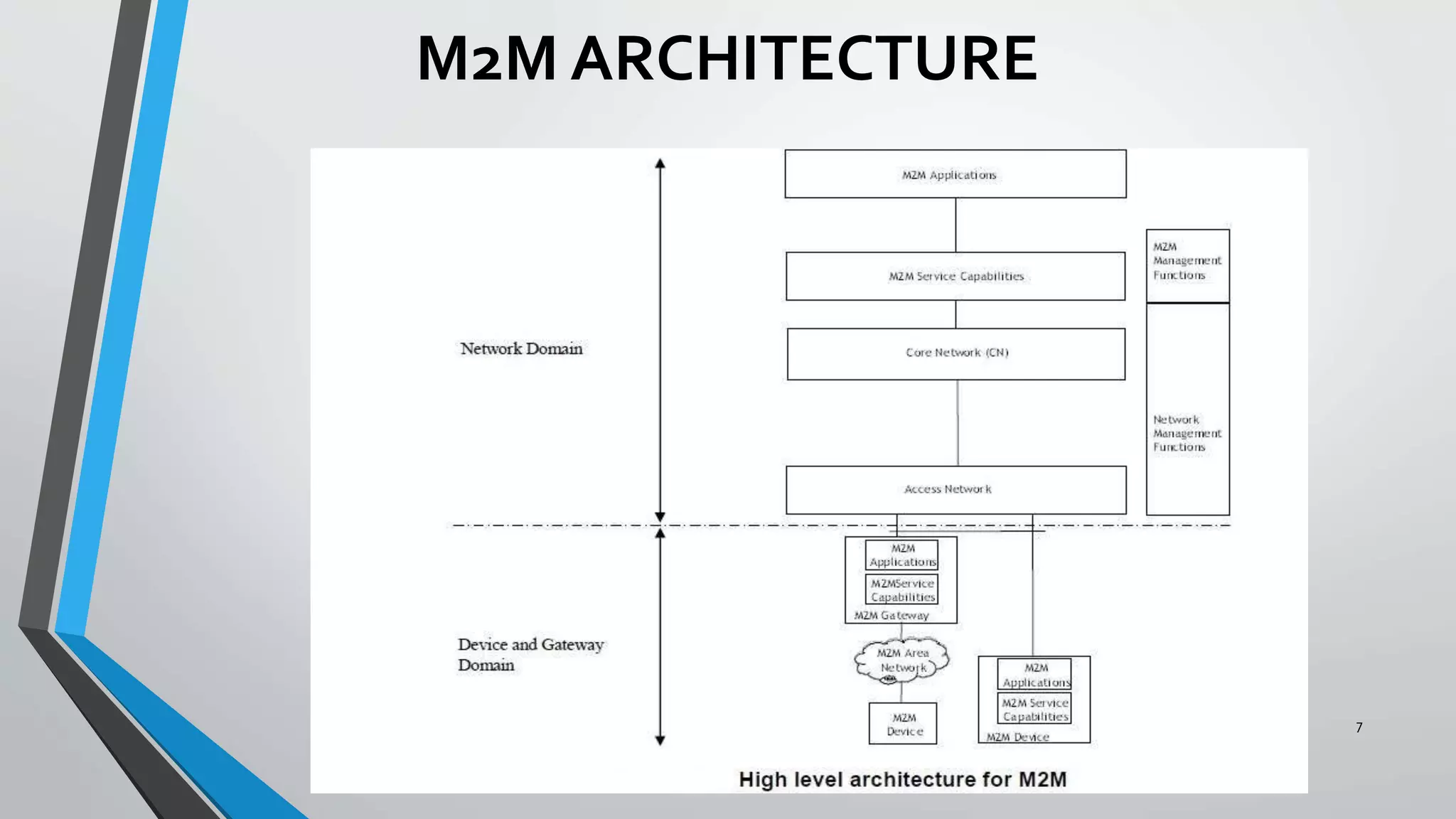
This document provides an overview of a project to develop a machine-to-machine communication device for medical applications and disaster management. It discusses:
1) The literature review on existing M2M systems for medical consultation, smart metering, and context awareness.
2) The proposed system which would measure a person's pulse/heart rate or temperature and send the data over LAN to a monitoring device to analyze for threshold levels and prevent intoxicated driving.
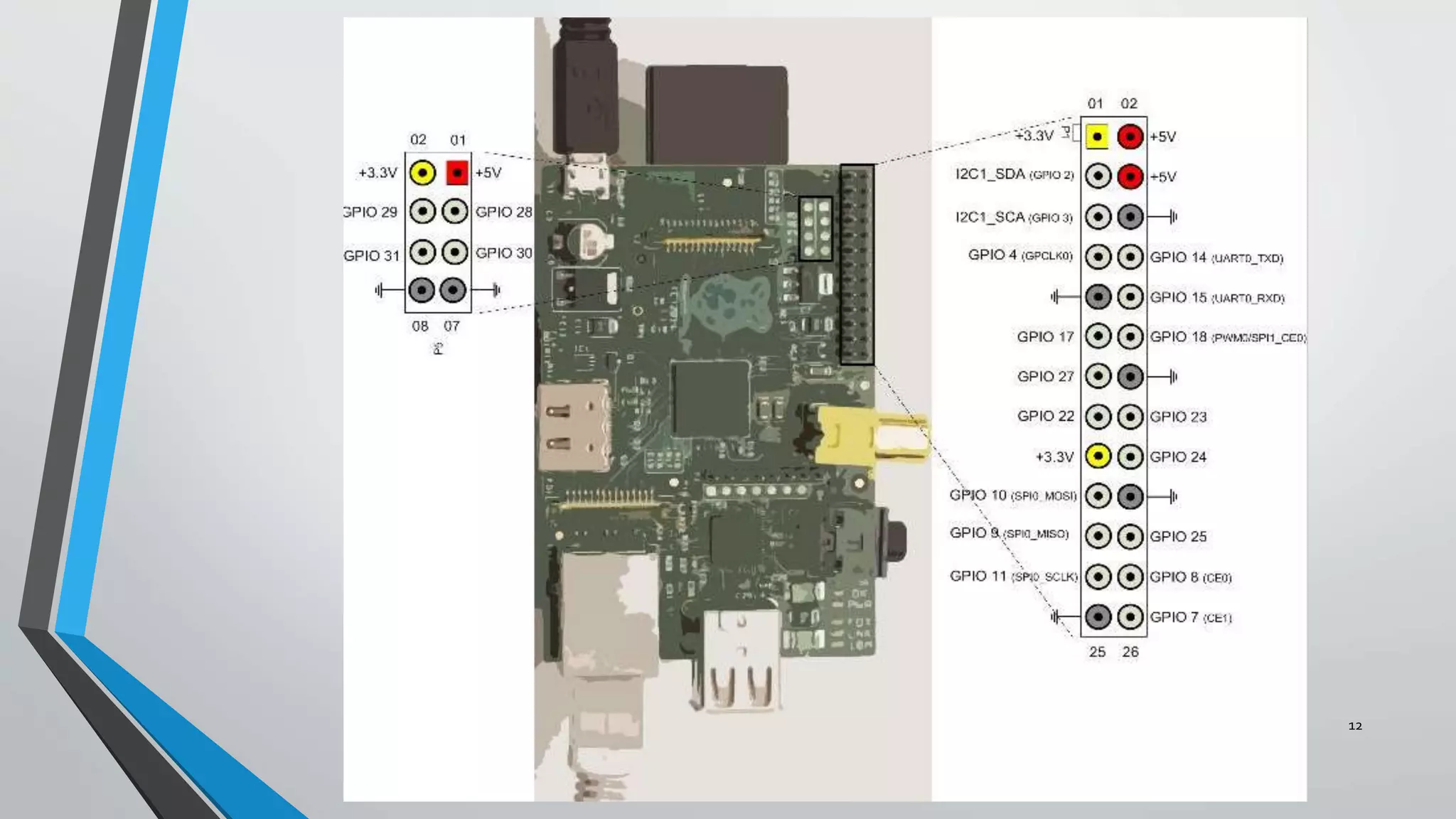
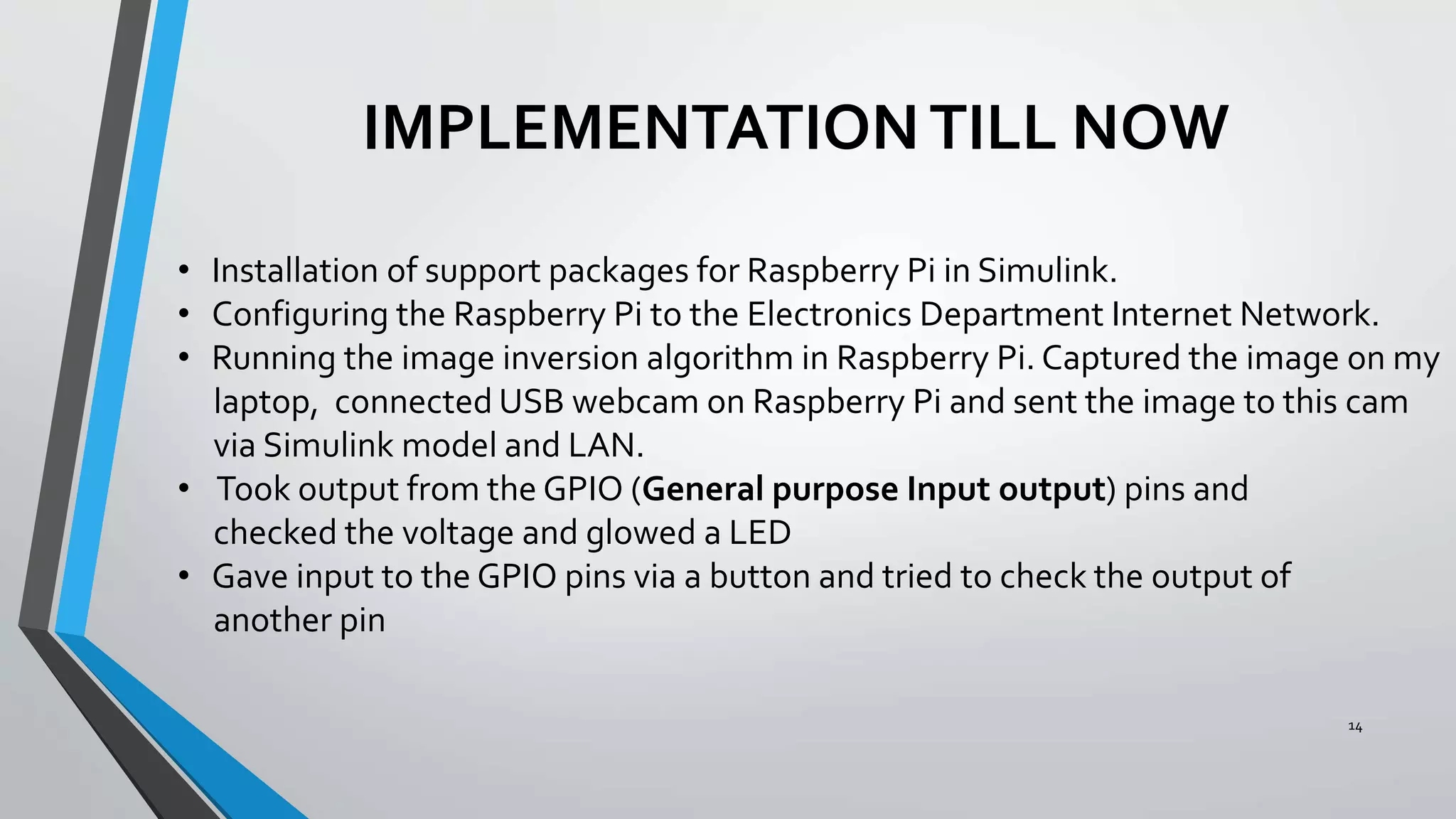
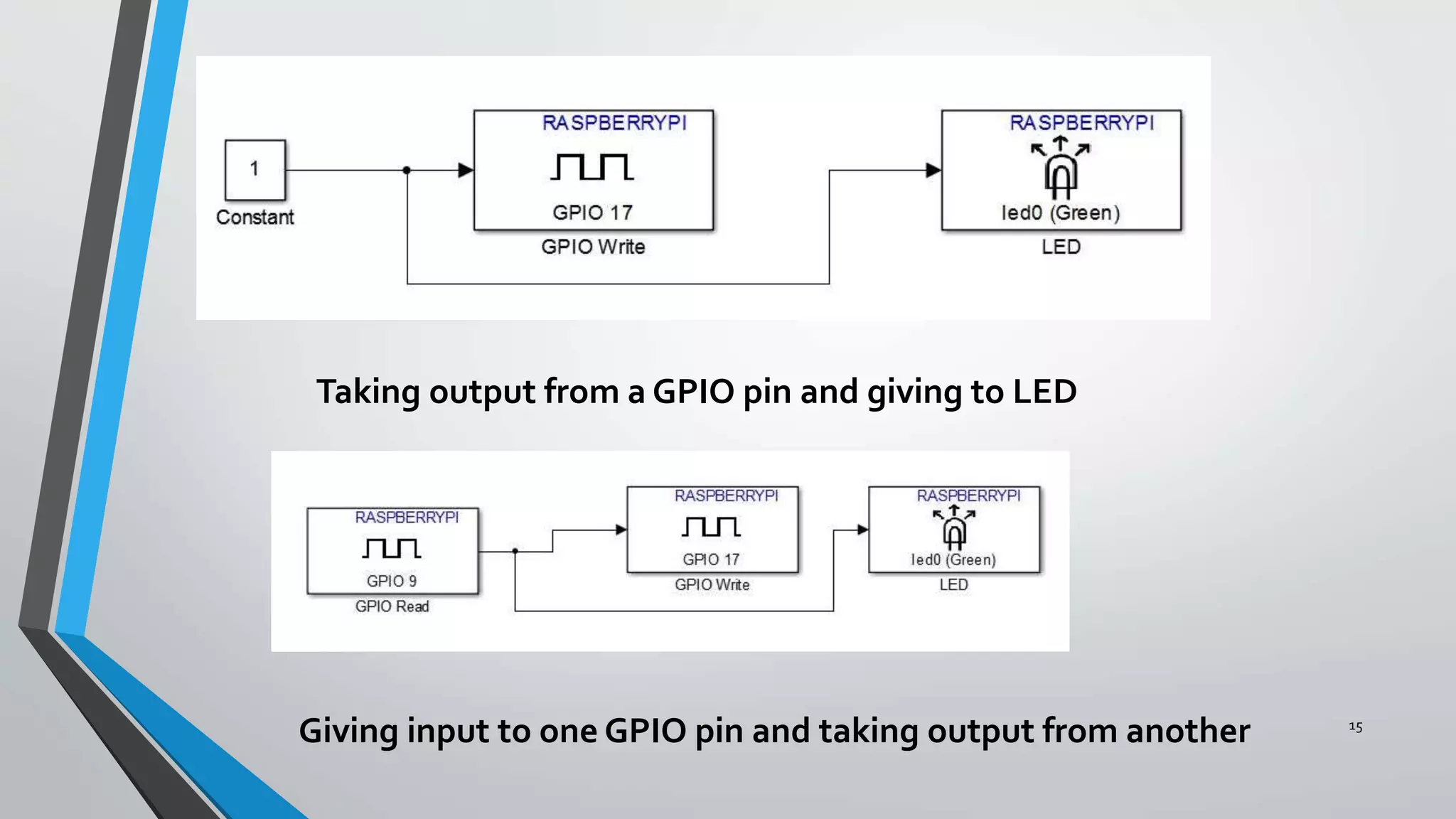
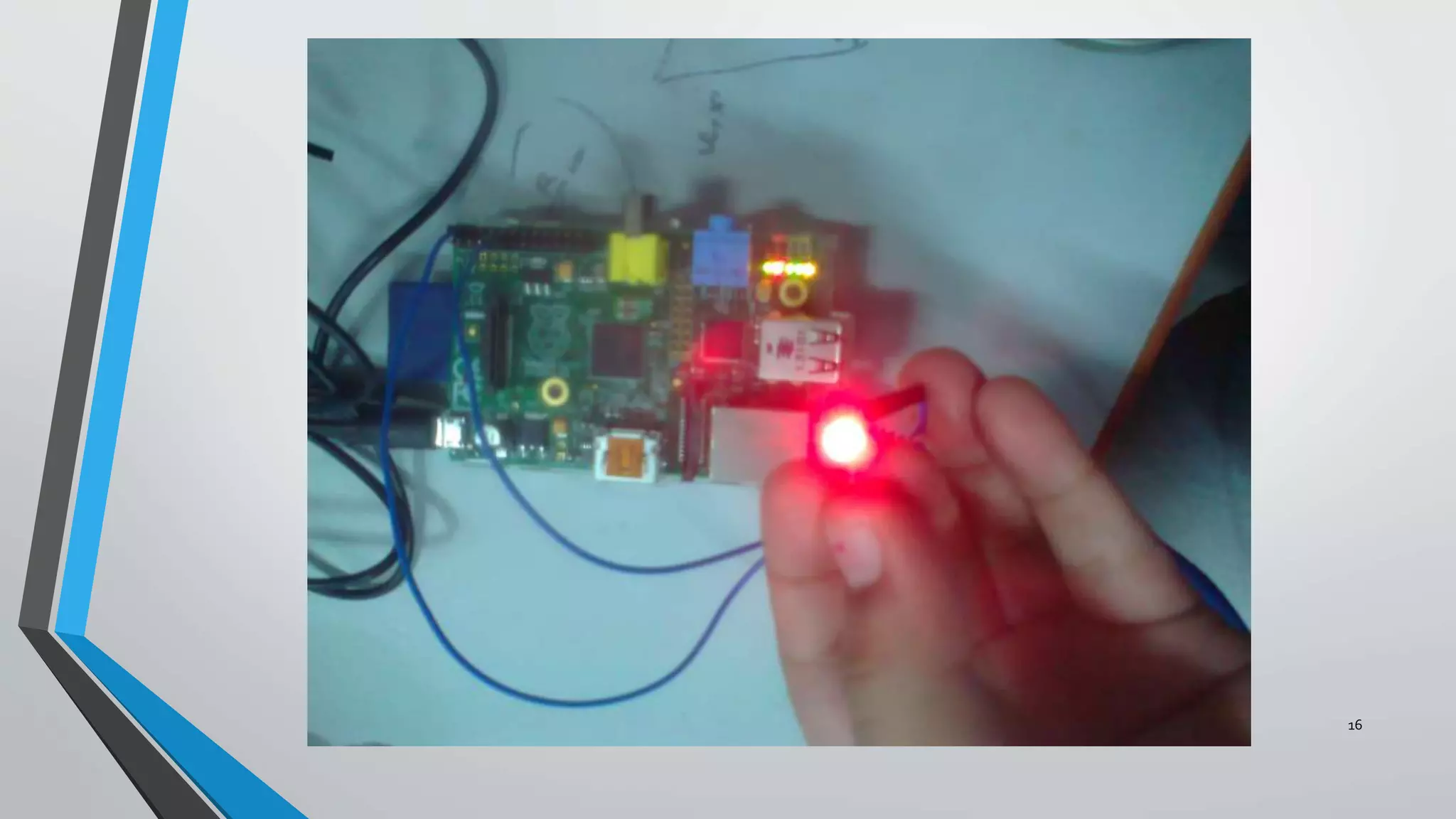
3) The implementation progress including running image processing on a Raspberry Pi over LAN, testing GPIO input/output, and establishing communication between the Pi and laptop.