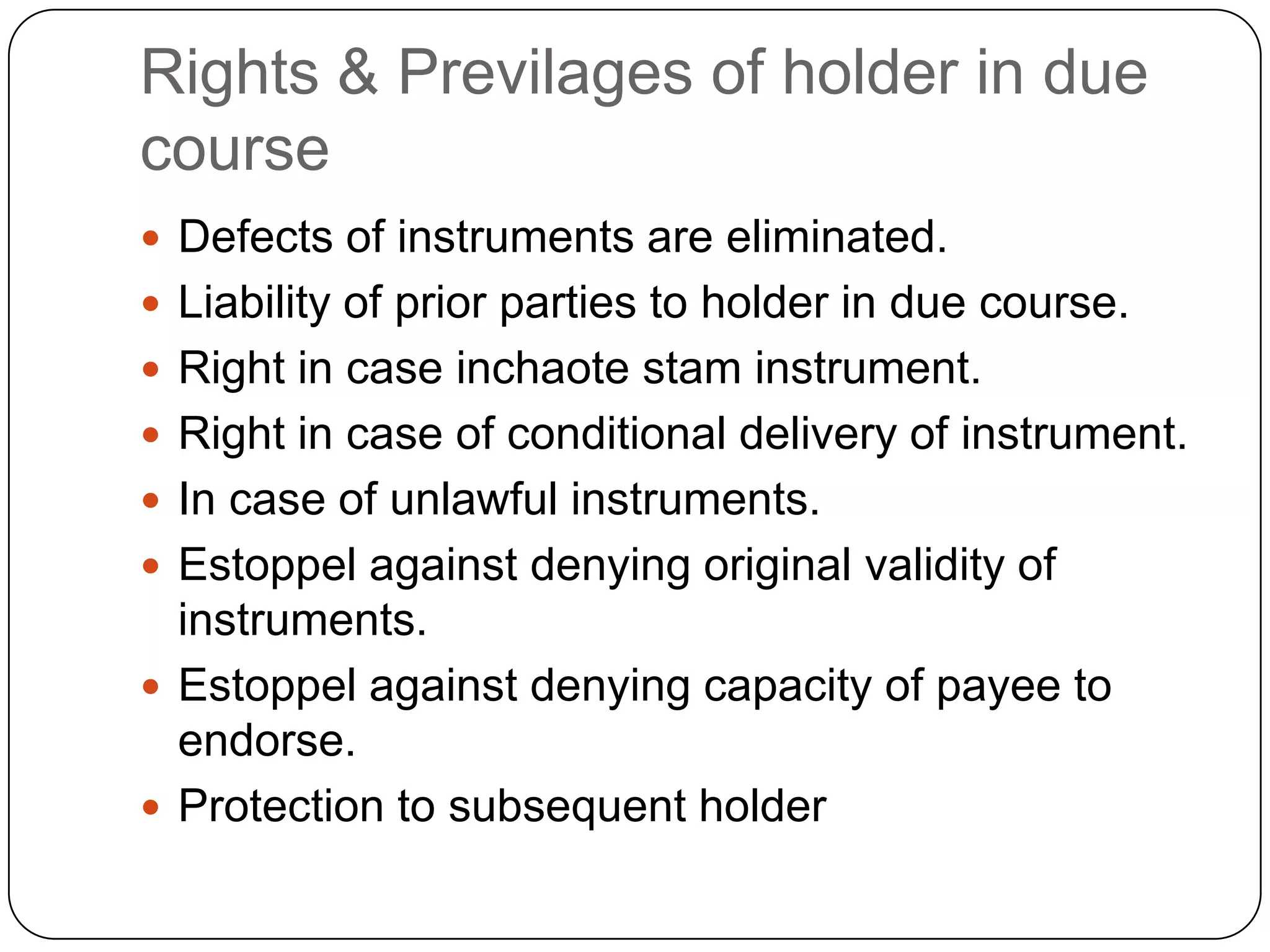
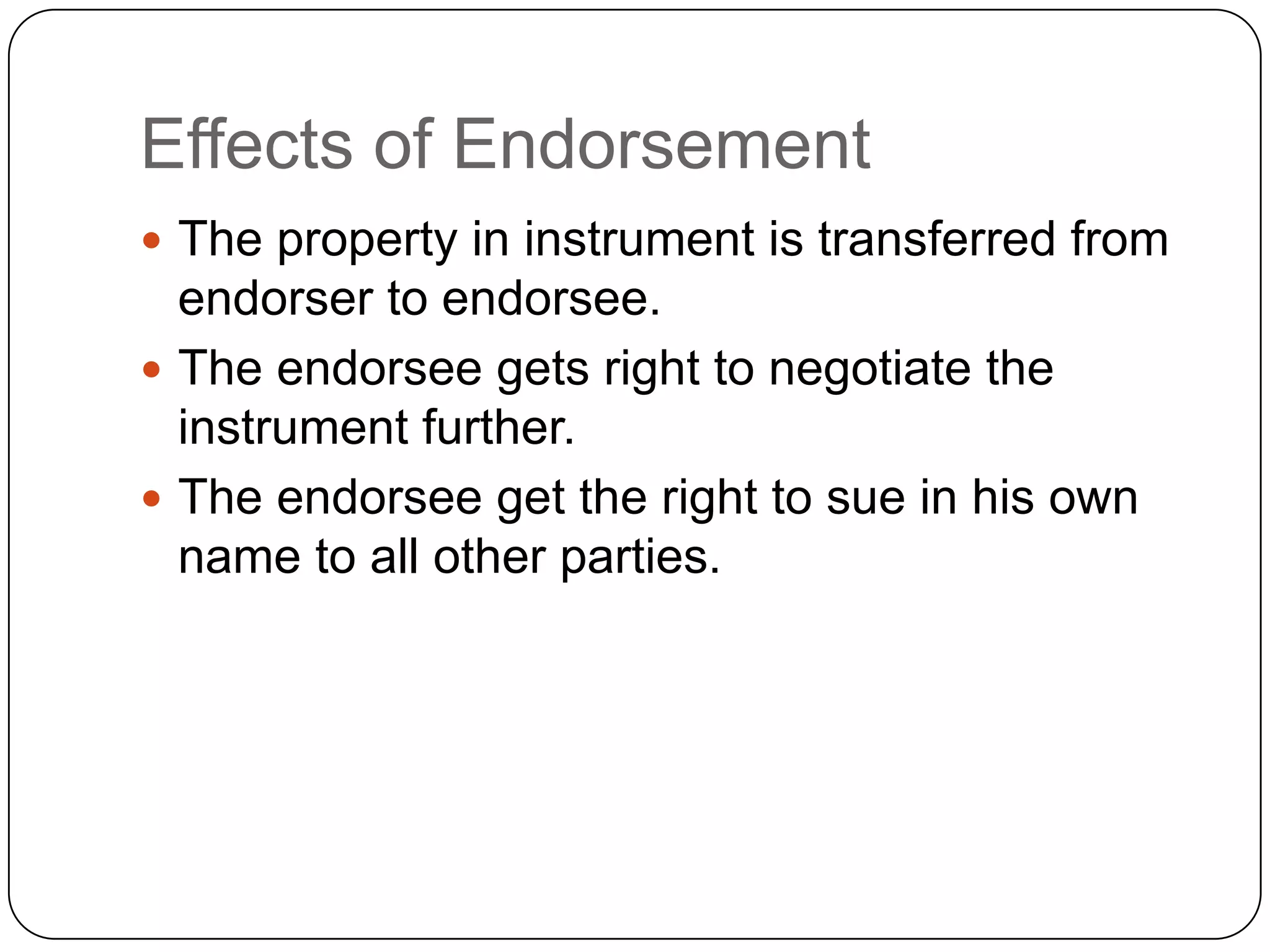
The document discusses key aspects of negotiable instruments under the Negotiable Instruments Act 1881. It defines negotiable instruments as promissory notes, bills of exchange, or cheques payable to order or bearer. Instruments can be negotiable by statute or usage. Negotiation involves transferring possession with intent to pass title to the transferee. Holders in due course take the instrument for value before maturity and in good faith, gaining defenses against certain claims. Endorsement involves signing to transfer ownership, and can take various forms like blank, special, or restrictive.