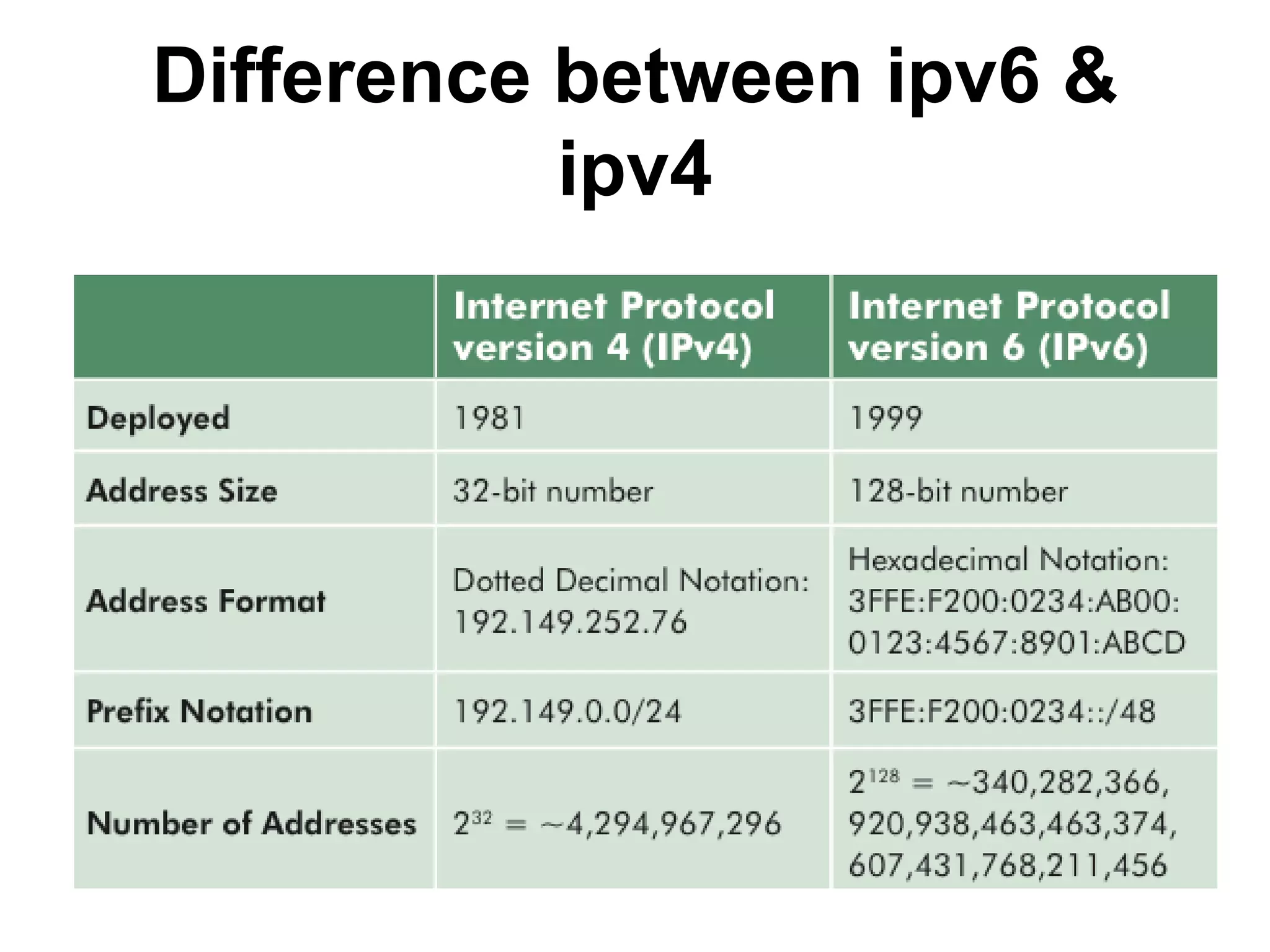
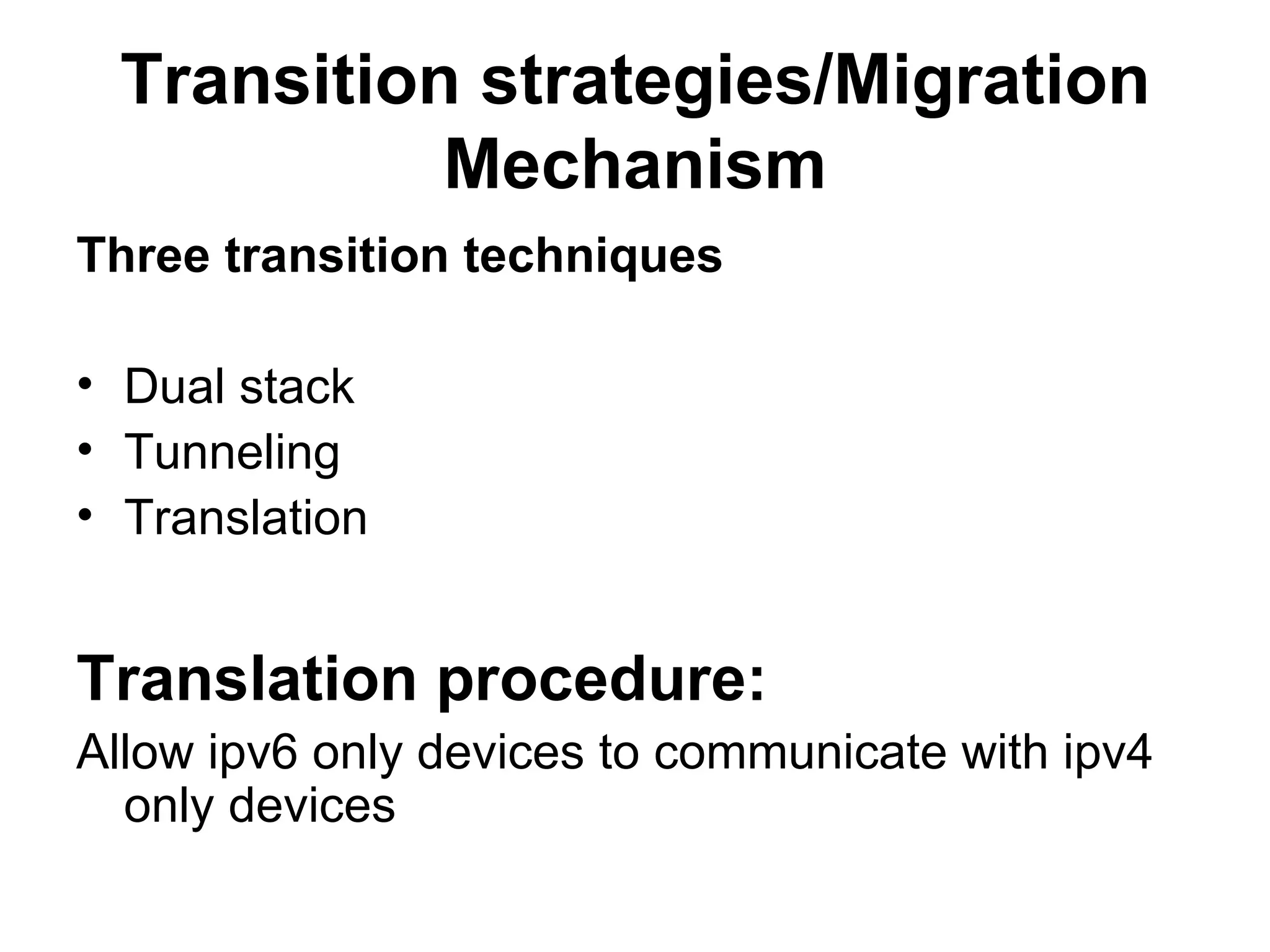
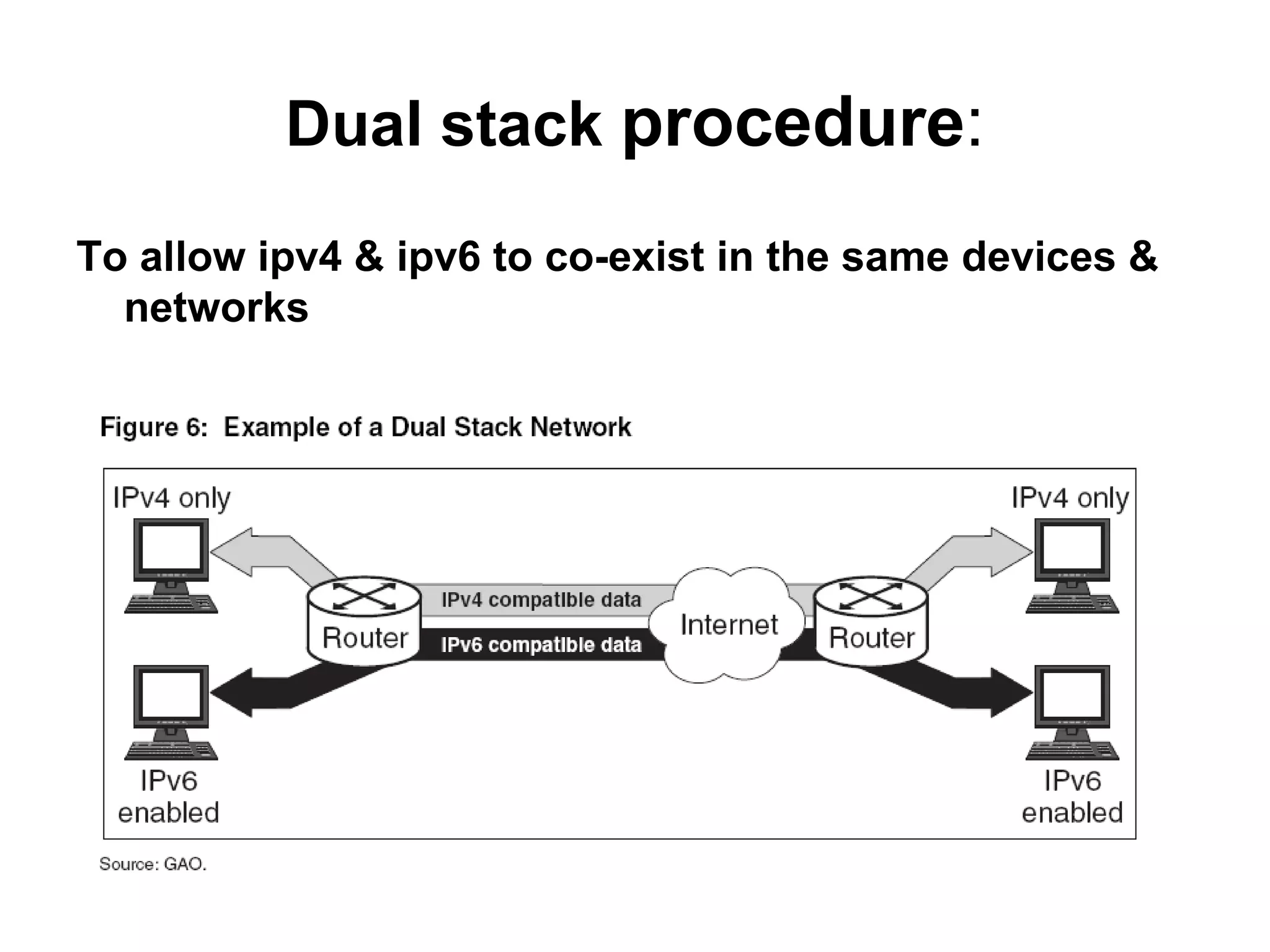
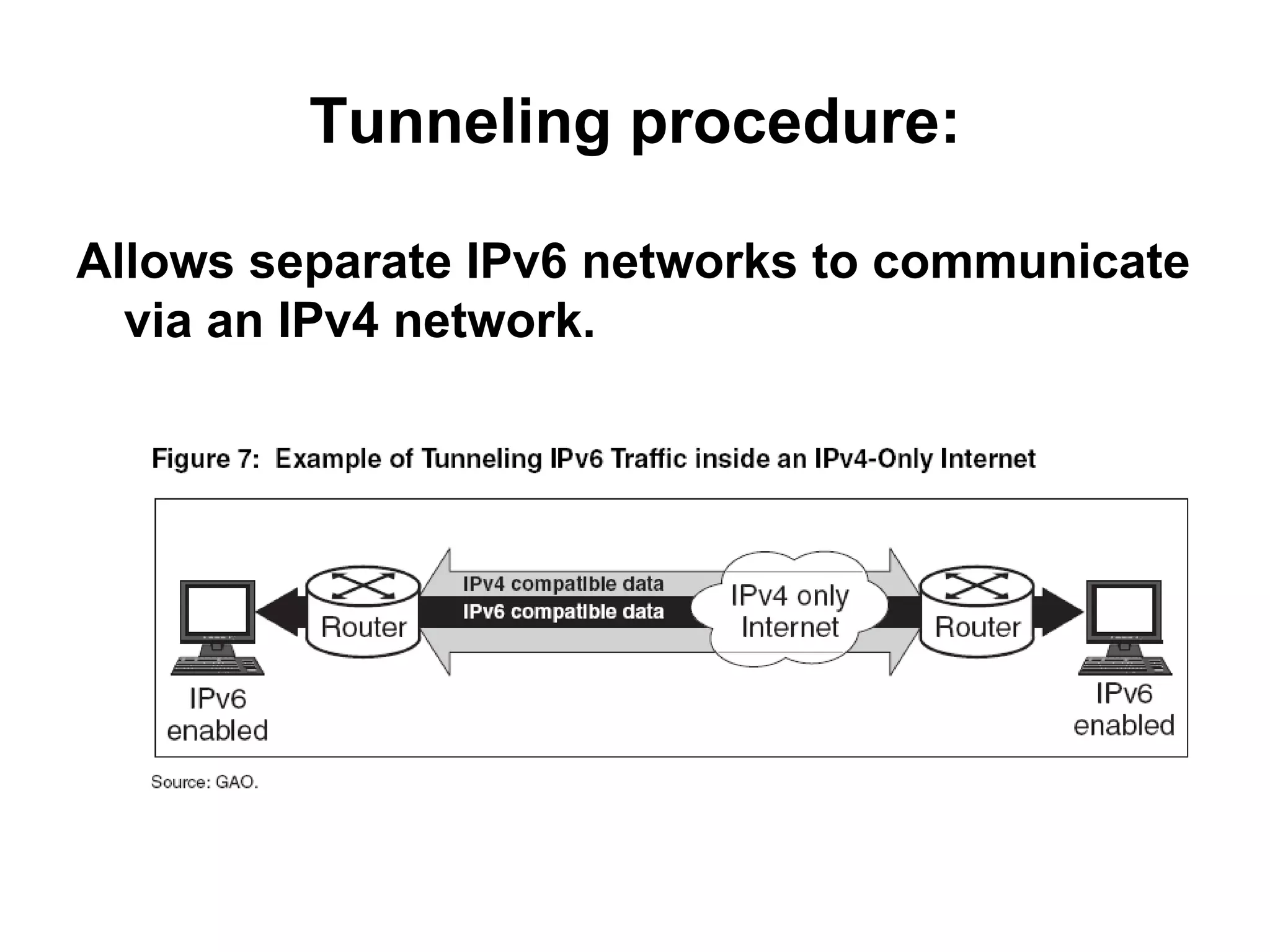
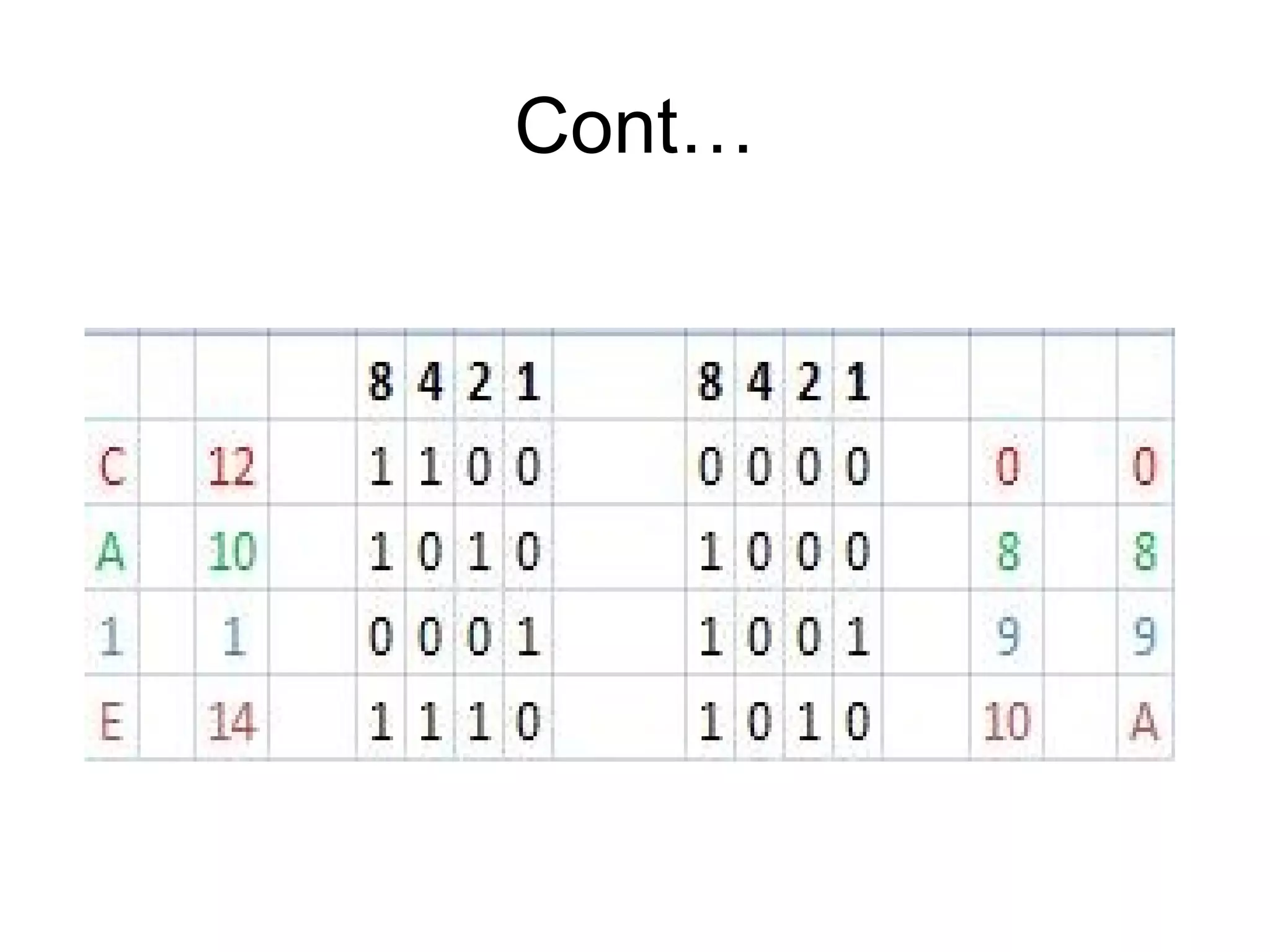
IPv4 and IPv6 are the two main versions of Internet Protocol. IPv4 is the original and most widely used version, but it is limited to 4 billion addresses which may not be enough for future needs. IPv6 was developed in 1999 and provides a much larger address space to meet future demand. There are various transition strategies for moving from IPv4 to IPv6, including dual stacking, tunneling, and translation methods to allow devices and networks using the different protocols to communicate with each other during the changeover process.