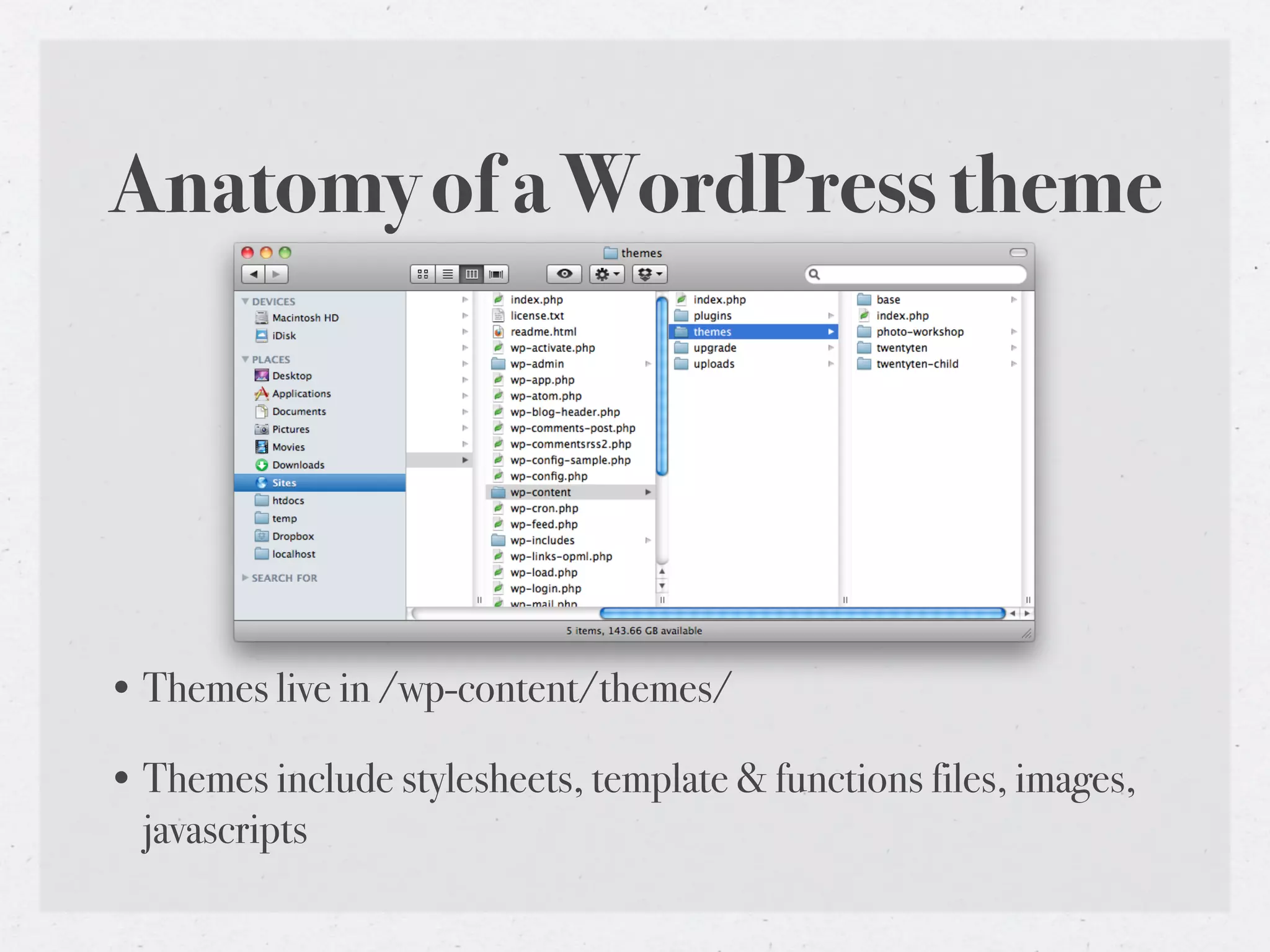
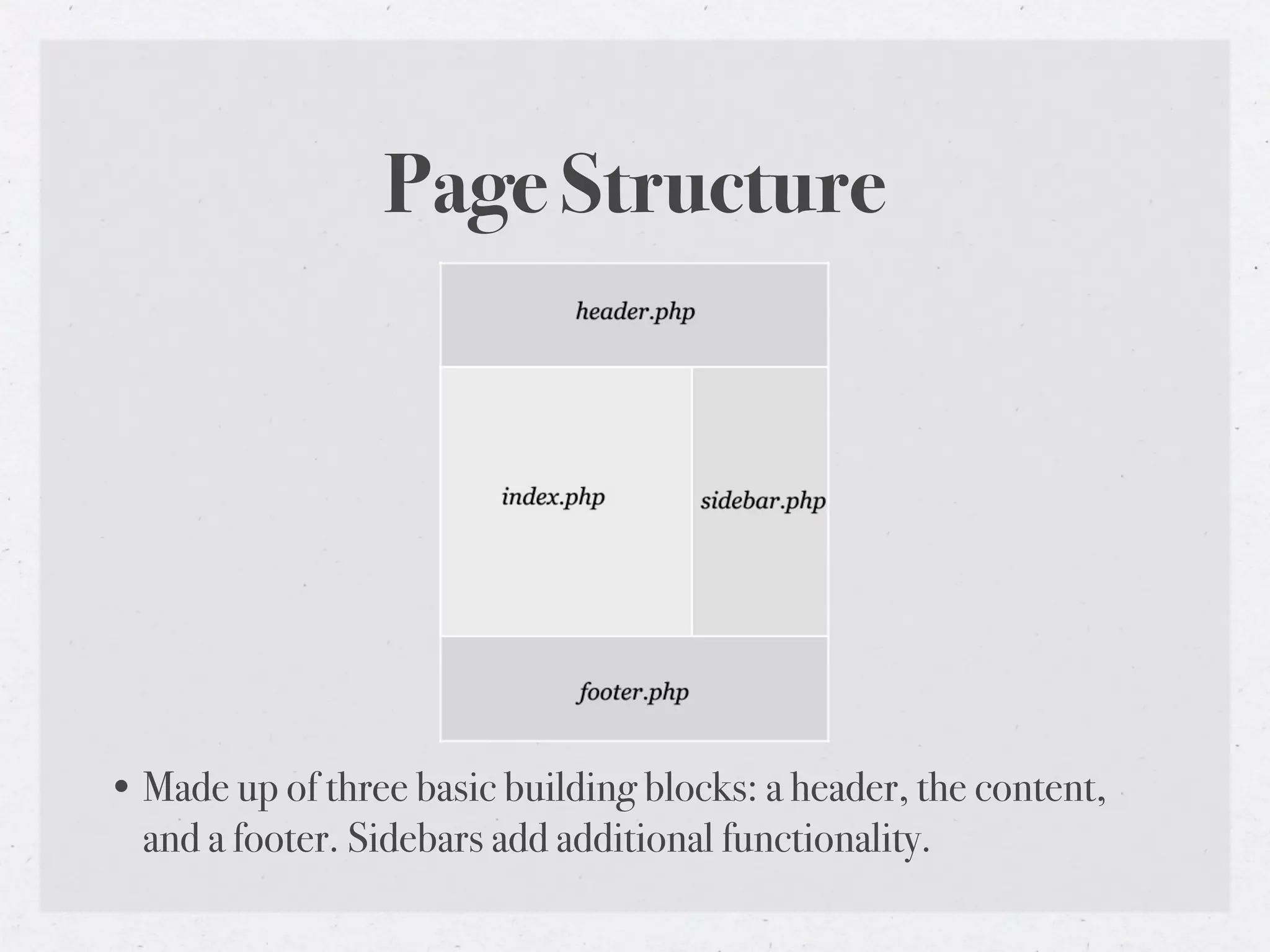
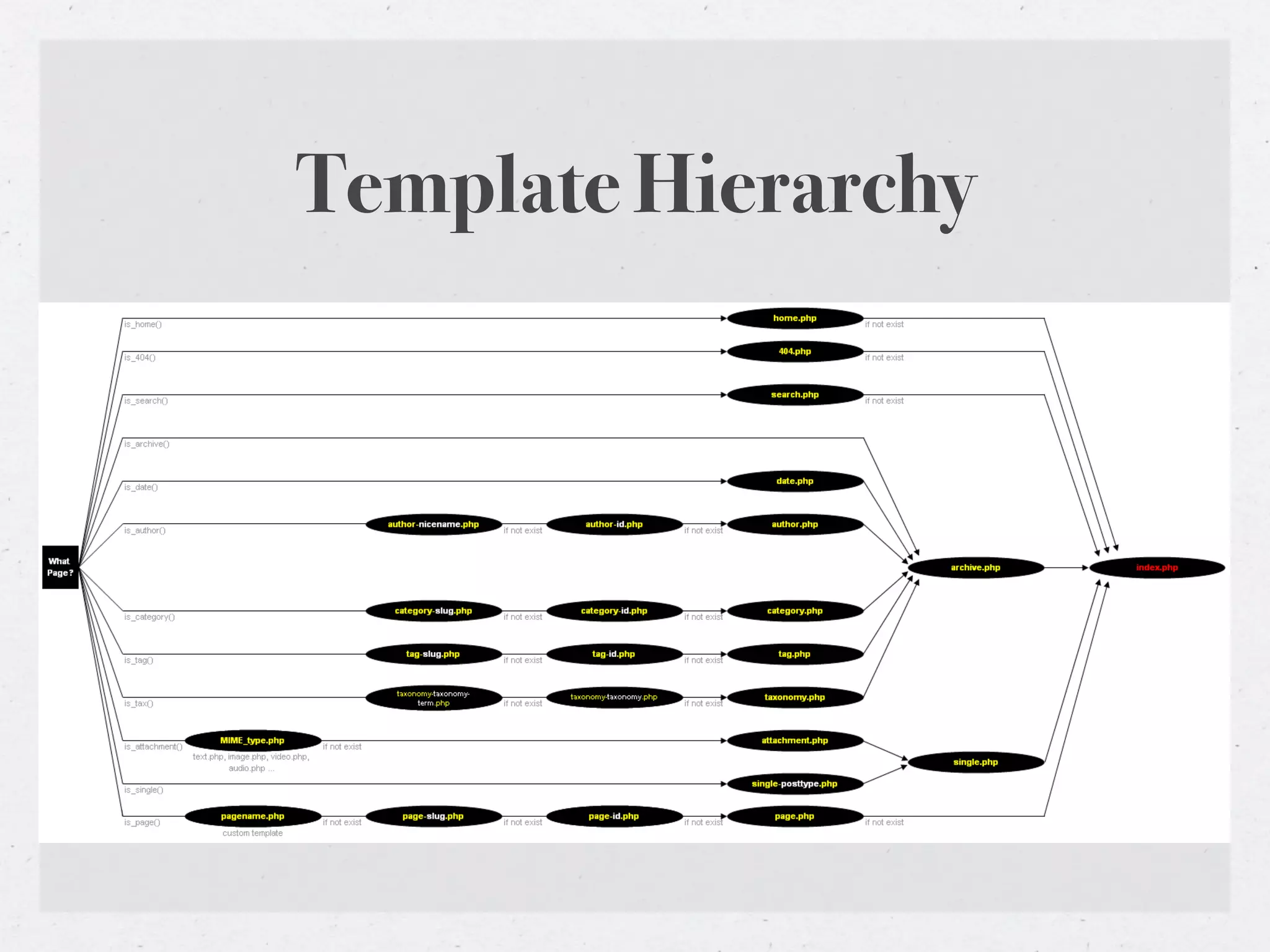
This document provides an introduction to WordPress theme development, covering the anatomy, structure, and essential files involved in creating themes. It details the template hierarchy, development environment, the loop, query posts, and how to use template tags effectively. Additionally, it discusses child themes, conditional tags, and theme testing tools for ensuring theme reliability and performance.