Here are the key approaches to caching in Django:
- Per site caching (generic approach) - Cache entire pages without GET/POST parameters and only for anonymous users.
- Per view caching (granular approach) - Cache responses of individual views by decorating them with @cache_page and setting timeouts.
- Template fragment caching (micro manage approach) - Cache fragments of templates, both static and dynamic, by using the {% cache %} tag and specifying keys.
- Low level caching (micro micro manage) - Cache individual parameters by storing and retrieving from the cache backend directly in the views.
The level of caching ranges from generic site-wide caching to fine-grained fragment caching. Per view and






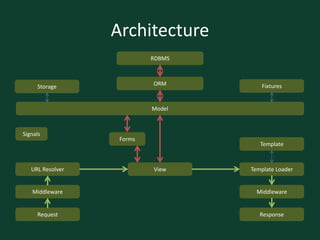
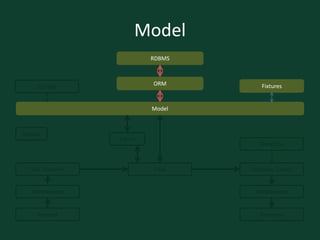


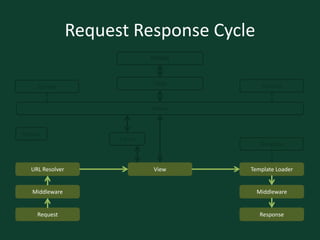

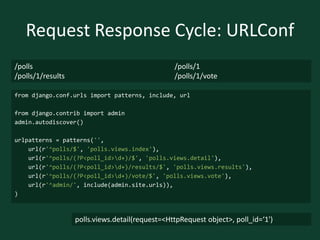
![Request Response Cycle: View
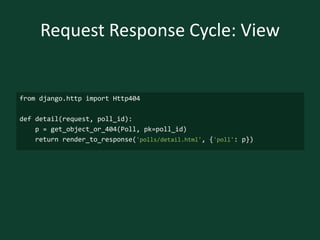
from django.shortcuts import render_to_response
from polls.models import Poll
def index(request):
latest_poll_list = Poll.objects.all().order_by('-pub_date')[:5]
return render_to_response('polls/index.html',
{'latest_poll_list': latest_poll_list})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/djangoboot-121114091104-phpapp02/85/Python-Django-TTT-14-320.jpg)
![Request Response Cycle: View
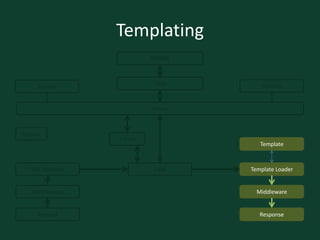
from django.shortcuts import get_object_or_404, render_to_response
from django.http import HttpResponseRedirect, HttpResponse
from django.core.urlresolvers import reverse
from django.template import RequestContext
from polls.models import Choice, Poll
def vote(request, poll_id):
p = get_object_or_404(Poll, pk=poll_id)
try:
selected_choice = p.choice_set.get(pk=request.POST['choice'])
except (KeyError, Choice.DoesNotExist):
return render_to_response('polls/detail.html', {
'poll': p,
'error_message': "You didn't select a choice.",
}, context_instance=RequestContext(request))
else:
selected_choice.votes += 1
selected_choice.save()
return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('polls.views.results', args=(p.id,)))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/djangoboot-121114091104-phpapp02/85/Python-Django-TTT-16-320.jpg)









![Application Server (AS)
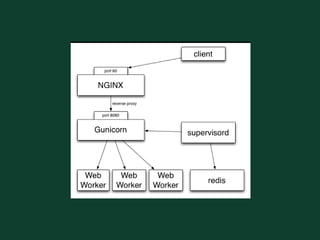
Web Server Gateway Interface (WSGI)
• PEP 333 [P. J. Eby, dec 2010]
• Common ground for portable web applications
– Routing, environment variables, load balancing,
forwarding, post-prosessing
• 2 parts:
– Gateway (= server)
– Framework (= application)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/djangoboot-121114091104-phpapp02/85/Python-Django-TTT-32-320.jpg)













