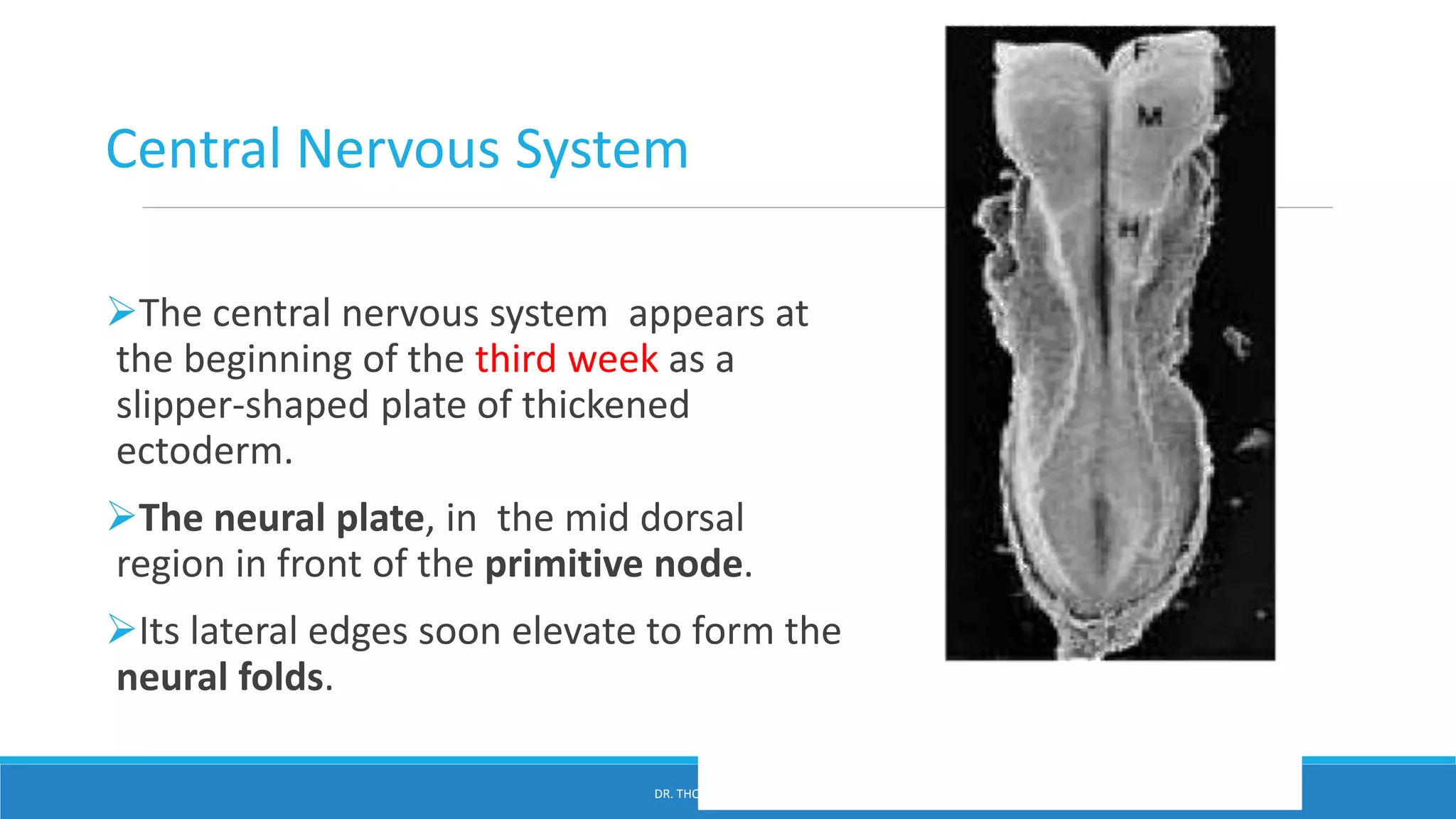
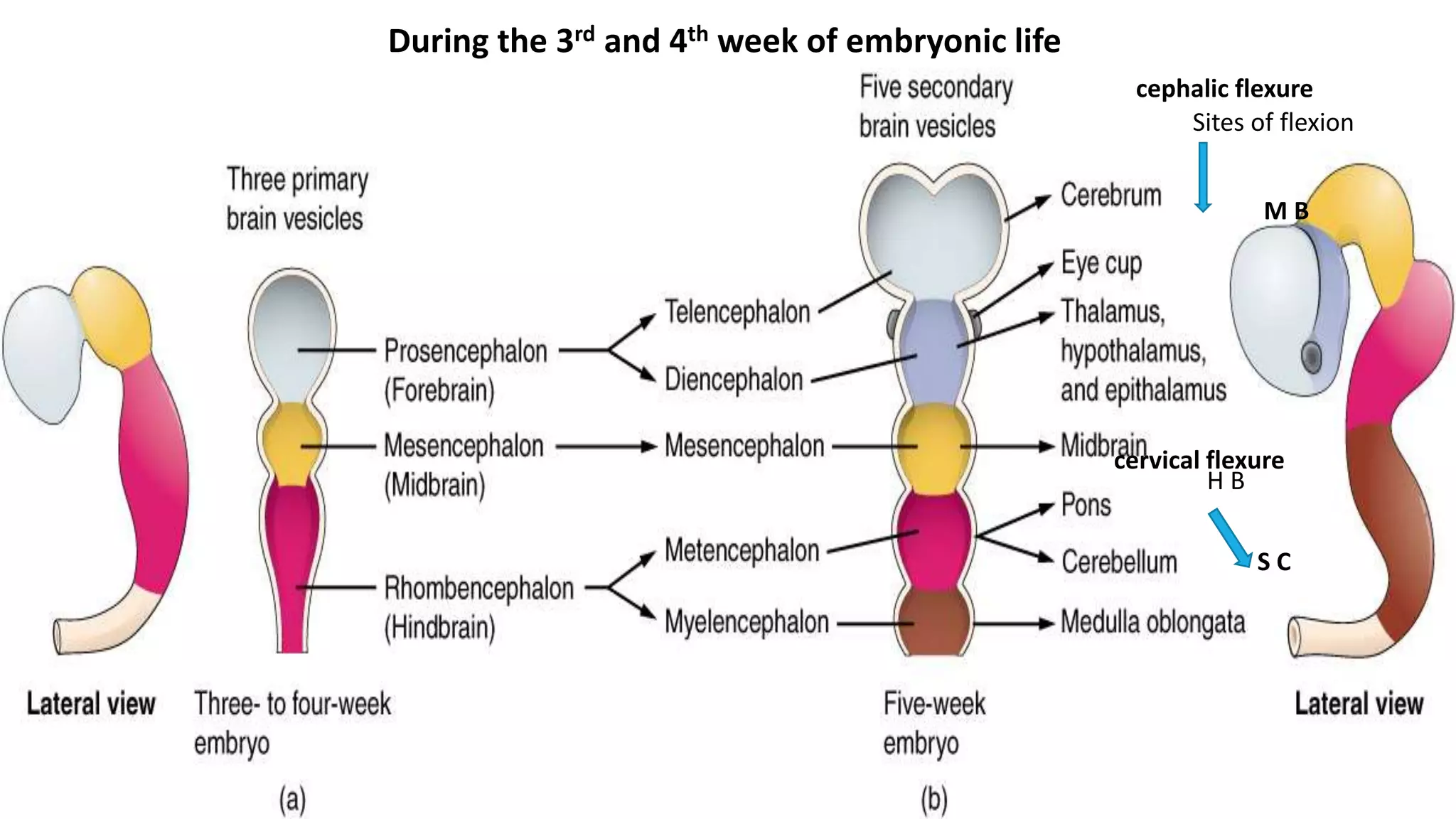
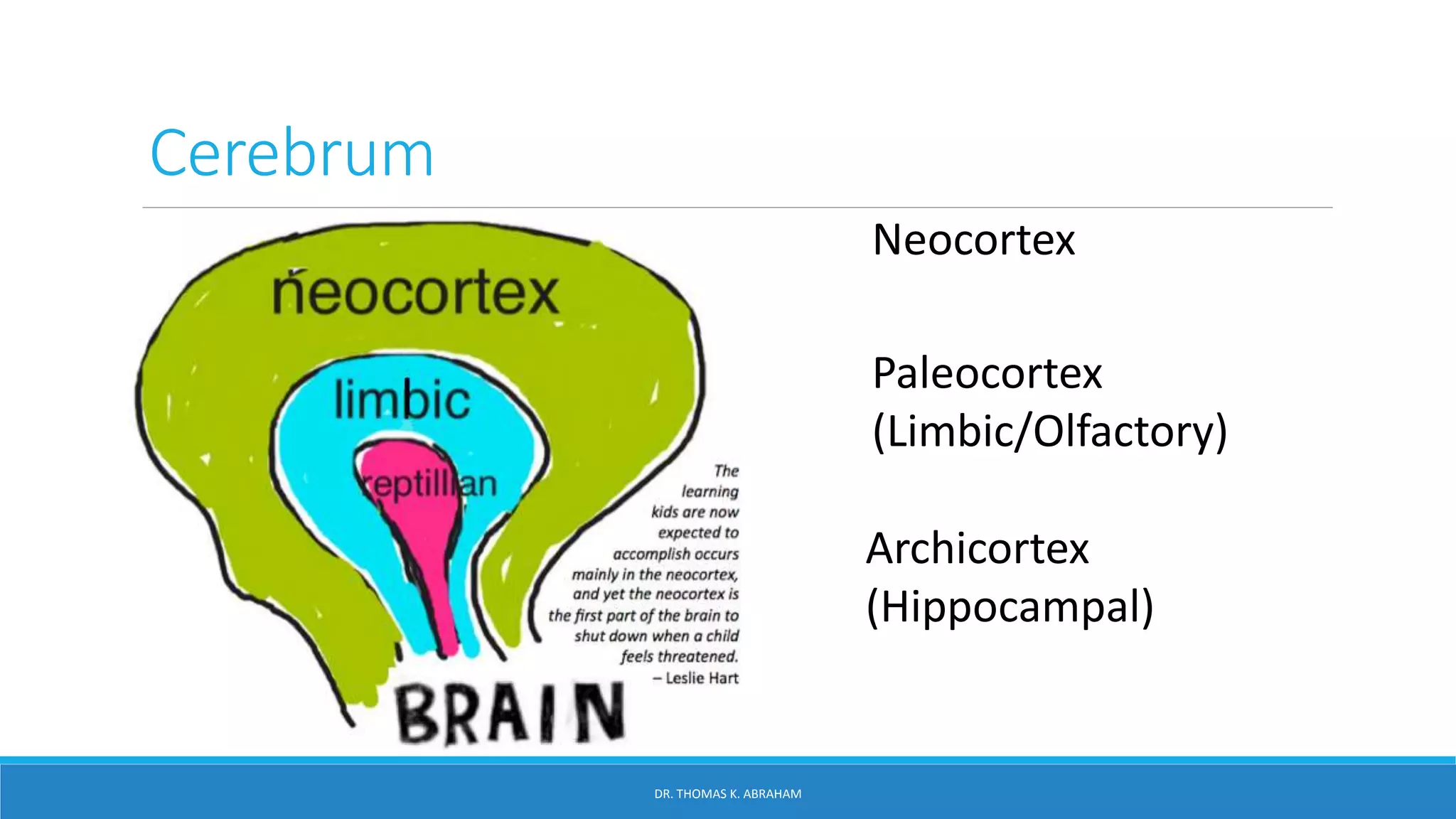
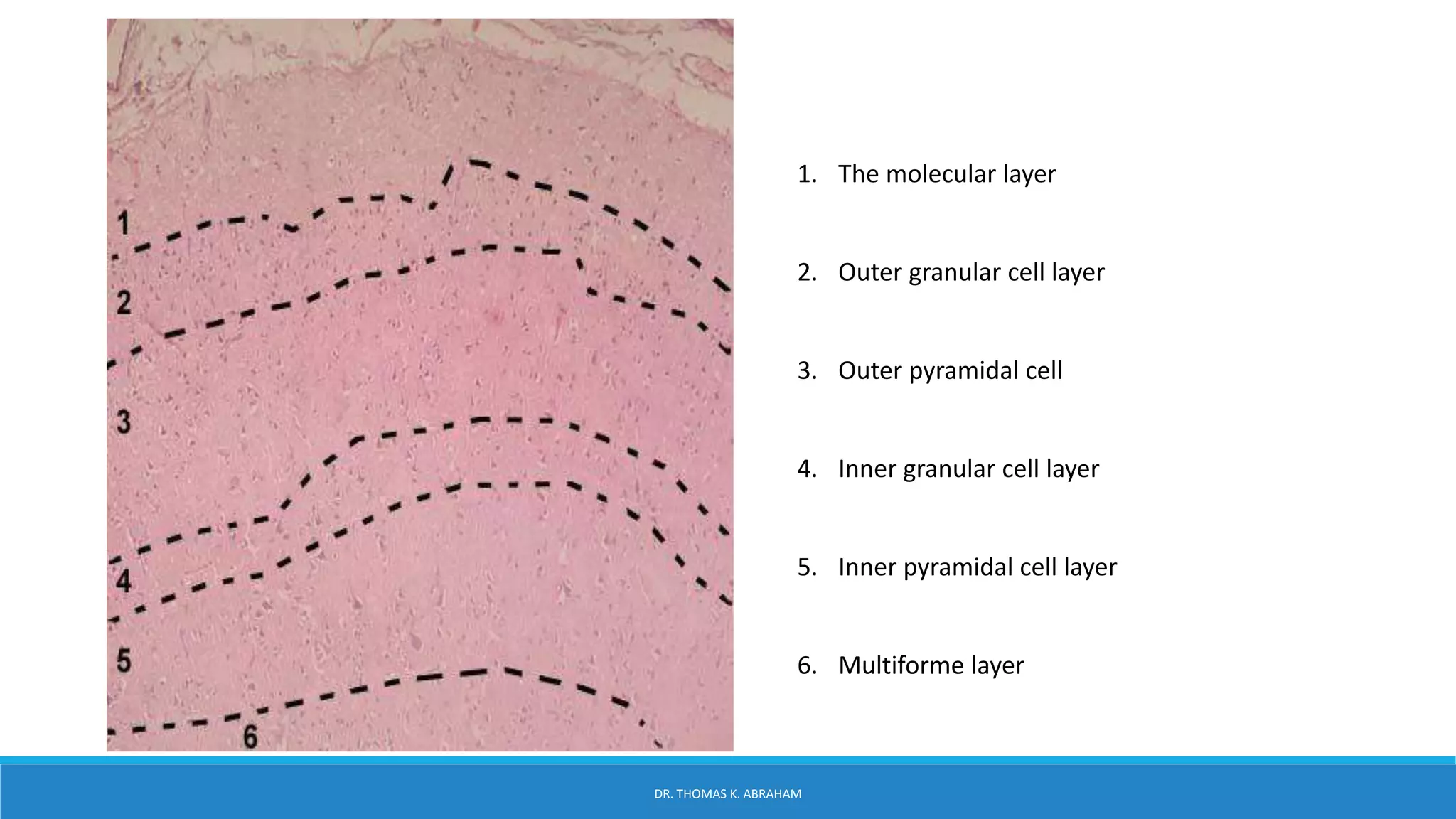
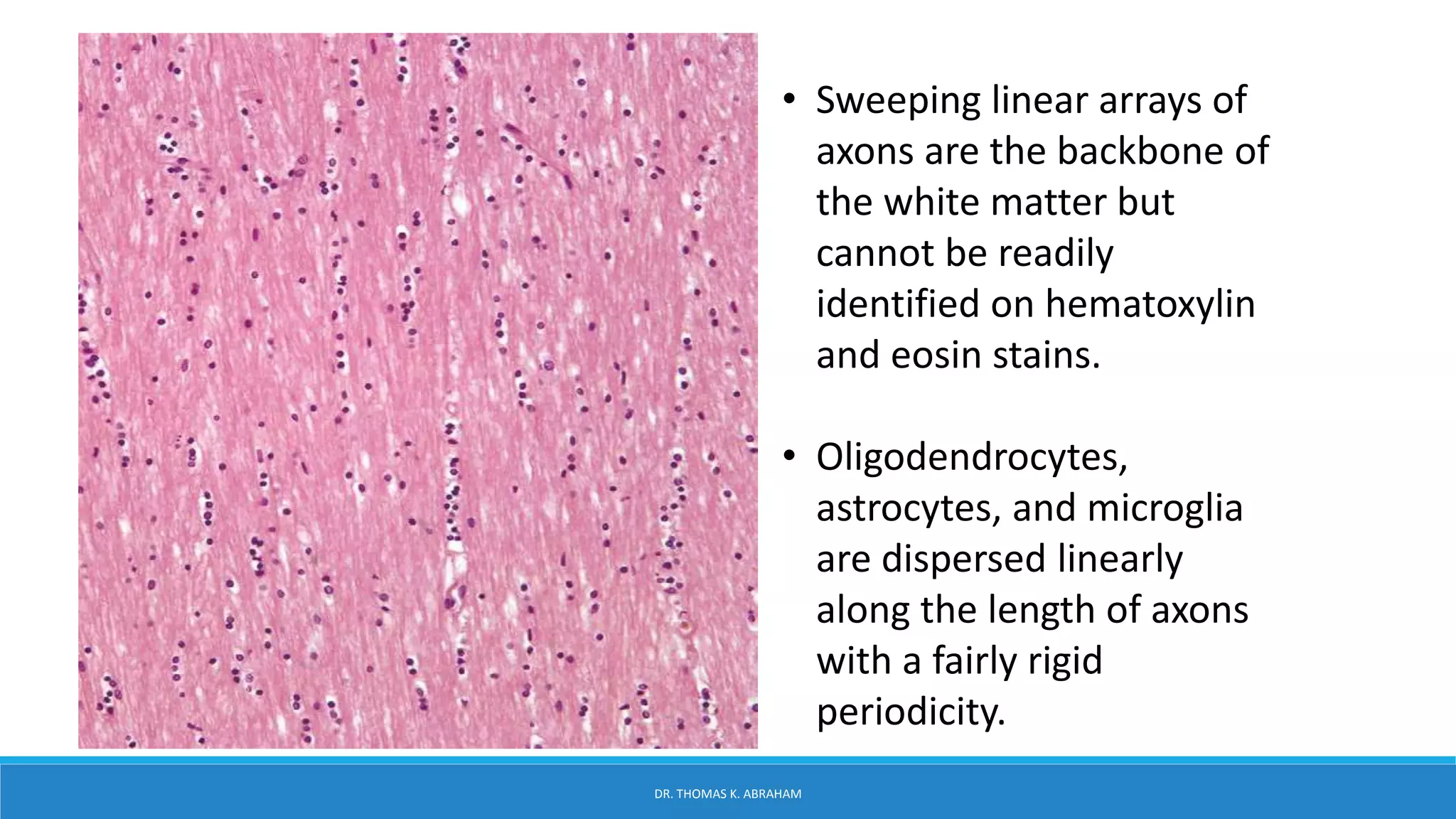
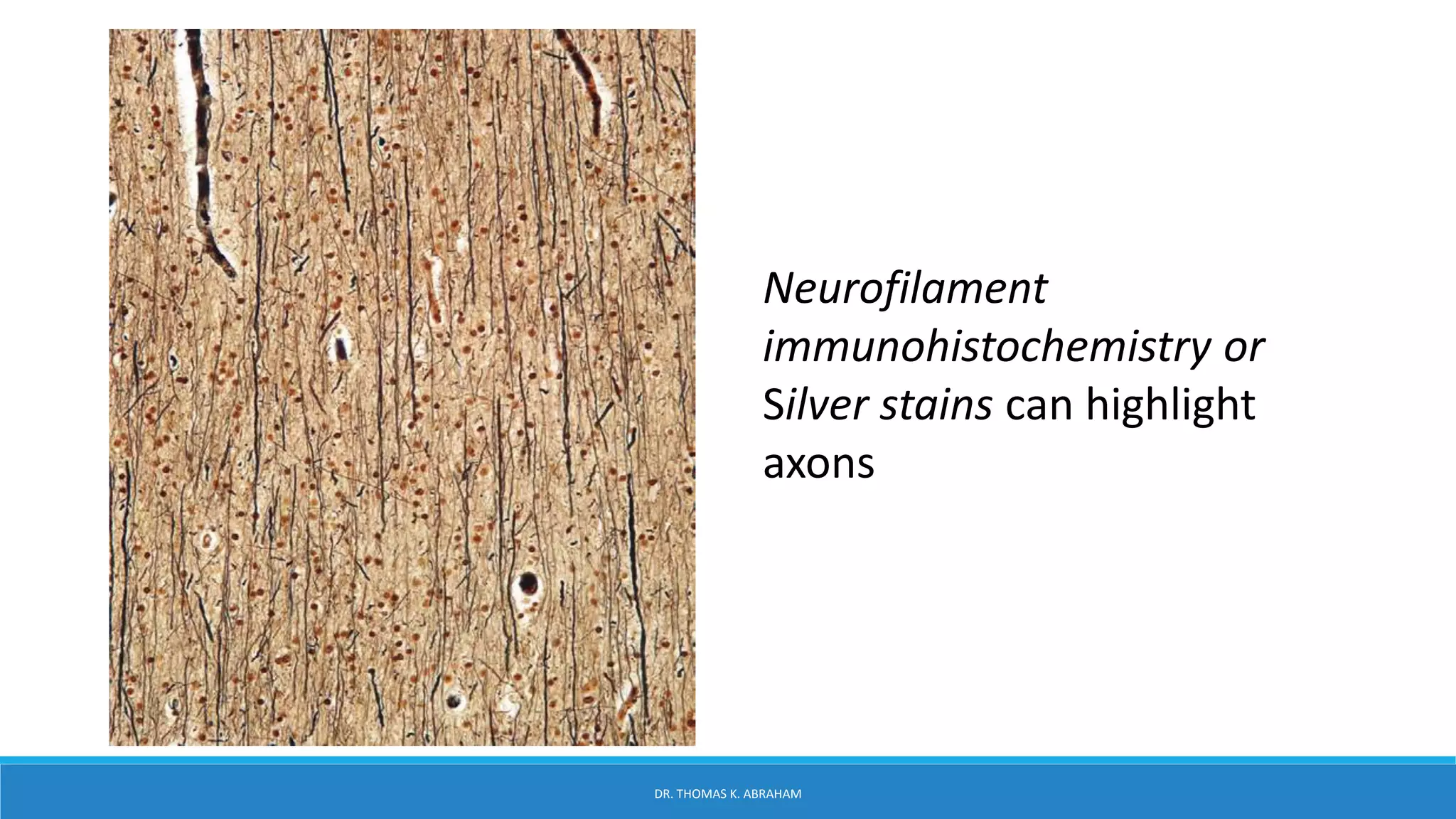
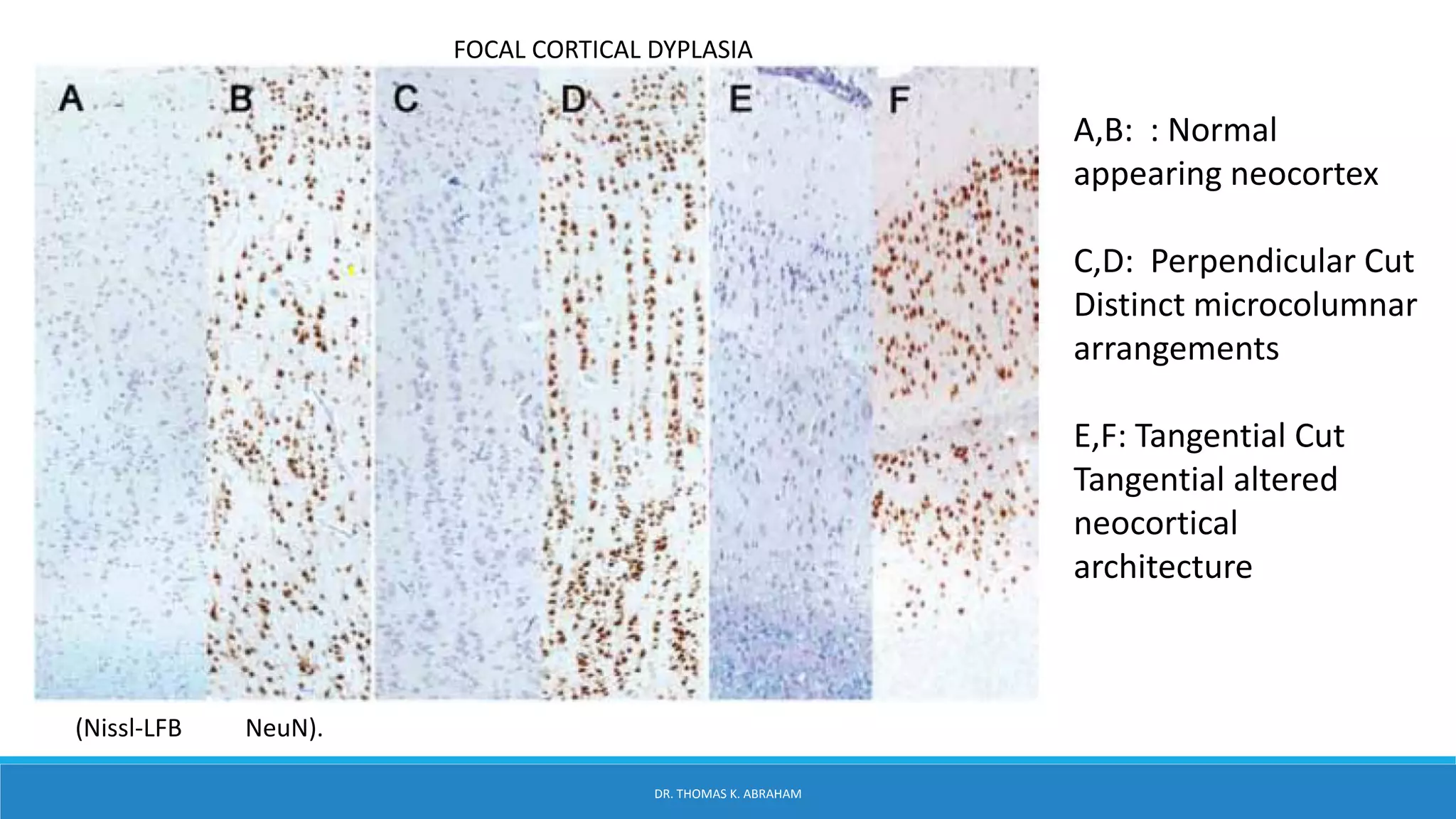
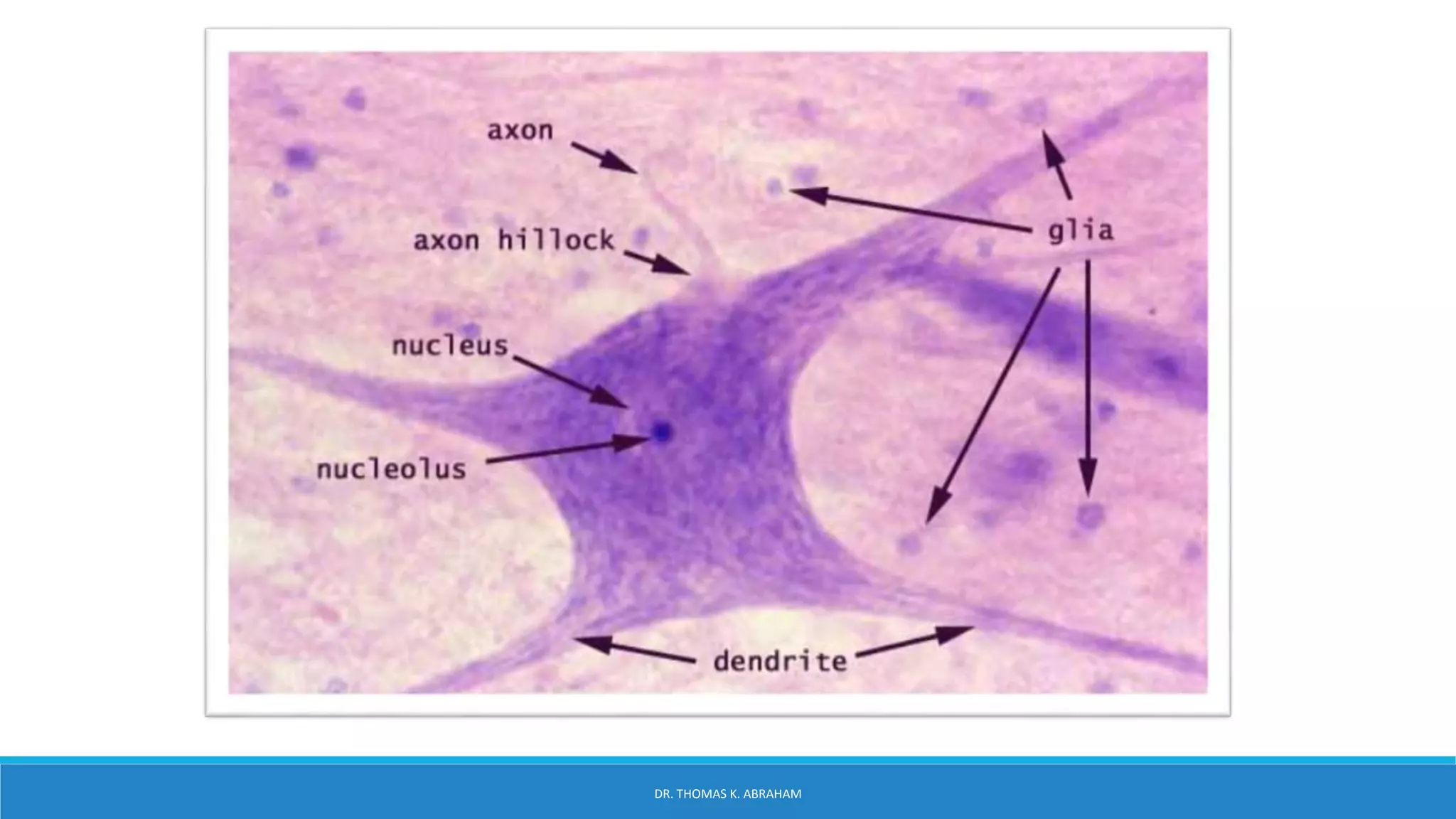
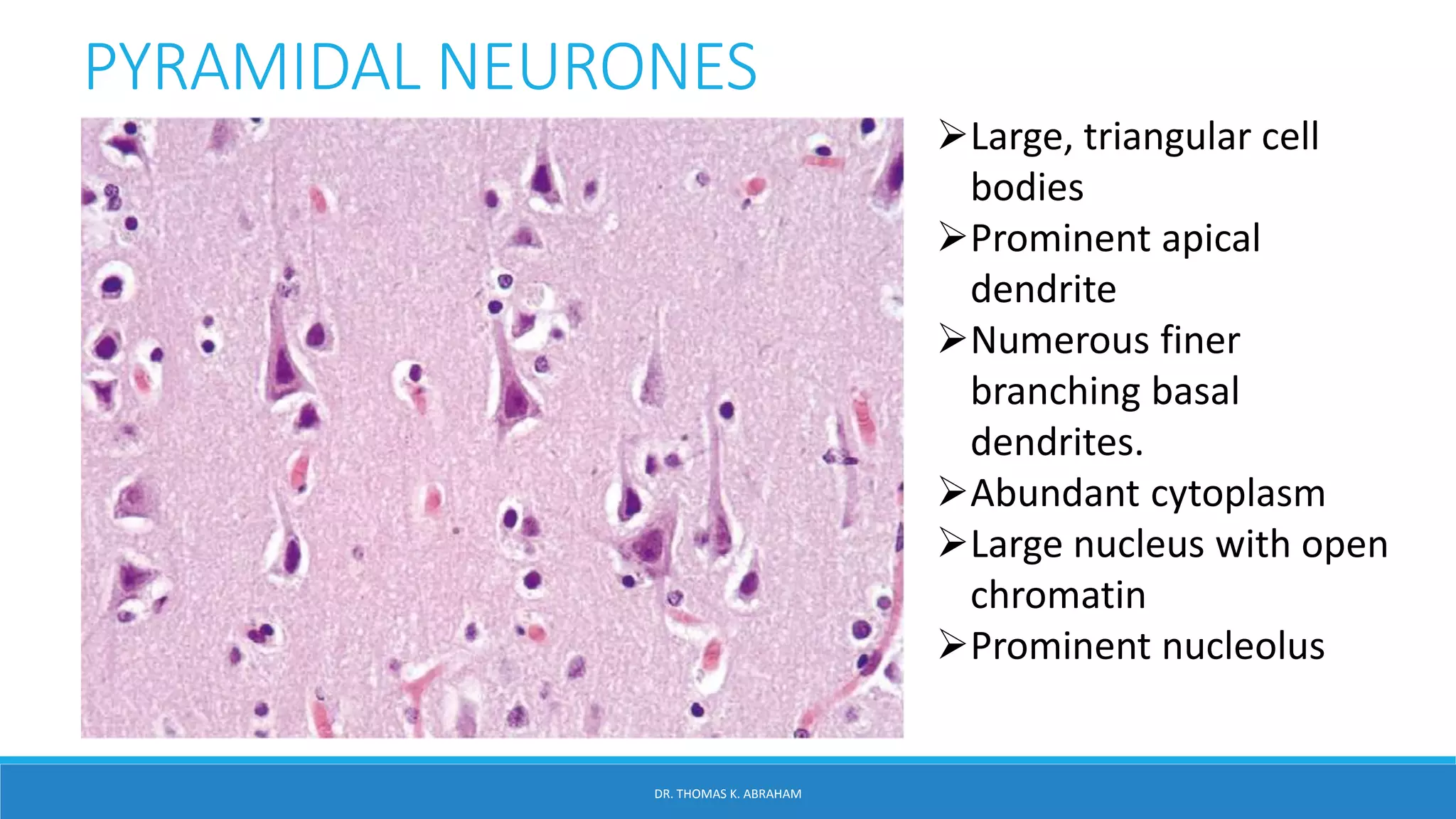
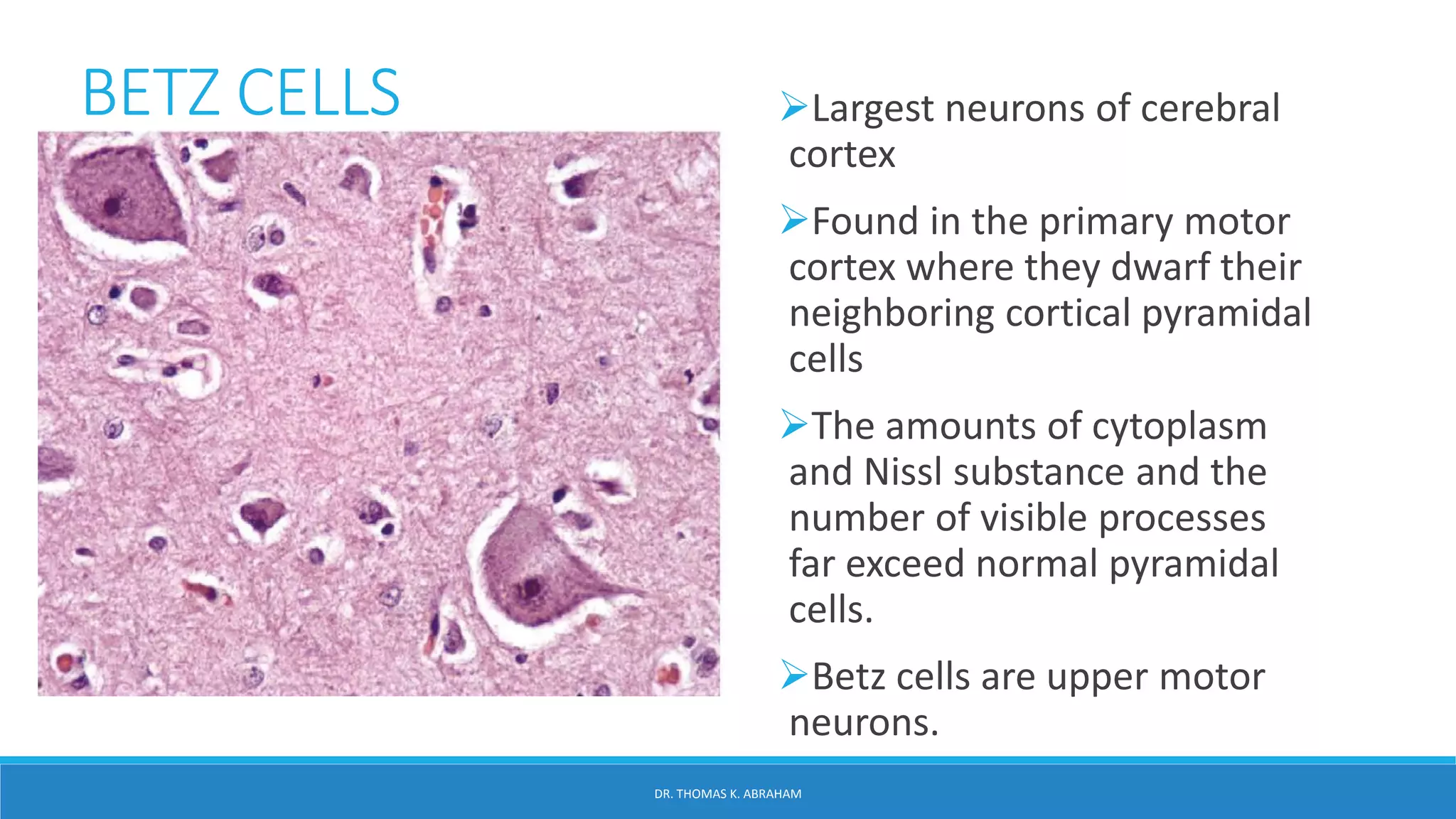
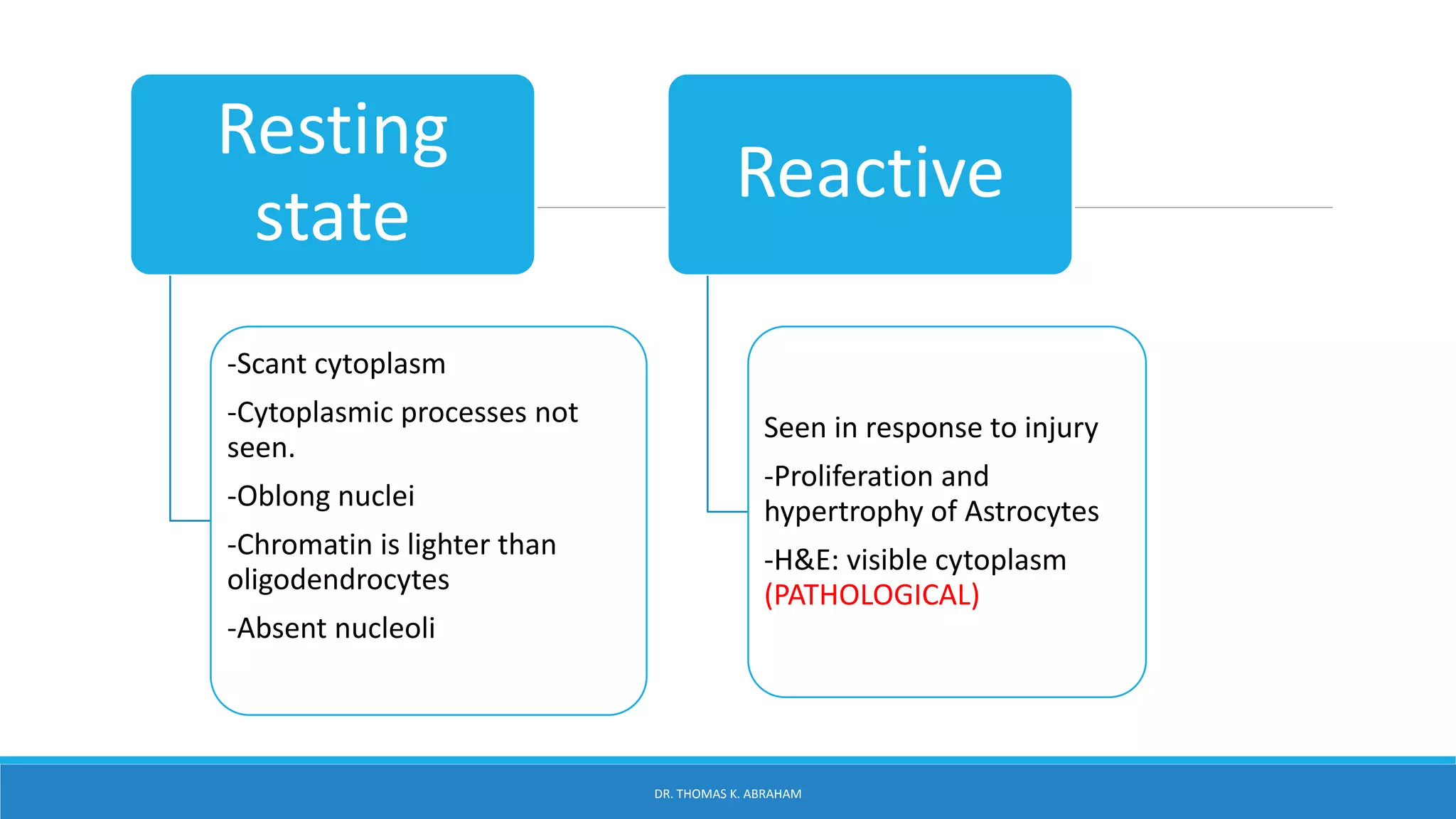
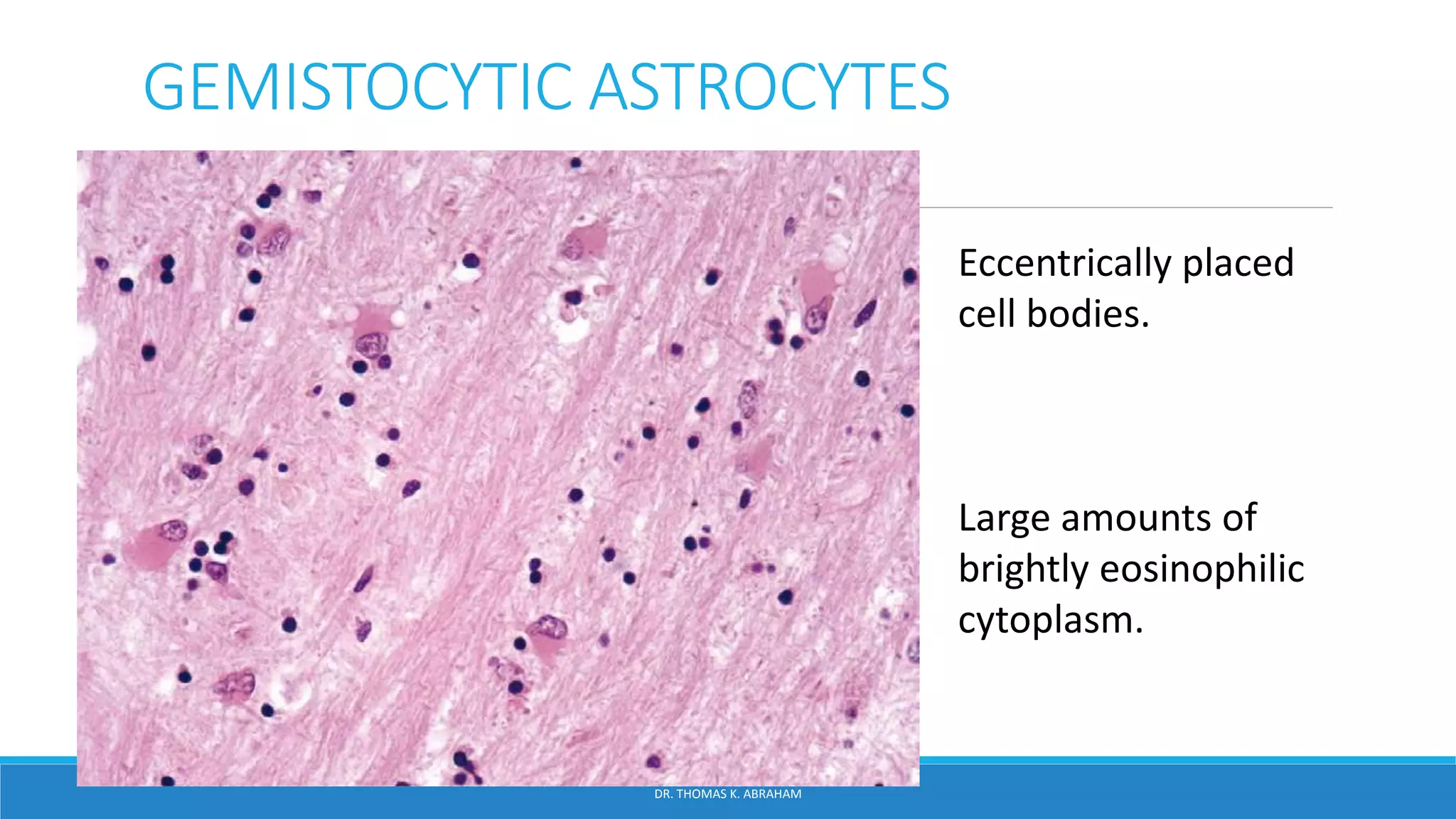
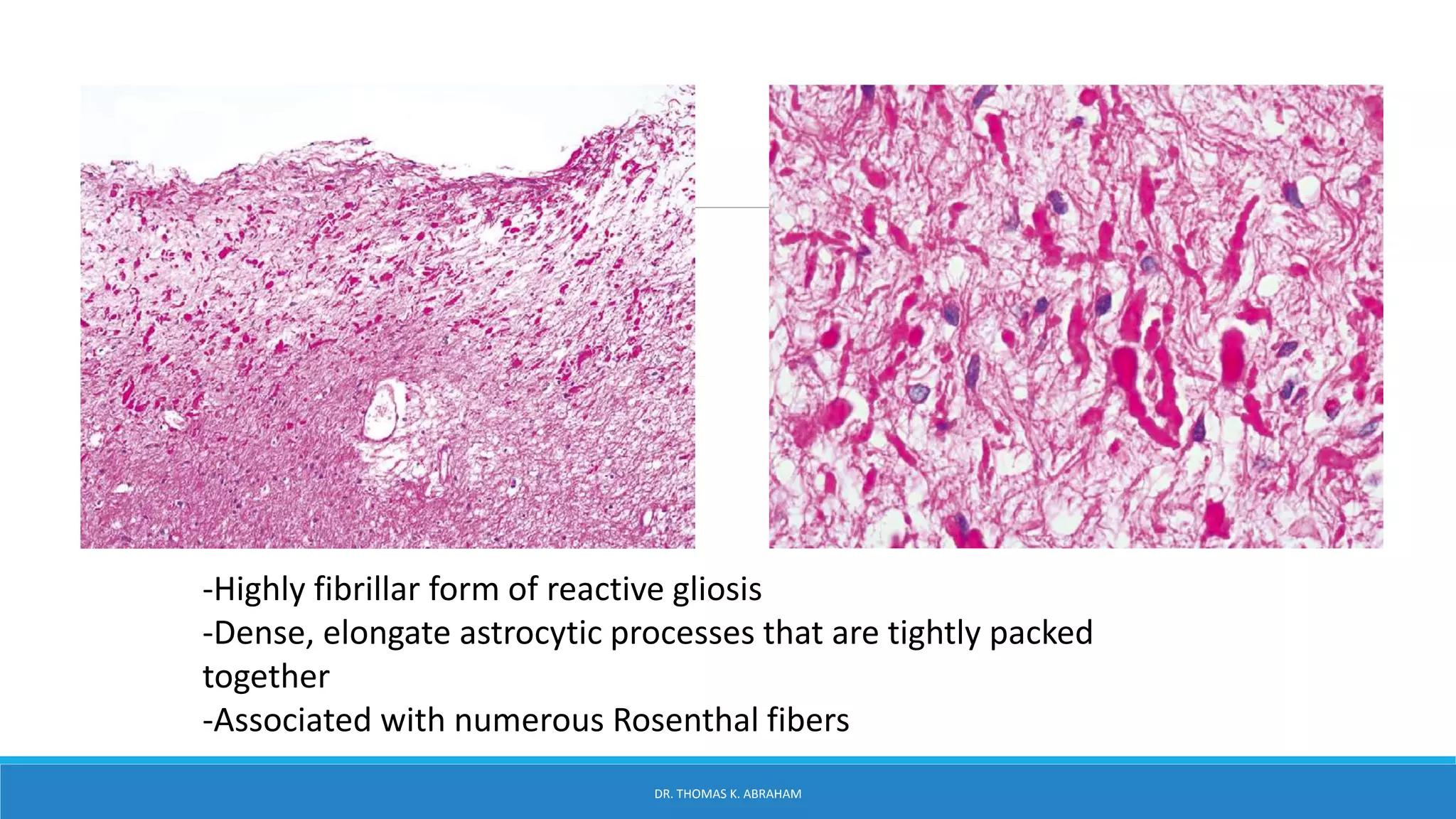
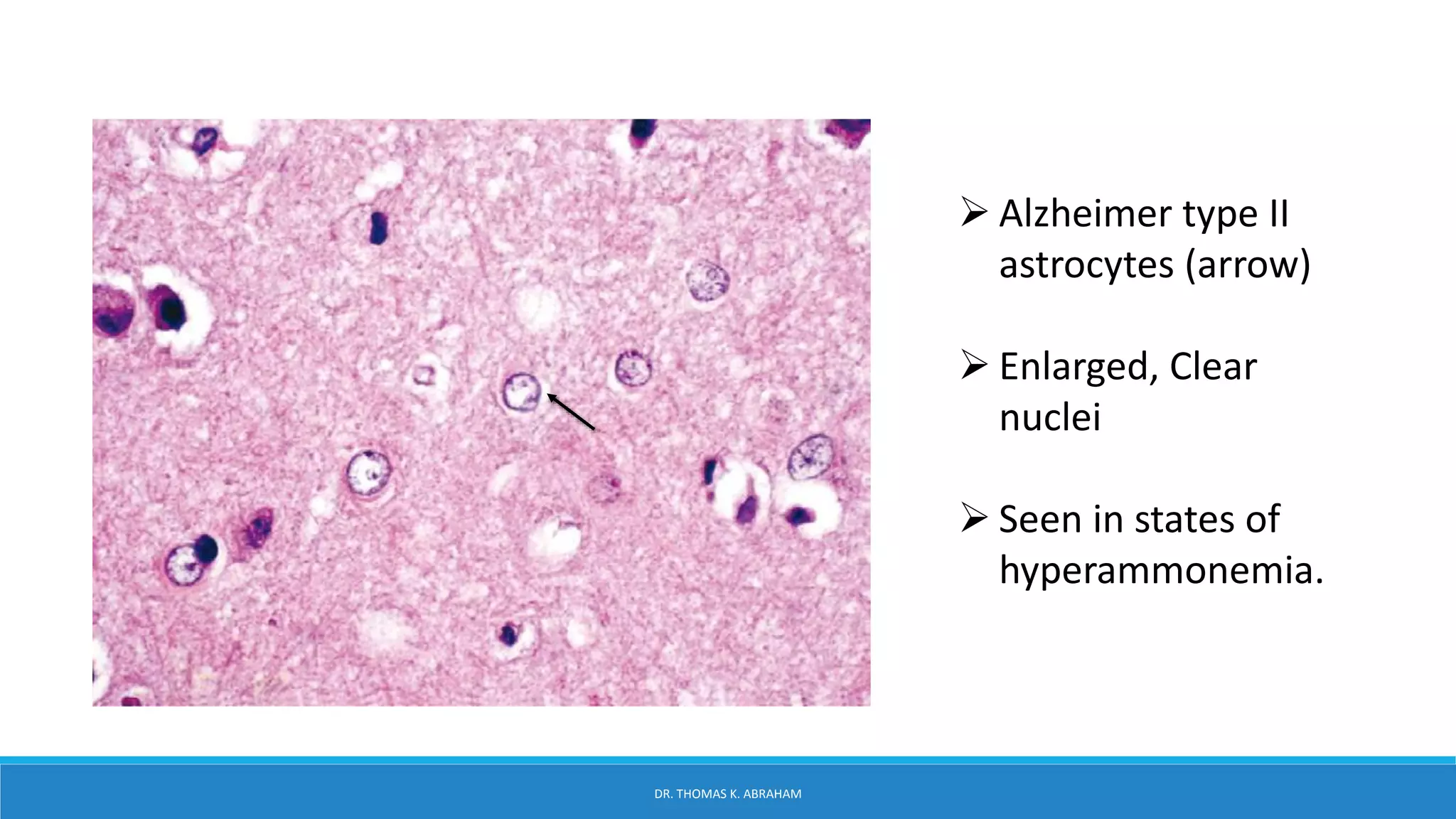
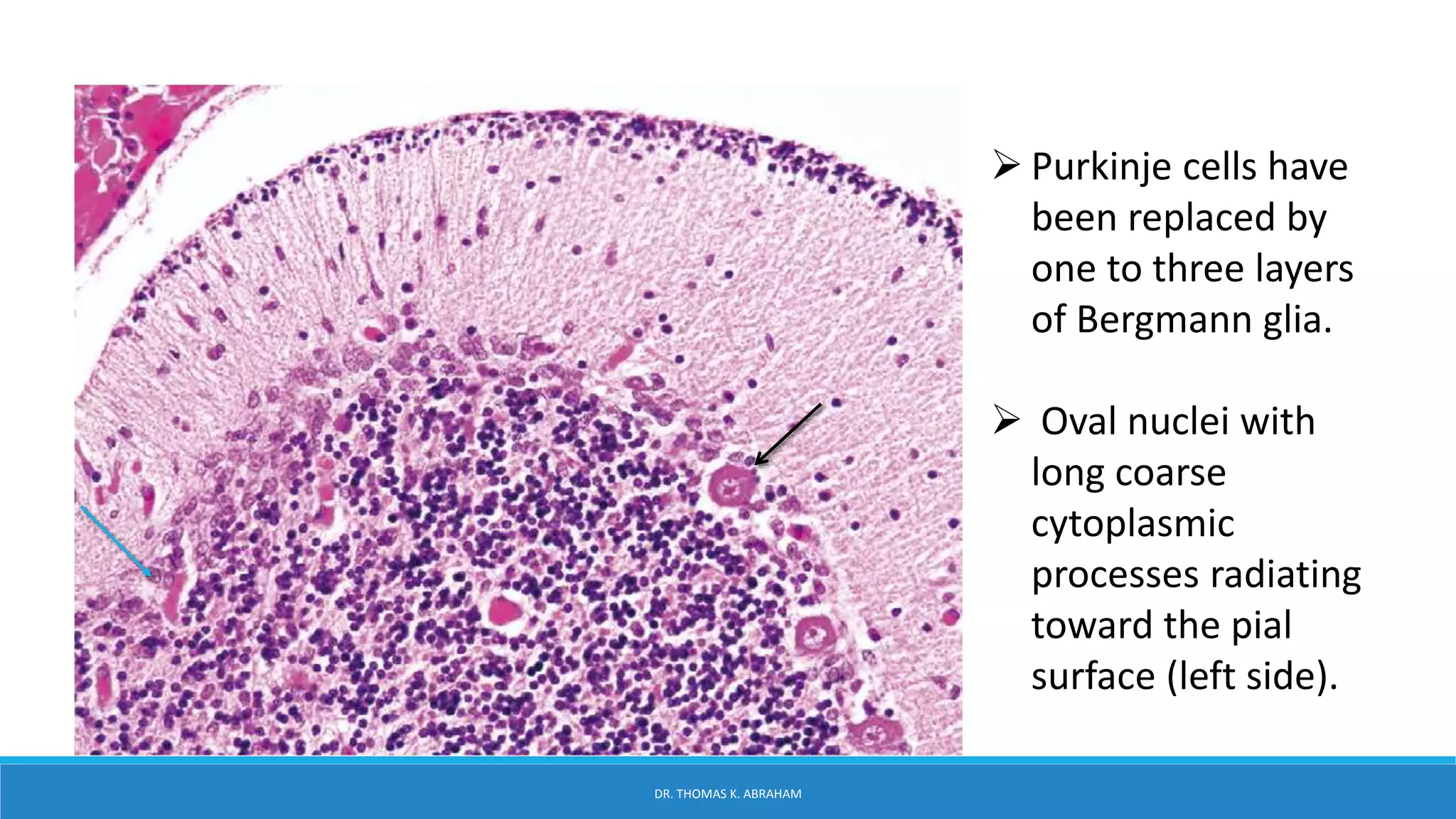
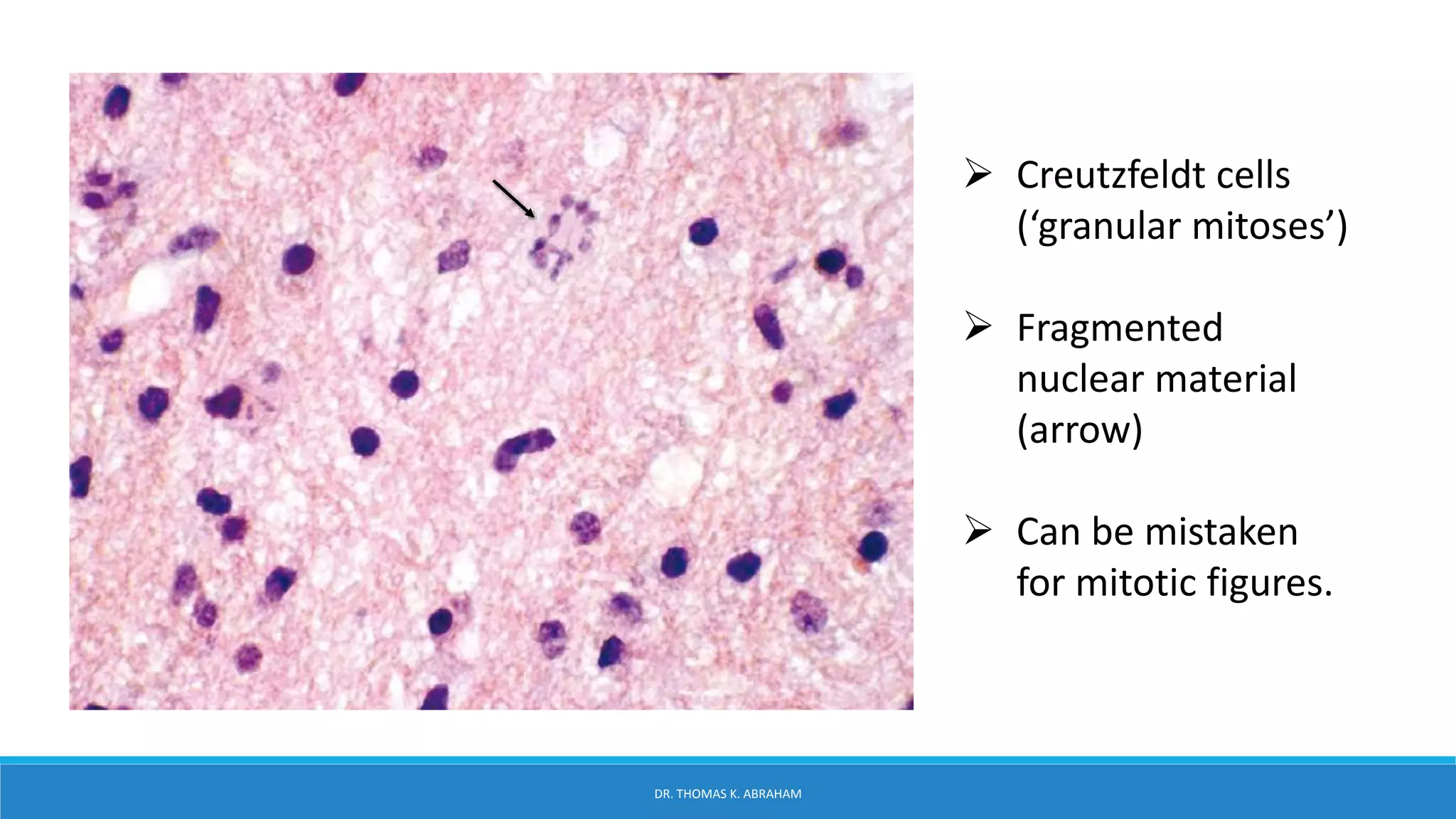
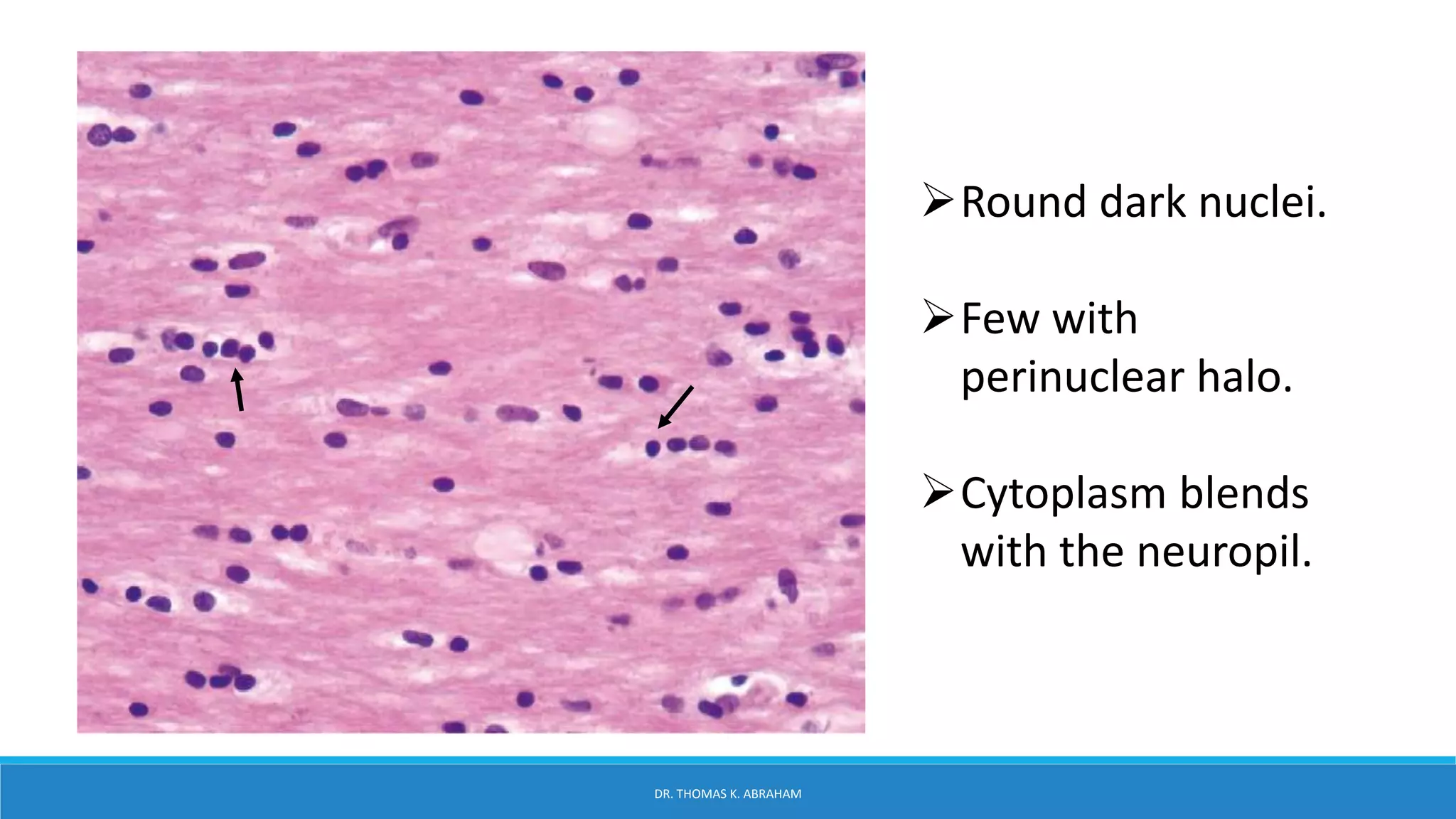
This document provides an overview of central nervous system histology and embryology. It discusses the development of the neural plate and neural folds during the third week of embryonic life. It describes the various tissue organizations in the brain, including the six layers of the cerebral cortex and cell types such as pyramidal and granular neurons. It also covers the two main cell types - neurons and glia, with subtypes including astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and ependymal cells. Special stains and features in aging are also briefly mentioned.