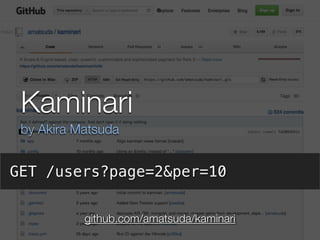
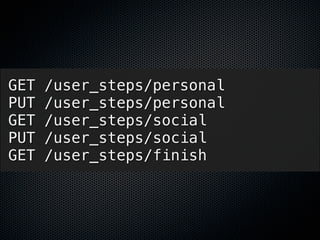
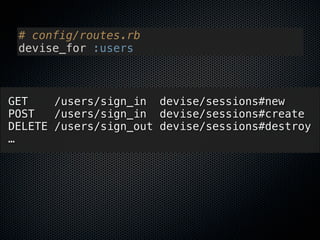
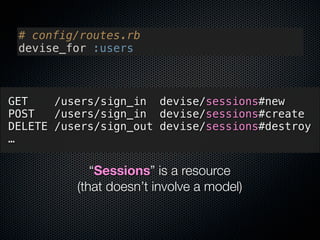
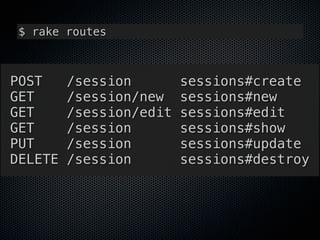
1) The document discusses how Rails realizes RESTful resource modeling patterns through the use of "resources" in config/routes.rb.
2) It argues that focusing on RESTful patterns, including resources, encourages good resource design. RubyGems can also help with resource modeling by implementing specific patterns.
3) If creating a Rails gem, the author recommends designing around resources when possible. Sticking to fundamental patterns allows gems to realize RESTful modeling patterns.









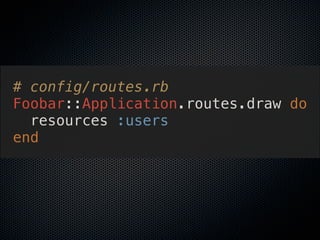

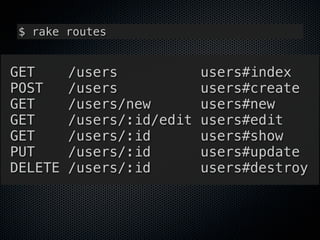































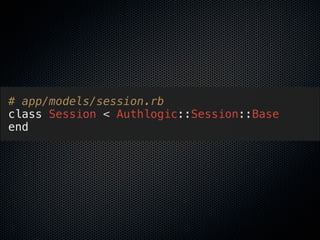

![# app/controllers/sessions_controler.rb
class SessionsController < ApplicationController
# POST /session
def create
@session = Session.new(session_params)
if @session.save
flash[:notice] = "Login successful!"
redirect_back_or_default account_url
else
render :action => :new
end
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rubykaigi2013railsgemsrealizerestfulmodelingpatterns-130531234529-phpapp01/85/Rails-Gems-realize-RESTful-modeling-patterns-51-320.jpg)




![GET /users?q[name_cont]=tkawa
GET /users?q[created_at_lt]=2013-01-01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rubykaigi2013railsgemsrealizerestfulmodelingpatterns-130531234529-phpapp01/85/Rails-Gems-realize-RESTful-modeling-patterns-57-320.jpg)