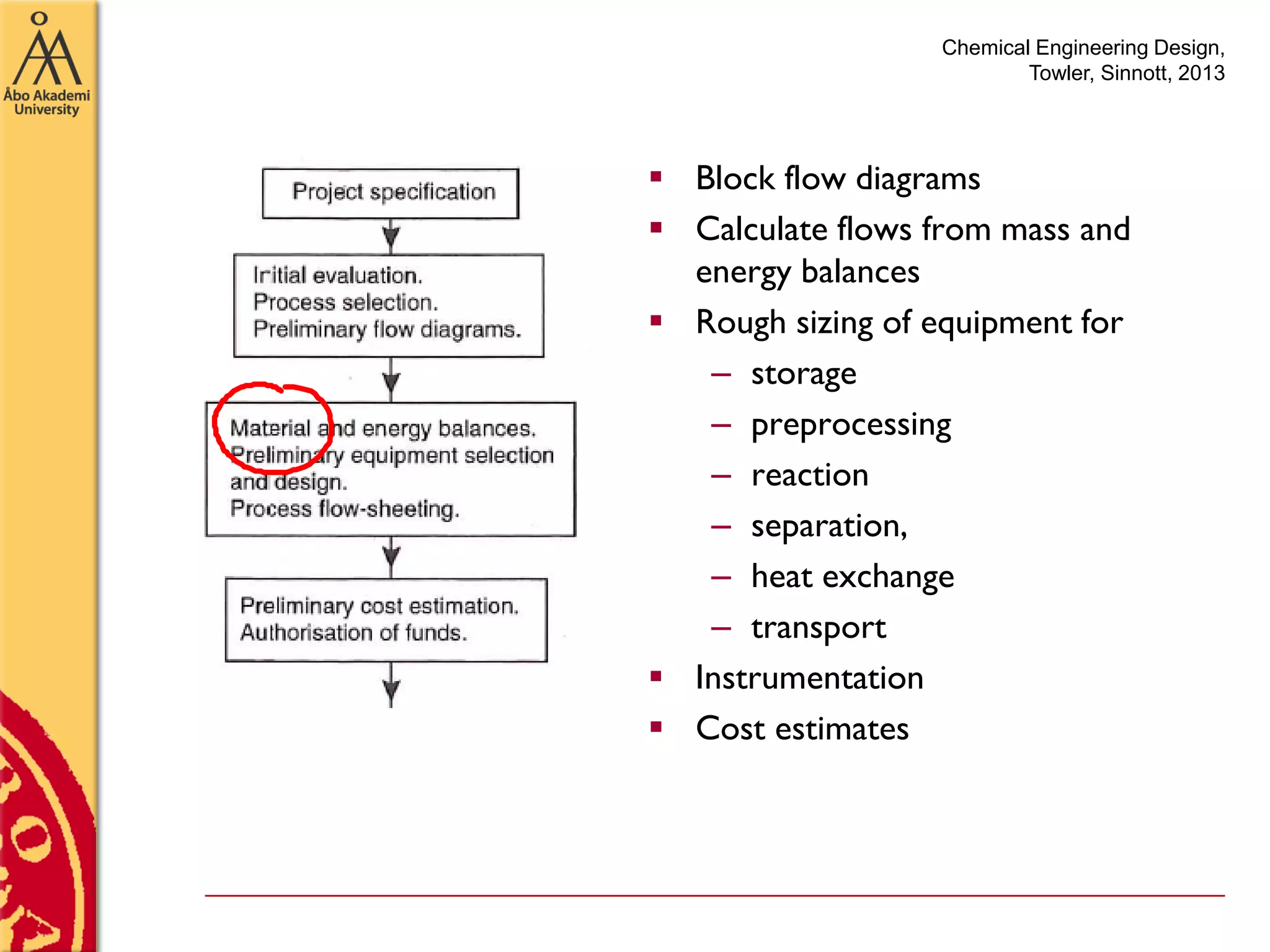
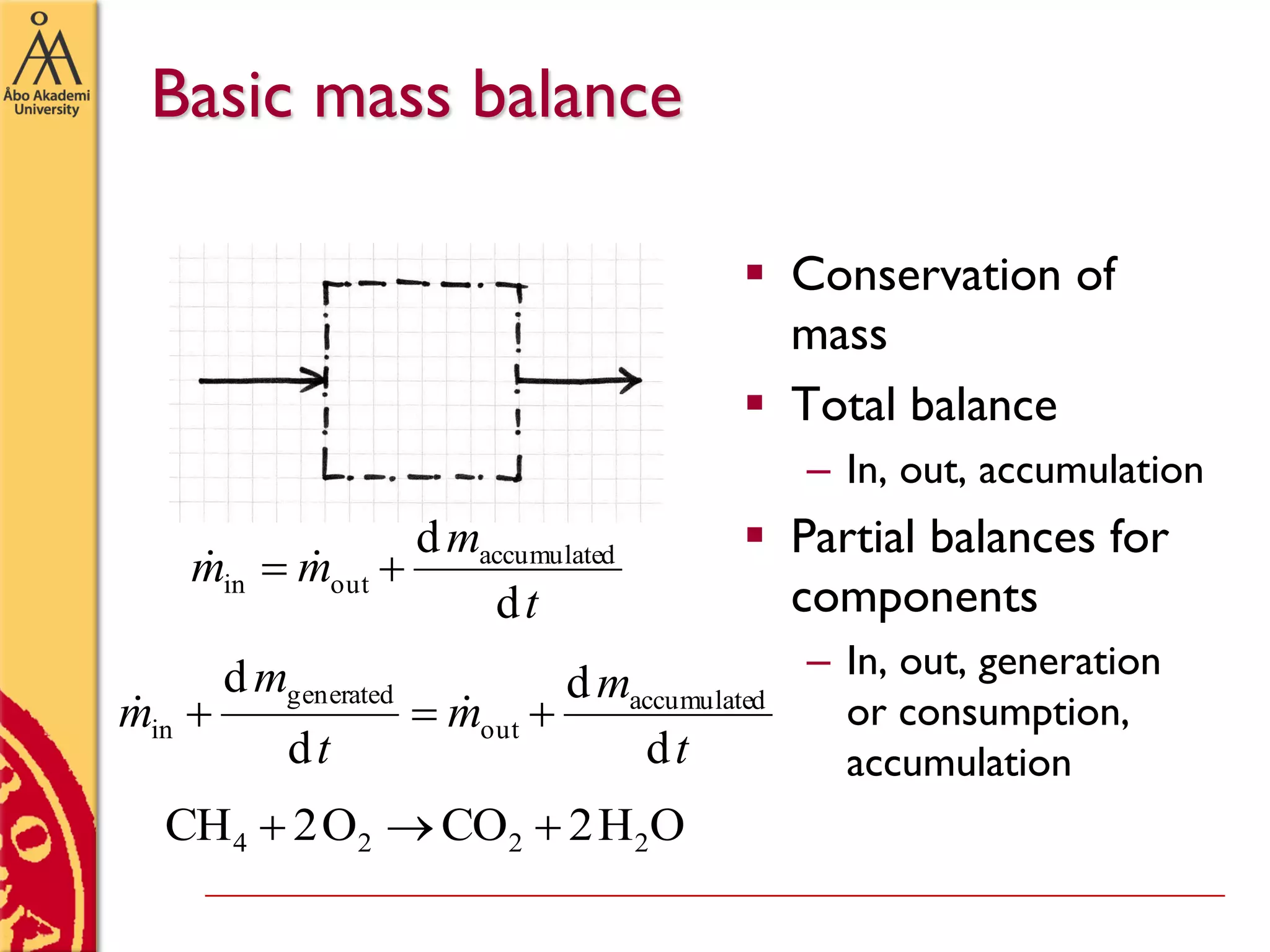
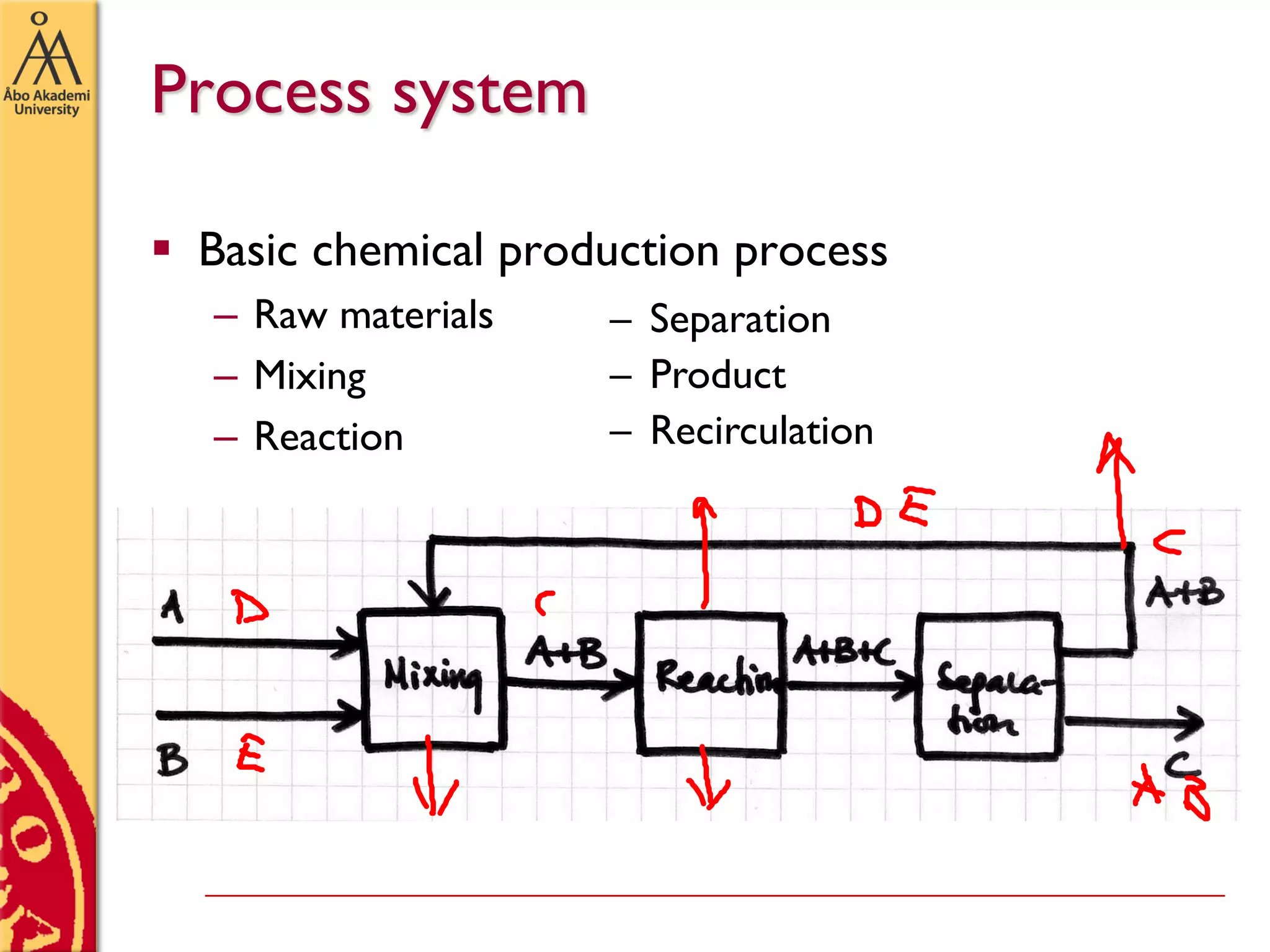
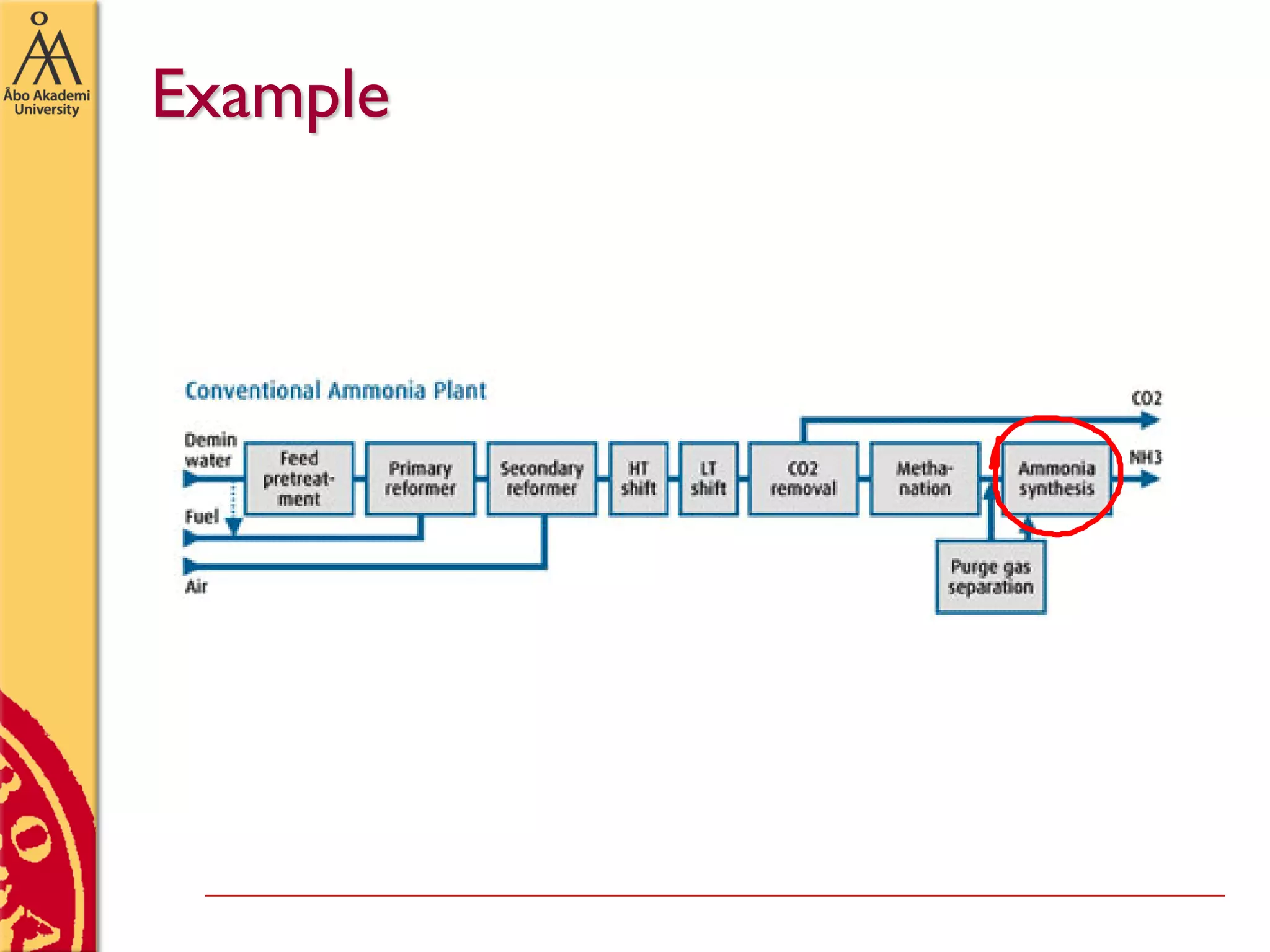
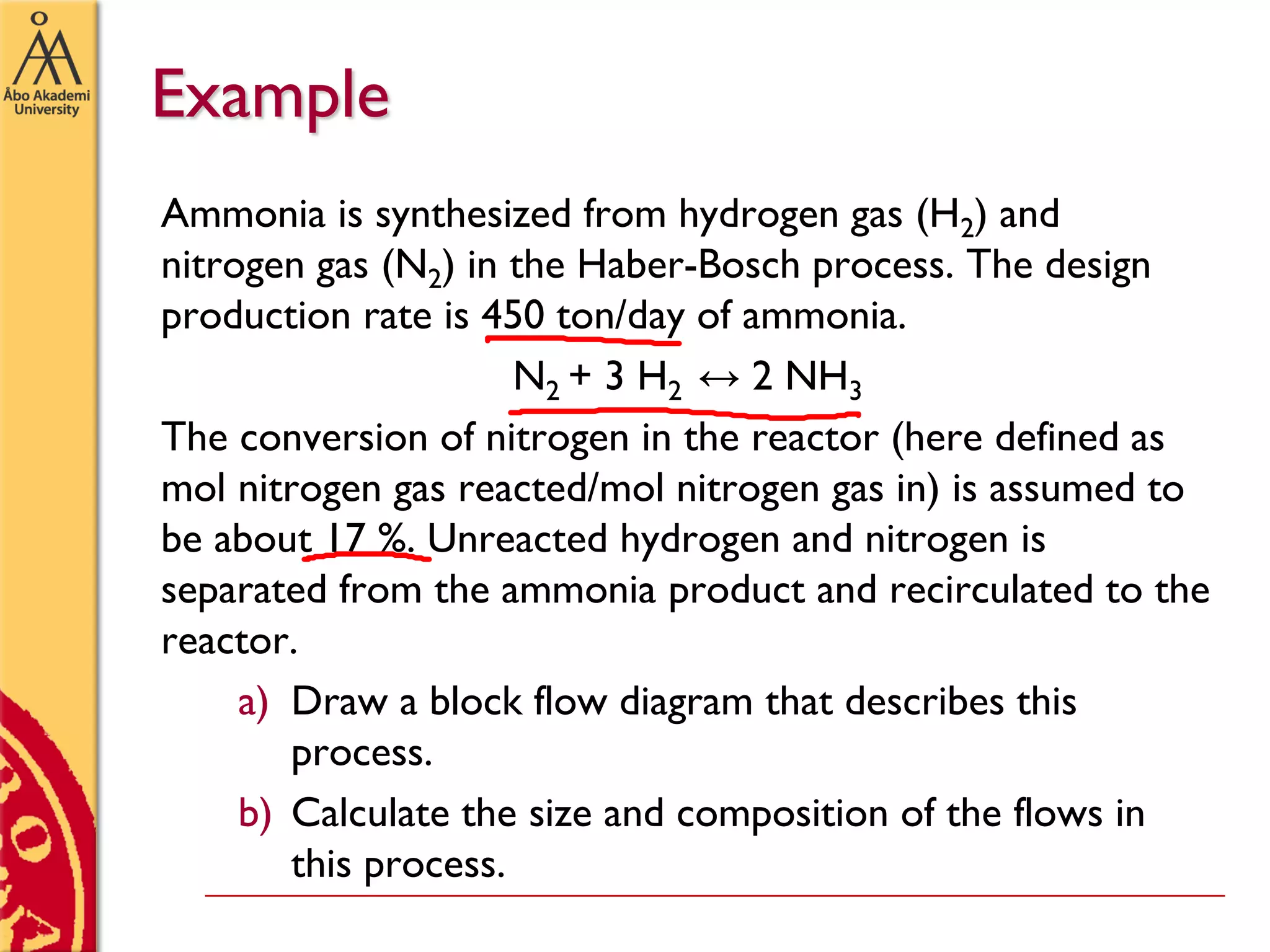
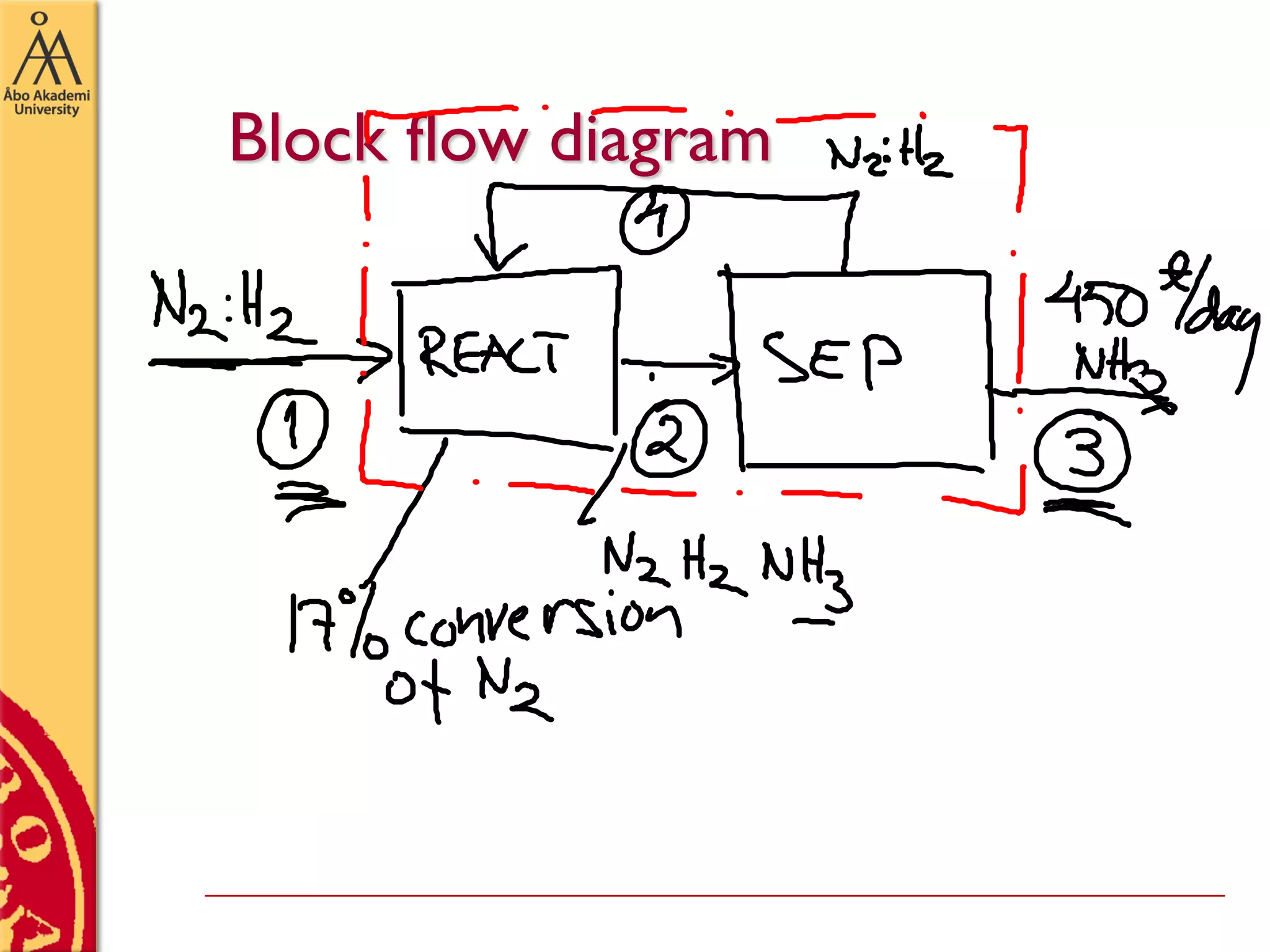
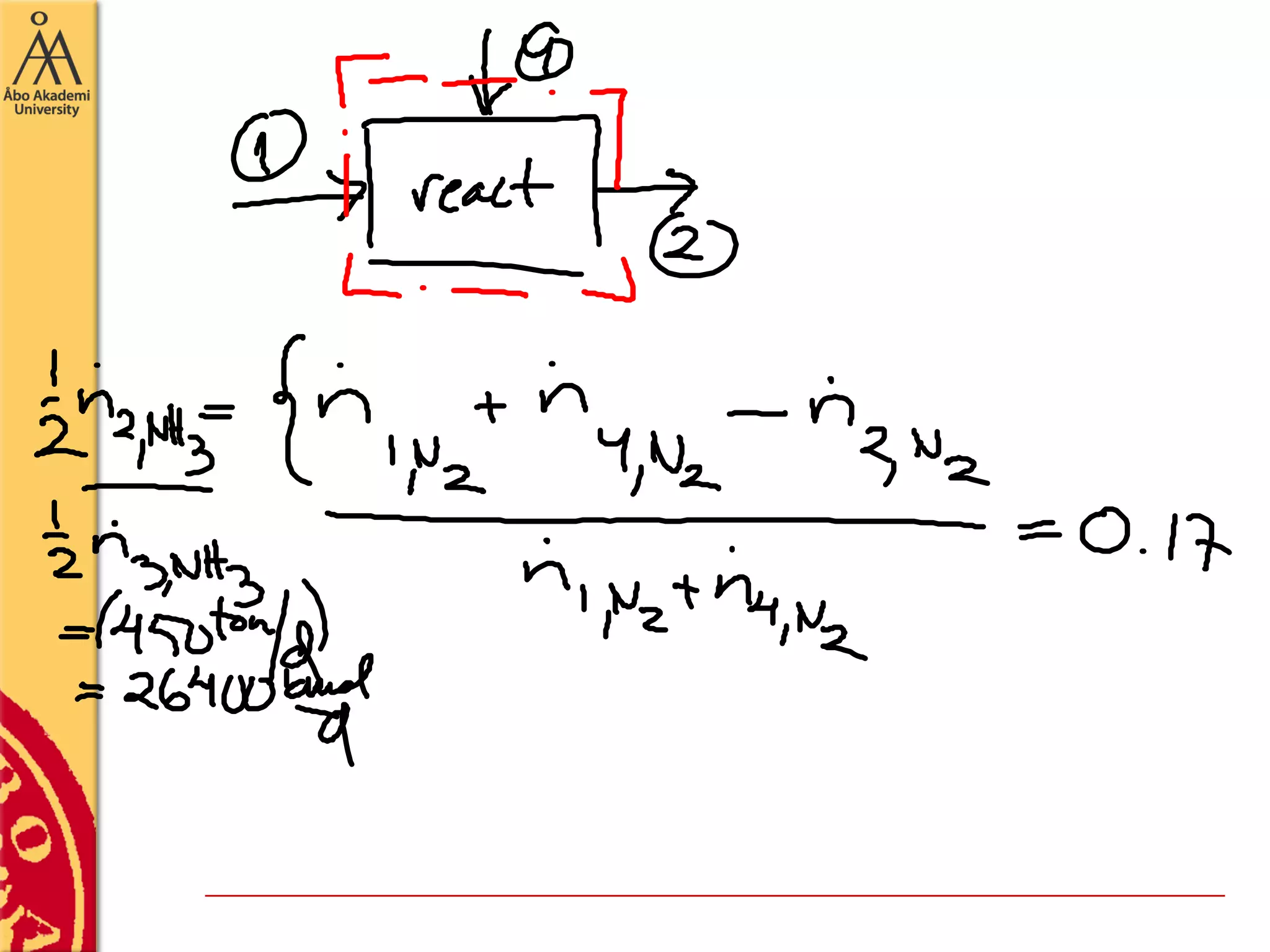
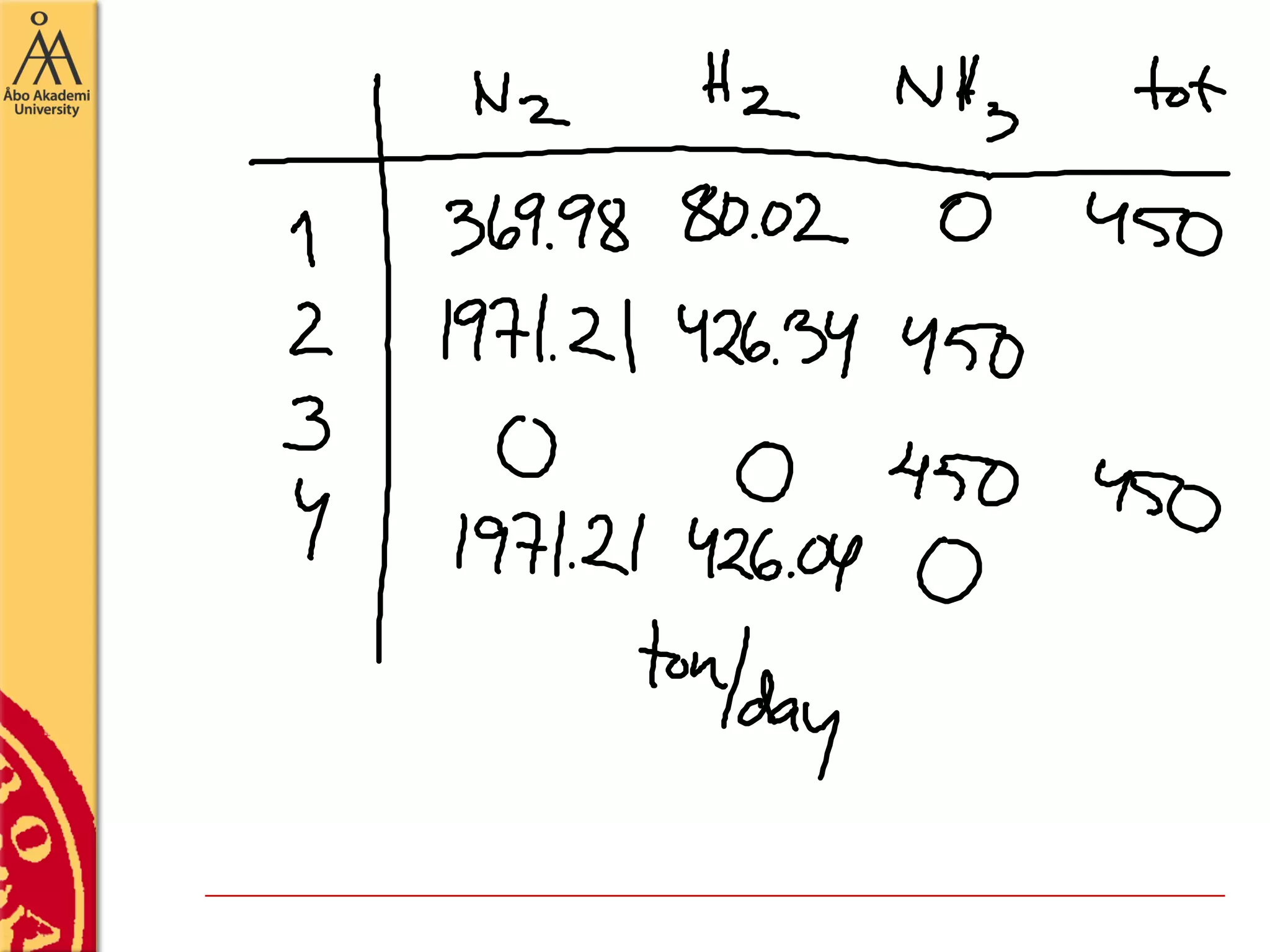
This document discusses basics in process design including mass balances, block flow diagrams, equipment sizing, and modeling processes. It provides an example of modeling the Haber-Bosch process for ammonia synthesis. The example problem asks the reader to (1) draw a block flow diagram of the process and (2) calculate the size and composition of flows given a production rate of 450 tons per day of ammonia and 17% conversion of nitrogen in the reactor. The document outlines how to set up and solve mass balances by hand or using simulation software.