This document provides an overview of learning to code for a startup minimum viable product (MVP) using Ruby on Rails. It discusses setting up a development environment, using Git version control, the Ruby programming language basics, Rails models and object-relational mapping, authentication with Devise, Rails controllers and routing, and using scaffolding to build out a sample Mini Twitter app with Posts and Users models. The goal is to provide attendees with the necessary skills to build a basic MVP for a startup.









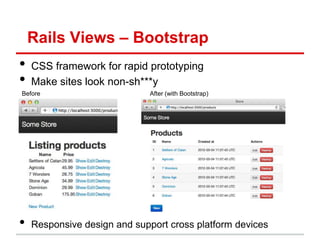
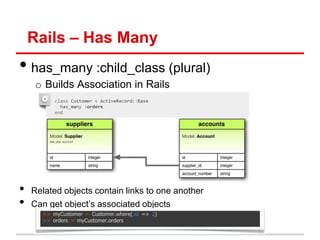
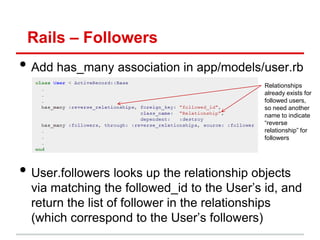
![Rails MVC – Quick Review
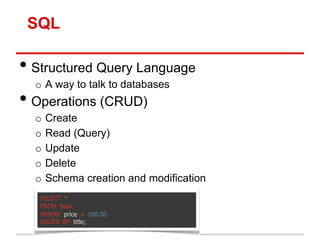
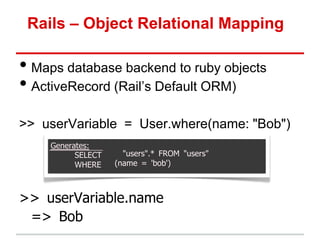
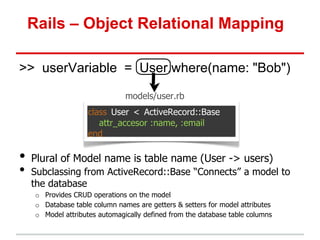
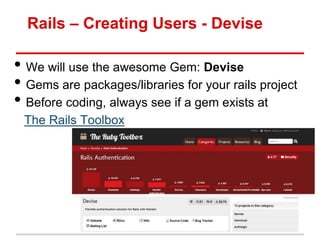
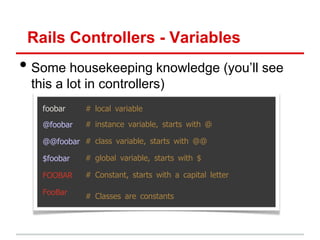
• Model: methods to get/manipulate data“
/app/models/post.rb
Post.where(...), Post.find(...)
• Controller: get data from Model, make available to View
/app/controllers/posts_controller.rb
def show
@movie = Post.find(params[:id])
end
• View: display data, allow user interaction“
/app/views/users/*.html.erb
– Show details of a Post (description, timestamp, etc)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningtocodeforstartupmvpsession3-121126202153-phpapp01/85/Learning-to-code-for-startup-mvp-session-3-16-320.jpg)
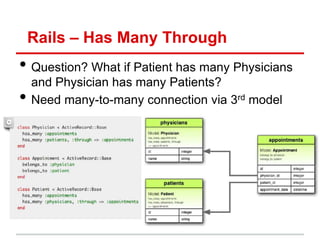
![Rails Controllers - Params
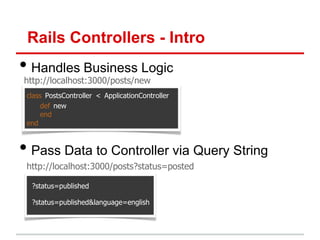
• Params (hash) – get data from url
• Instance variables – pass data to view
http://localhost:3000/posts?status=published
def index
@status = params[:status]
if @status == “published"
@clients = Post.published
else
@clients = Post.removed
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningtocodeforstartupmvpsession3-121126202153-phpapp01/85/Learning-to-code-for-startup-mvp-session-3-19-320.jpg)
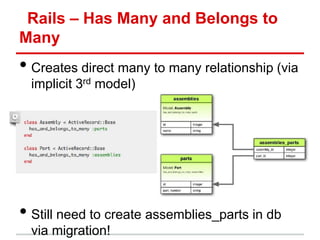
![Rails Controllers – Params Hash
• Receive Hashes from Forms
o Great for handling data and user input
Form
<form action="/clients" method="post">
<input type="text" name="client[name]" value="Acme" />
<input type="text" name="client[phone]" value="12345" />
<input type="text" name="client[address][postcode]" value="12345" />
</form>
Hash
params[:client] # =>
{name: “Acme”,
phone: “12345”,
address: {postcode: “12345”} <- Notice the nested hash
(corresponding to nested form)
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningtocodeforstartupmvpsession3-121126202153-phpapp01/85/Learning-to-code-for-startup-mvp-session-3-20-320.jpg)

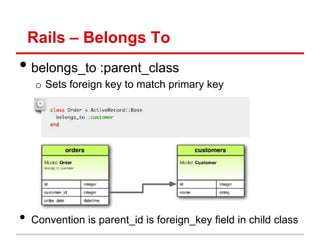
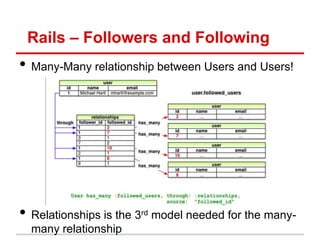
![Rails Router – Overview
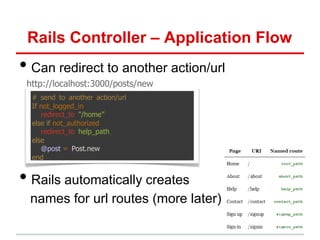
1. Routes (in routes.rb) map incoming URL s tocontroller
actions and extract any optional parameters!
– Route s “wildcard” parameters (eg:id), plus any stuff after “?” in URL,
are put into params[] hash accessible in controller actions"
2. Controller actions set instance variables, visible to views"
– Subdirs and filenames of views/ match controllers & action names"
3. Controller action eventually renders a view"
app/controllers/movies_controller.rb app/views/movies/show.html.haml
def show <li>
id = params[:id] Rating:
@mv=Movie.find(id) = @mv.rating
config/routes.rb end
GET /movies/:id
{:action=>'show',:controller=>'movies'}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningtocodeforstartupmvpsession3-121126202153-phpapp01/85/Learning-to-code-for-startup-mvp-session-3-23-320.jpg)

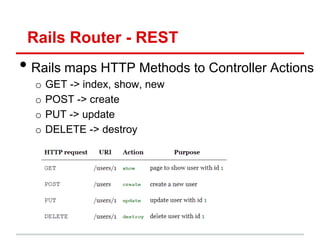
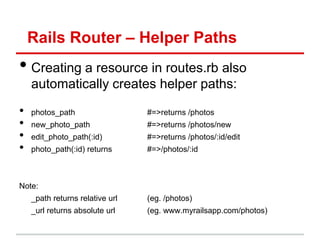
![Rails Router - Resources
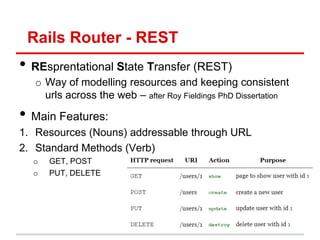
• Can automatically specify resources in
routes.rb and Rails will create 7 url mappings
routes.rb
resources: Photo
Method name in photos_controller.rb
Passed to
params hash
When you visit, localhost:3000/photos/2 (GET request), Rails will call
PhotosController#show and will pass Params[:id] = 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningtocodeforstartupmvpsession3-121126202153-phpapp01/85/Learning-to-code-for-startup-mvp-session-3-27-320.jpg)