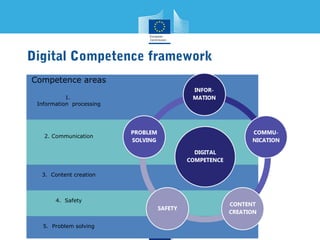
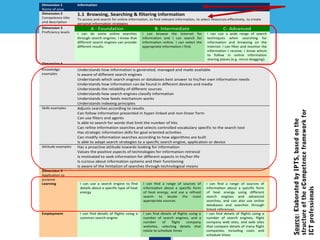
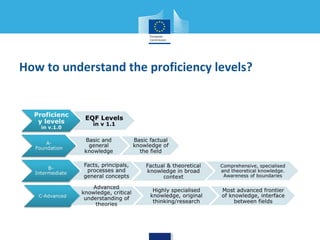
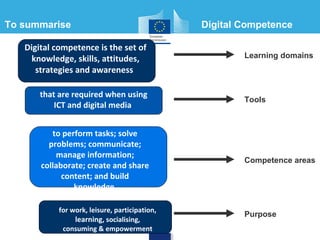
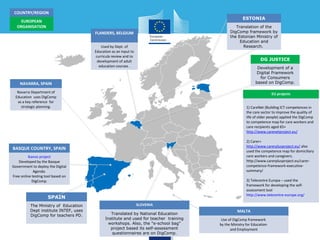
This document discusses a digital competence framework called DigComp that was developed to help improve students' digital skills. It presents the framework, which includes 5 competence areas and 21 specific competences. The framework is intended to provide common guidelines and assessment tools for developing digital competence in Europe. The document then provides examples of how the DigComp framework has been applied by various countries and organizations, such as for strategic planning, teacher professional development, and developing online self-assessment tools. It concludes by discussing how the framework could be used to help design eTwinning activities that develop students' digital competences.