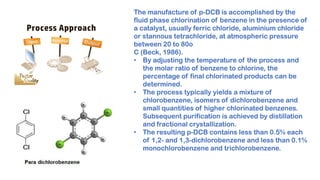
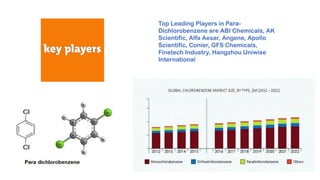
Paradichlorobenzene is manufactured through the fluid phase chlorination of benzene with chlorine in the presence of a catalyst such as ferric chloride. This process produces paradichlorobenzene along with other byproducts, so purification is needed through distillation and fractional crystallization. While some paradichlorobenzene plants have closed due to low profits, leading producers like Lanxess have increased capacity by modifying existing facilities and shifting production to focus more on paradichlorobenzene.