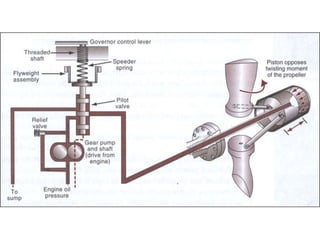
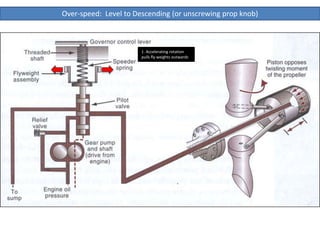
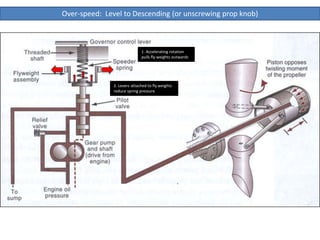
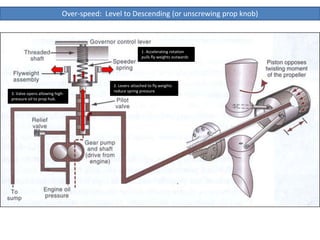
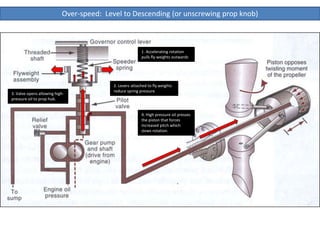
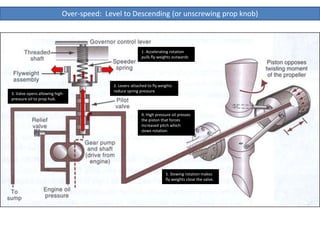
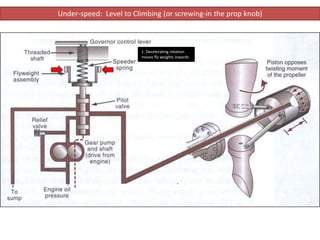
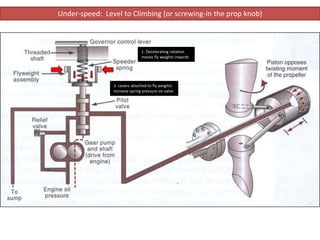
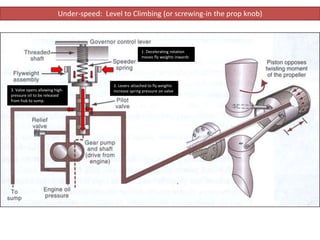
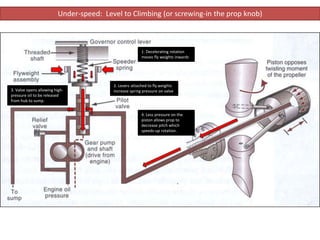
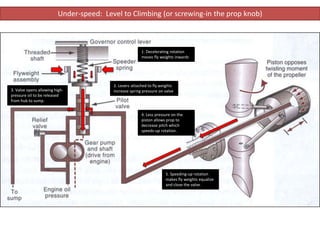
The document describes how a propeller governor system regulates propeller speed during flight. It works by using fly weights, levers, springs and a valve to control high-pressure oil flow to the propeller hub. During over-speed conditions, accelerating rotation pulls the fly weights outwards, reducing spring pressure and opening the valve to allow oil to the hub. This increases propeller pitch and slows rotation. During under-speed conditions, the opposite occurs - decelerating rotation pushes the fly weights inwards, increasing spring pressure and releasing oil from the hub to decrease pitch and speed up rotation.