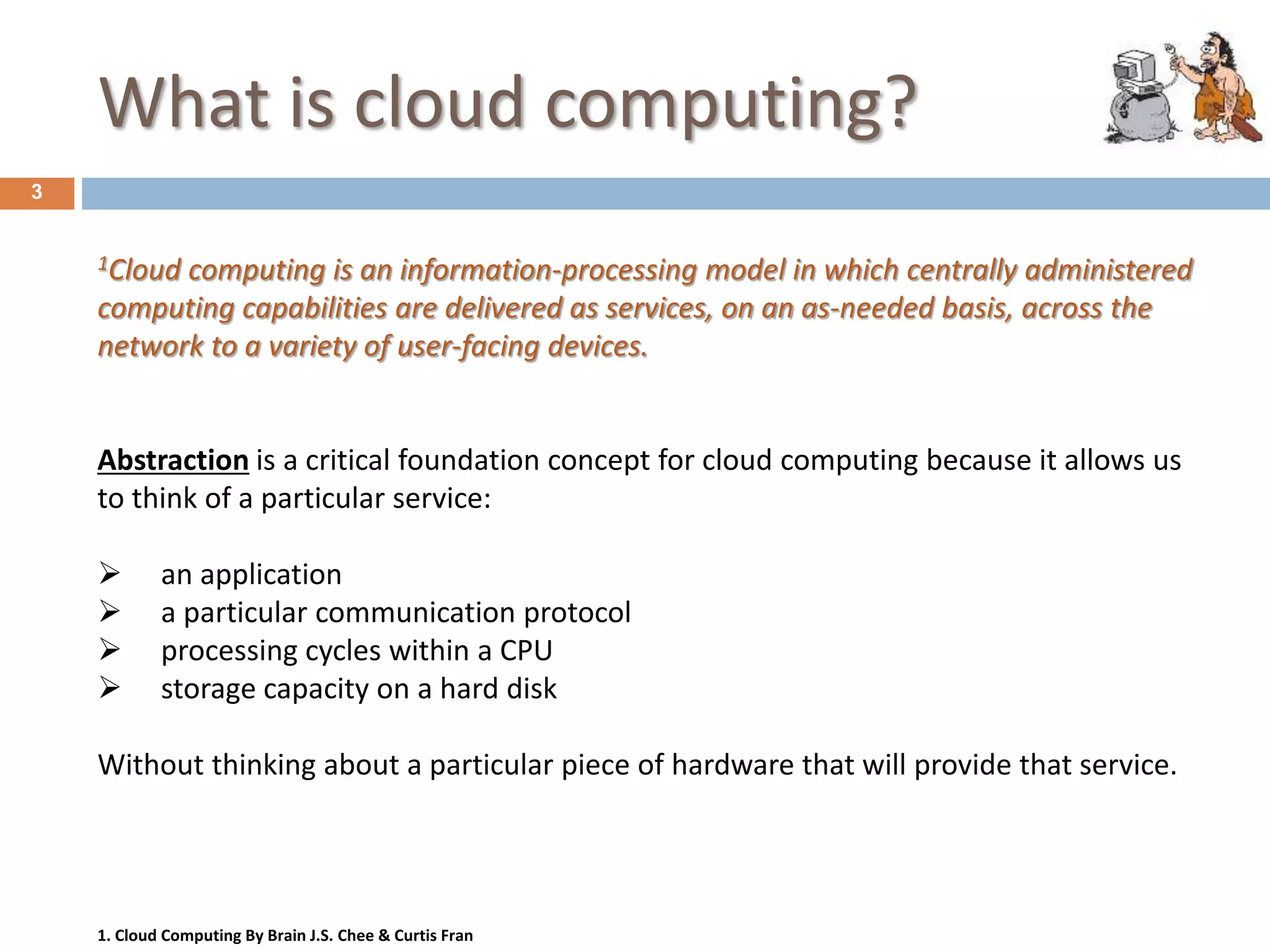
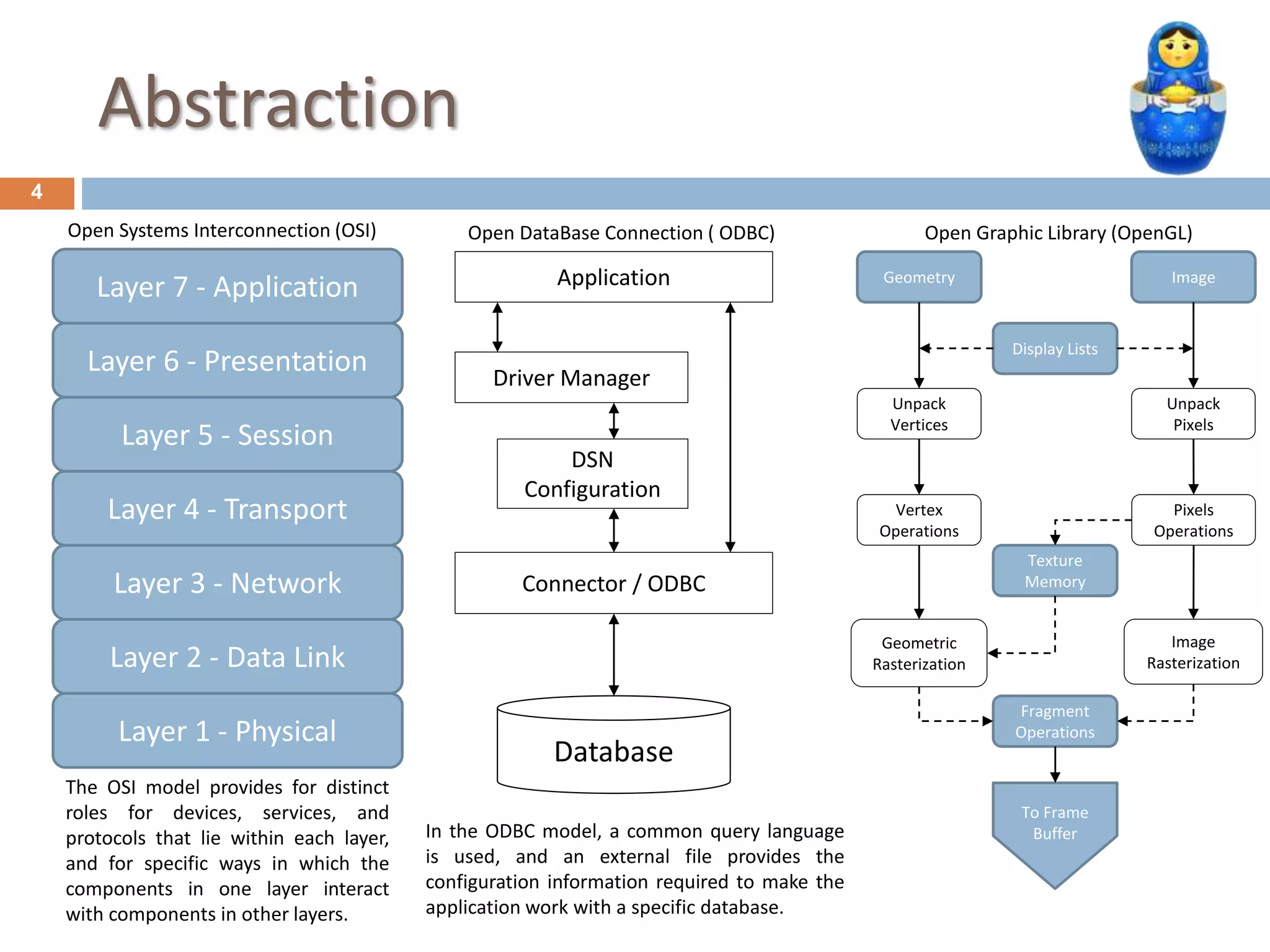
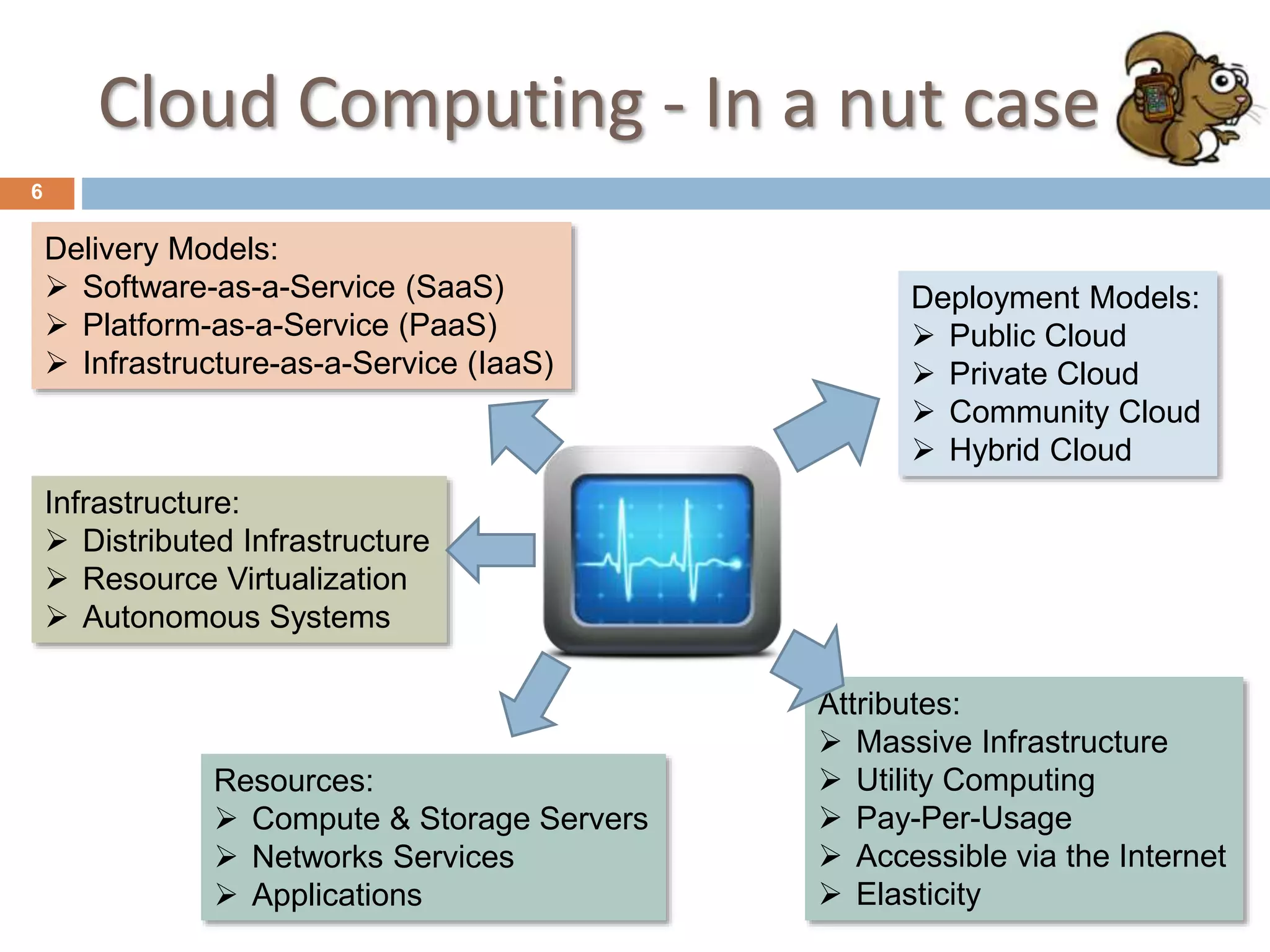
Cloud computing is a model for delivering computing capabilities as services over the network on an as-needed basis. It involves centrally hosted resources that are accessible via the internet. There are various deployment models including public, private, community and hybrid clouds. Resources are delivered through common models of software as a service, platform as a service, and infrastructure as a service. Key attributes include massive infrastructure, utility computing, pay-per-usage, elasticity, and accessibility via the internet.


![Software-as-a-Service [SaaS]
8
Gives users the capability to use
applications supplied by service
provider.
Not suitable for applications that
require real-time response, or
hosting of local data.
Suitable for products like emails,
billing and payroll.
Suitable for need to access over
web or mobile.
API
Abstraction
Core
Connectivity
Hardware
Facilities](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputing2014-140618222059-phpapp01/75/Cloud-Computing-8-2048.jpg)
![Platform-as-a-Service [PaaS]
9
Gives the capability to deploy consumer-
created or acquired applications using
programming languages & tools.
User has full control over the deployed
application
Session Management
Device Integration
Sandboxes
Instrumentation and Testing
PaaS is not useful when application must
be portable or proprietary programming
languages are used.
API
Abstraction
Core
Connectivity
Hardware
Facilities
Integration &
Middleware](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputing2014-140618222059-phpapp01/75/Cloud-Computing-9-2048.jpg)
![Infrastructure-as-a-Service [IaaS]
10
Gives the capability to provision
processing, storage, network and
computing resources.
Services offered
Server hosting
Web Servers
Storage
Computing Hardware
Operating Systems
Virtual Instances
Load Balancing
API
Abstraction
Core
Connectivity
Hardware
Facilities
Integration &
Middleware
Data Metadata
Applications
API
Presentation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputing2014-140618222059-phpapp01/75/Cloud-Computing-10-2048.jpg)



![Offerings in the market
Compute
Compute Engine [IaaS]
App Engine [PaaS]
Storage
Cloud SQL
Cloud Storage
Cloud Datastore
Big Data
BigQuery
Services
Cloud Endpoints
Translate API
Prediction API
14 Google Cloud [https://cloud.google.com/products/]
Solutions
Mobile
Gaming
Hadoop [SaaS]
Developer Tools
Google Cloud SDK
Push-to-Deploy
Cloud Playground
Android Studio
Google Plugin for
Eclipse](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputing2014-140618222059-phpapp01/75/Cloud-Computing-14-2048.jpg)
![Offerings in the market
Compute
Elastic Compute Cloud
Elastic Load Balancing
Auto Scaling
WorkSpaces
Storage
Simple Storage Service (S3)
Glacier
Storage Gateway
Elastic Block Store
Import / Export
Database / BigData
Relational Database Service
DynamoDB
Redshift (petabyte)
SimpleDB (non-relational data
store)
ElasticCache
15 Amazon Cloud [http://aws.amazon.com/products/]
Solutions
AppStream
Simple Workflow
Service
Simple Notification
Service
CloudSearch
CloudFront
Developer Tools
AWS Cloud SDK
Eclipse
Visual Studio](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputing2014-140618222059-phpapp01/75/Cloud-Computing-15-2048.jpg)


