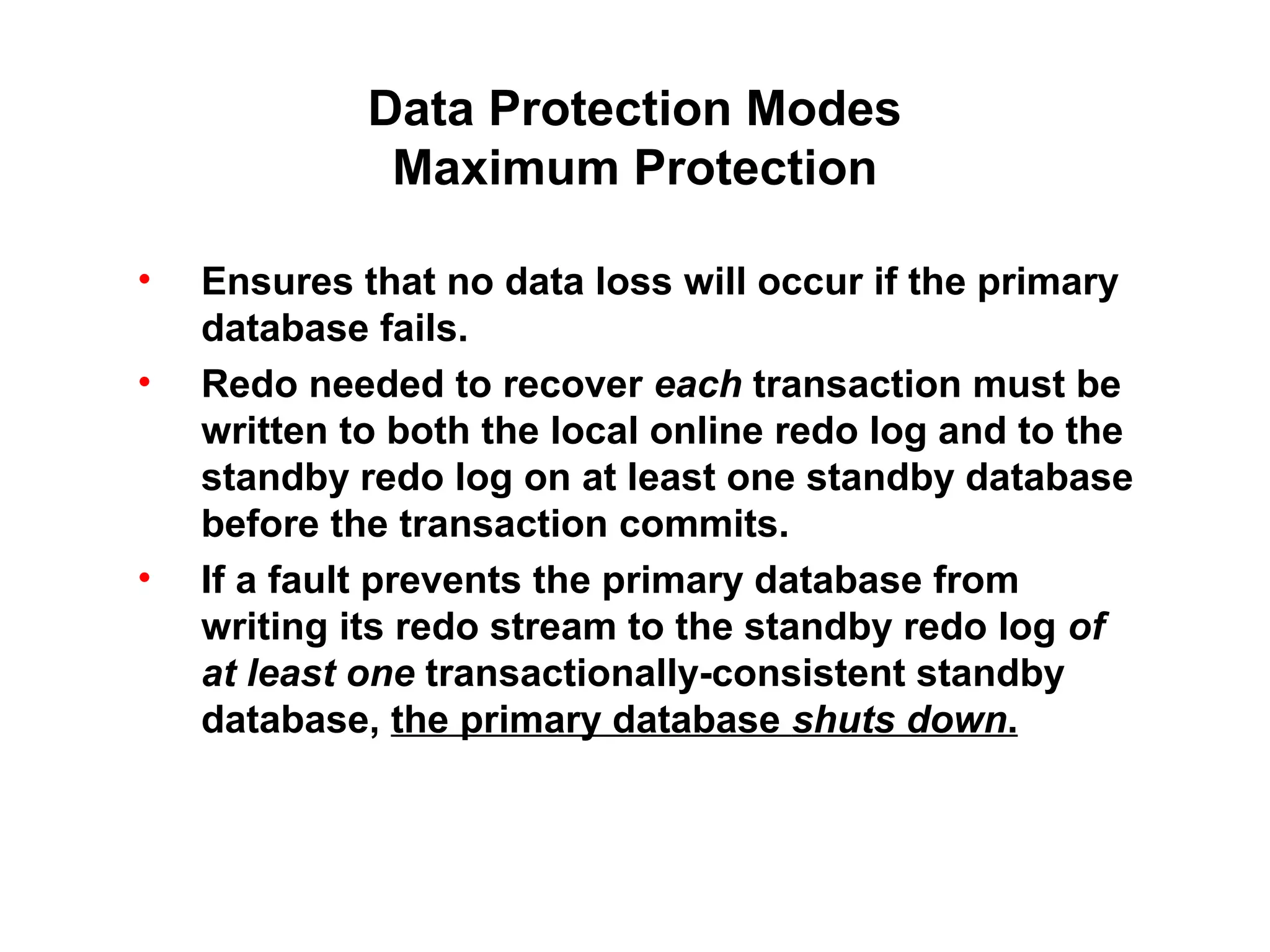
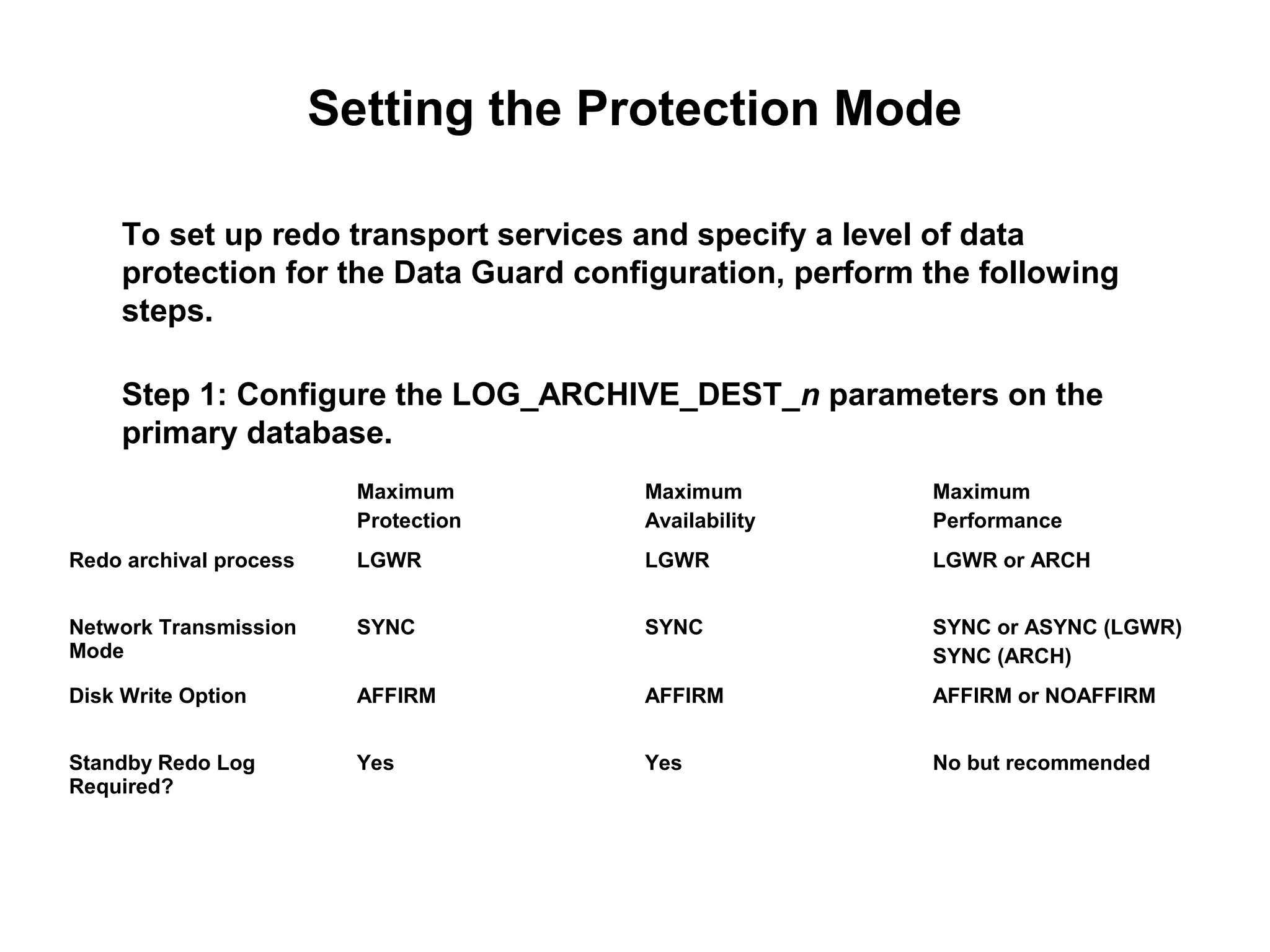
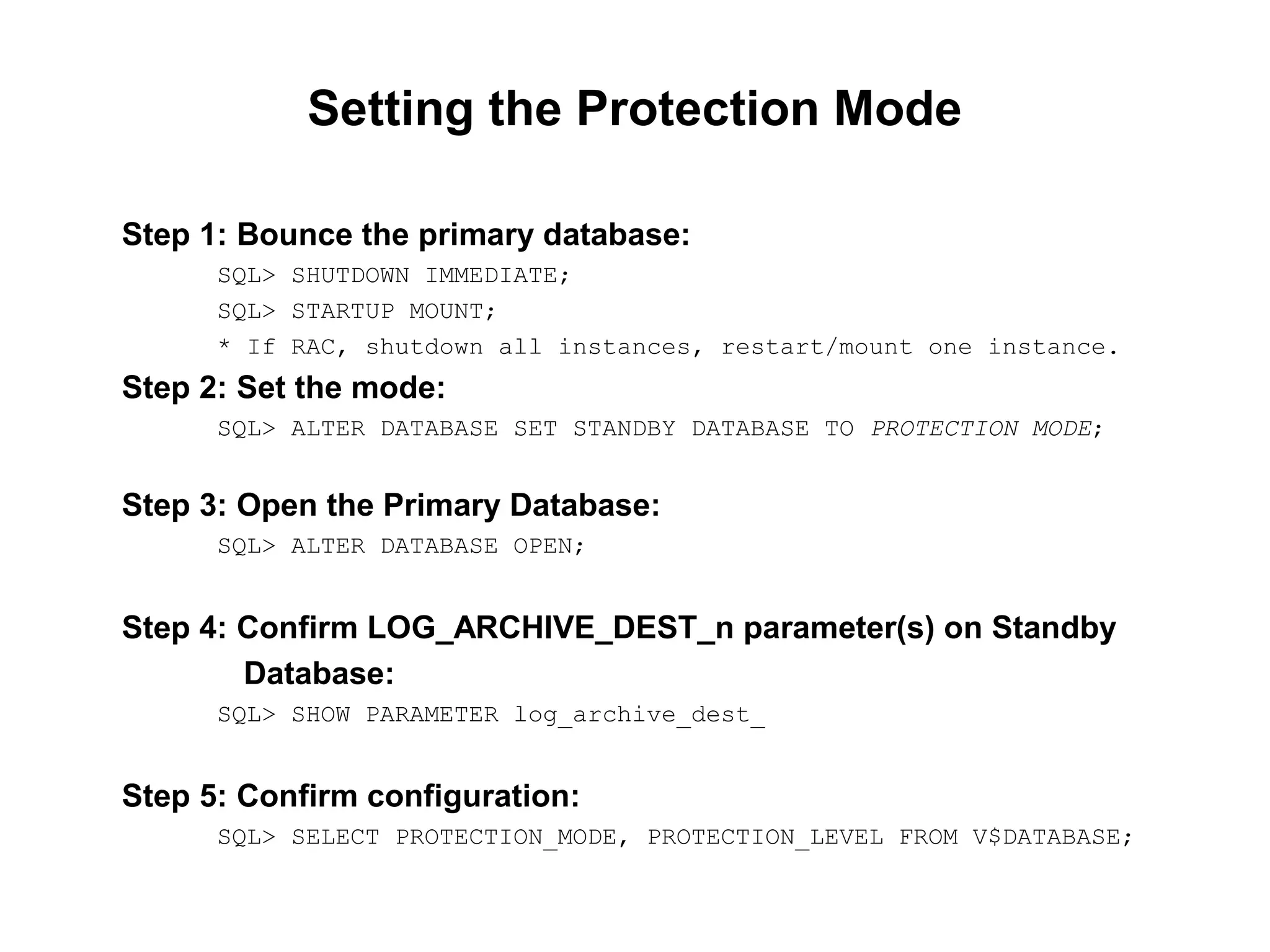
Oracle Data Guard provides several key benefits: continuous database service during disasters or data failures, complete data protection against corruptions and loss, and offloading of queries and backups from primary systems. It uses redo transport to transfer redo logs from a primary database to one or more standby databases, and log apply to maintain synchronization. Different protection modes like maximum protection or maximum performance allow balancing data protection against primary performance.