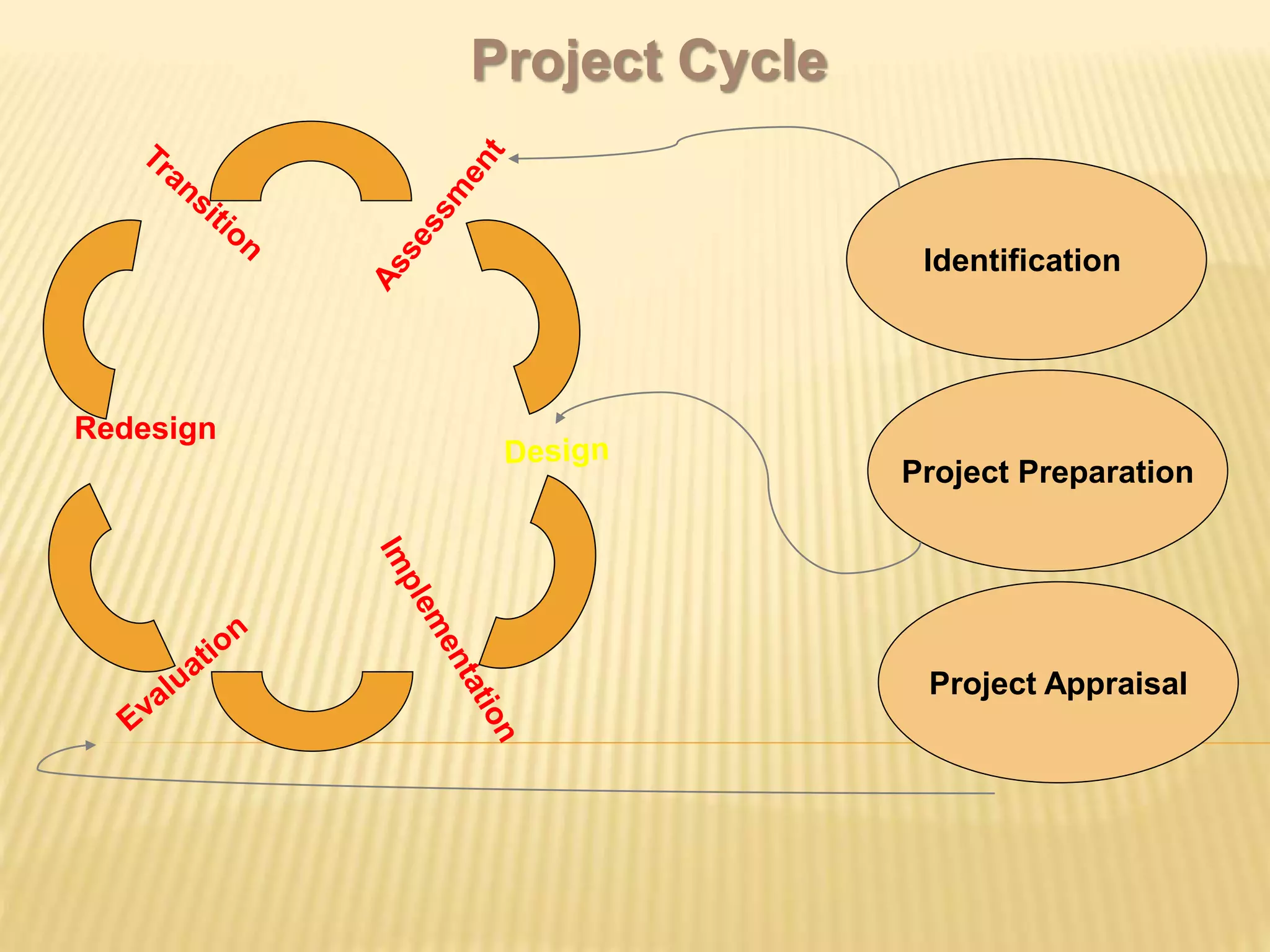
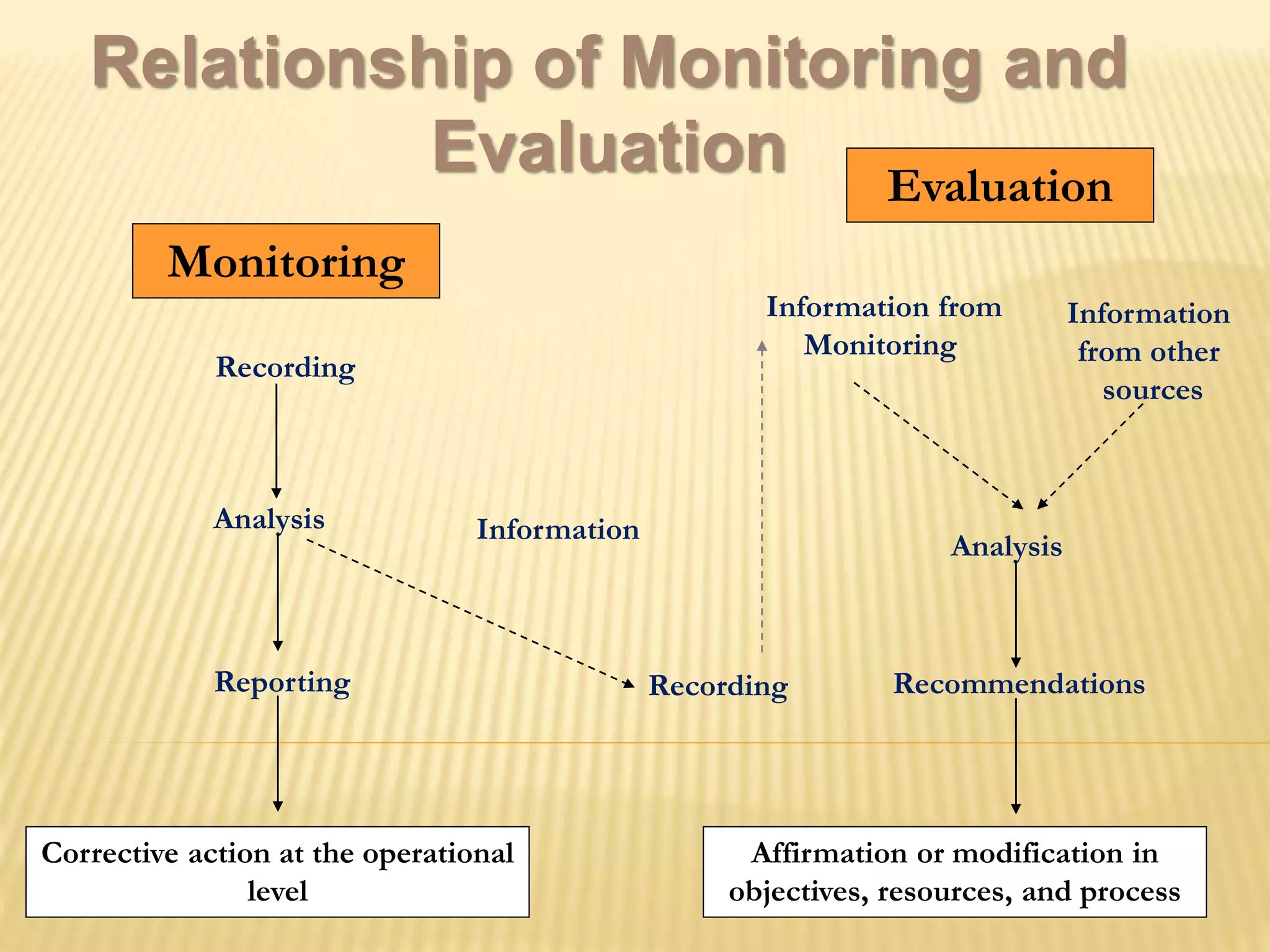
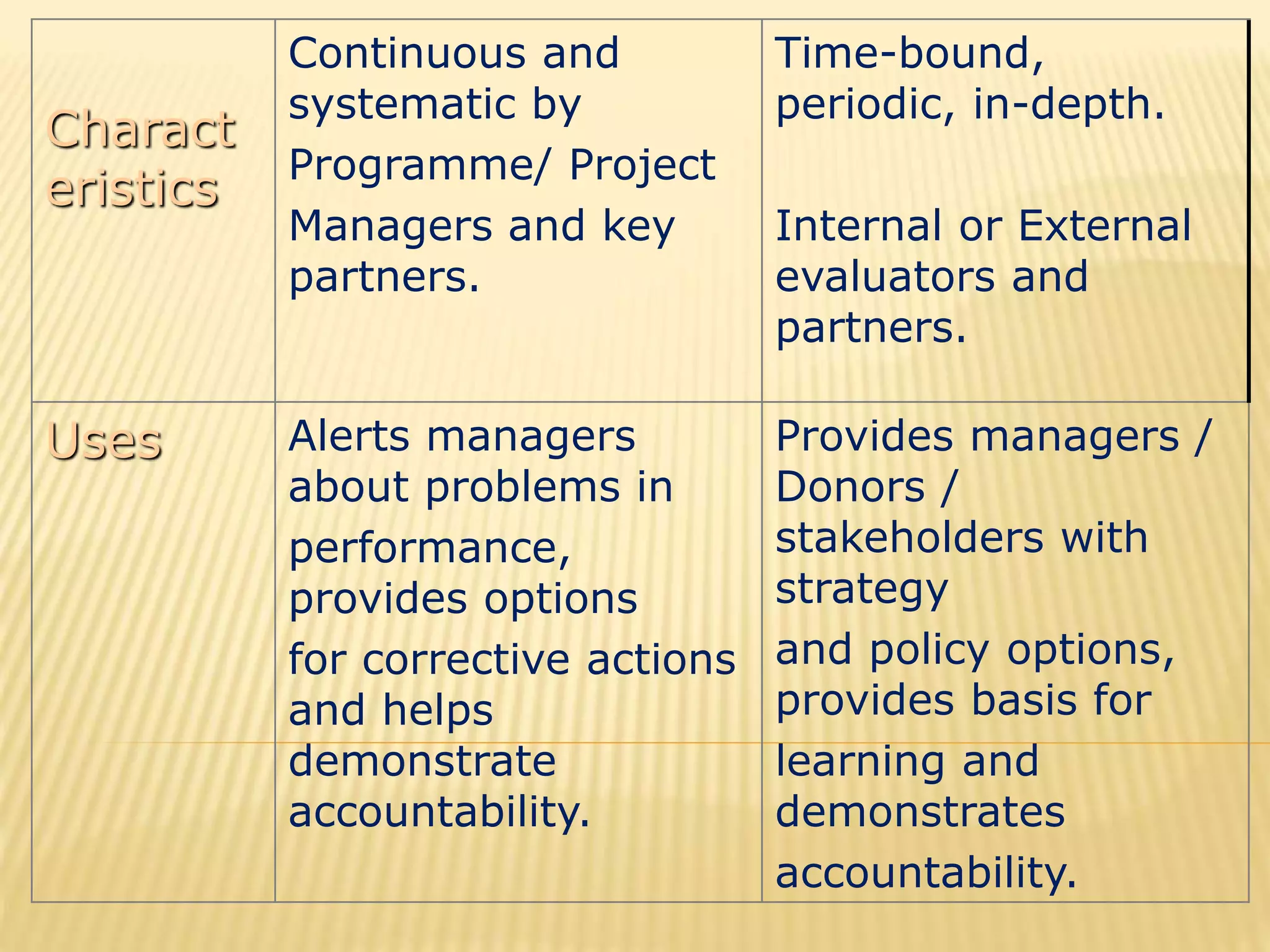
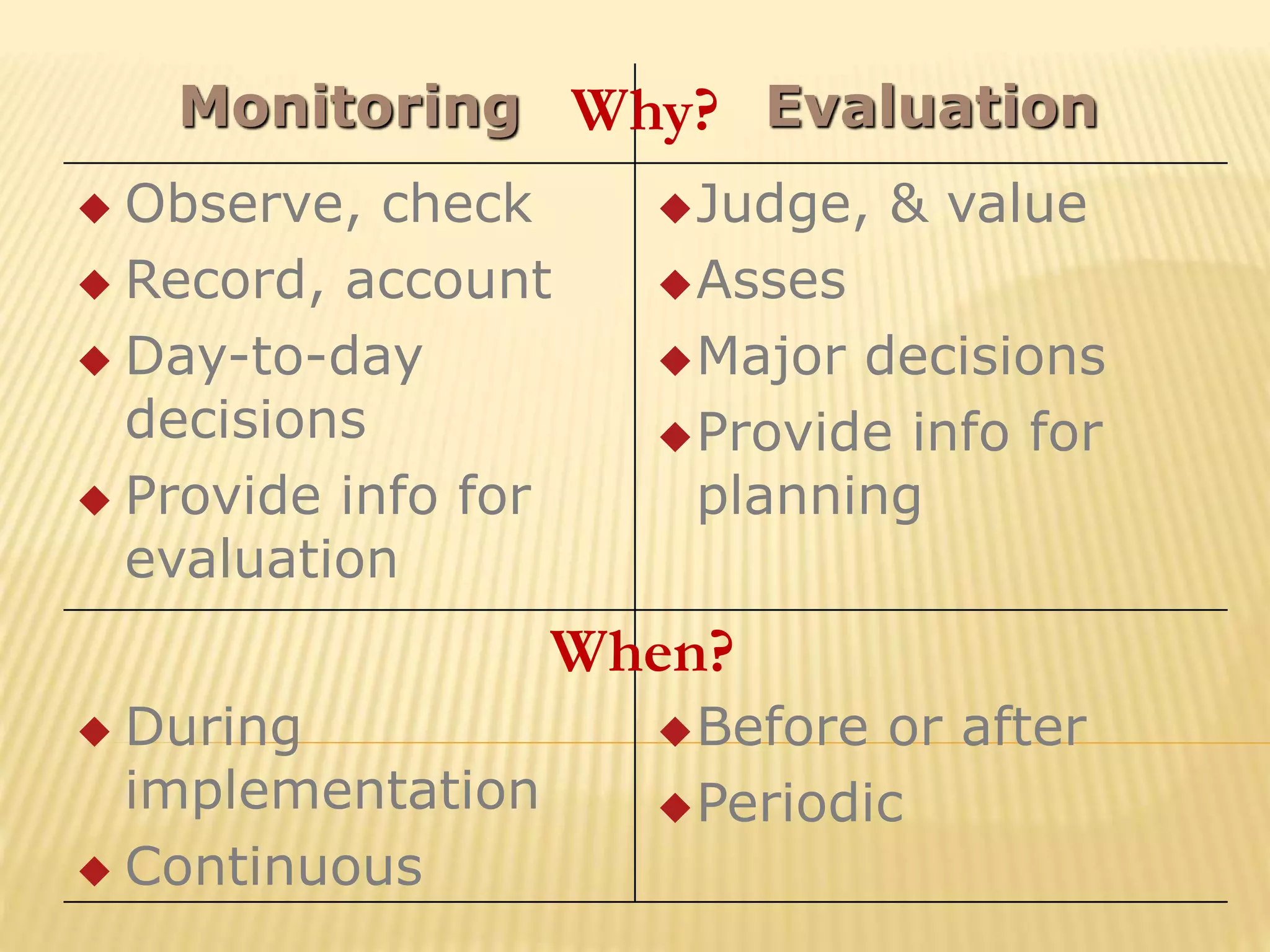
The document discusses monitoring and evaluation in project management. It defines monitoring as systematically recording information to check if a project's activities and outputs are proceeding according to plan. The goals of monitoring are to ensure inputs and activities are implemented properly and targets are met. Evaluation is assessing the project's overall worth and impact by examining relevance, effectiveness, efficiency, sustainability, and impact. It compares pre-and post-intervention conditions. Monitoring provides continuous feedback for operations while evaluation informs major decisions and lessons for future projects. Both are important for project accountability, performance improvement and decision making.