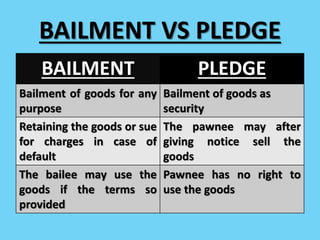
Pledge is the bailment of goods as security for repayment of a debt or performance of a promise. The pledger (bailor) delivers possession of movable property to the pledgee (bailee) as security. The pledgee has the right to retain the goods until repayment of the debt and expenses. The pledger can redeem the goods by repaying the debt within the agreed time or any subsequent time before goods are sold. Duties include the pledgee taking reasonable care of goods and the pledger repaying the debt. A non-owner can also pledge goods in some situations like a mercantile agent pledging with owner's consent.