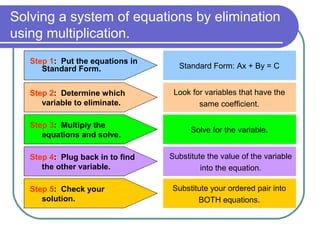
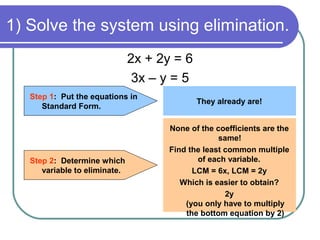
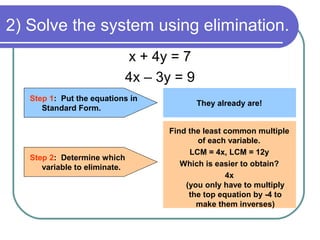
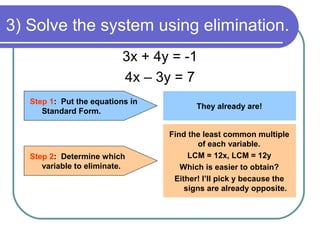
1) Put the equations in standard form if needed
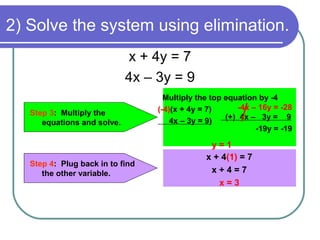
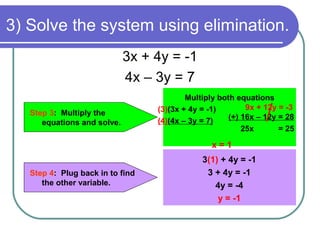
2) Determine that y can be eliminated by multiplying the top equation by 3
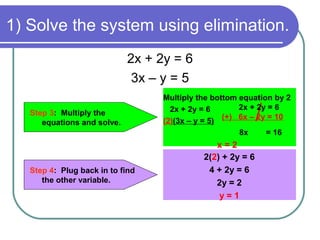
3) Multiply the top equation by 3 and add it to the bottom equation to eliminate y
4) Solve the resulting equation for the remaining variable
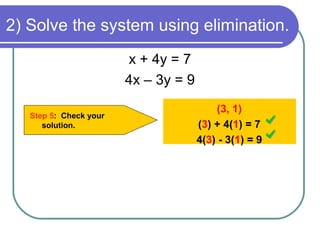
5) Substitute back into one of the original equations to find the other variable
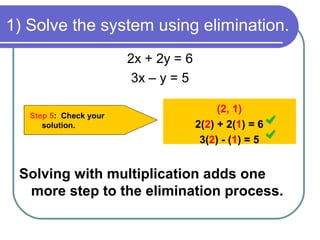
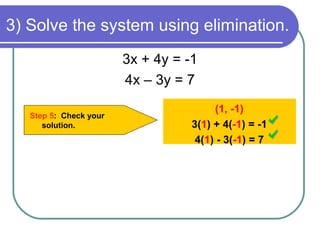
The solution to the system is (1, -2).