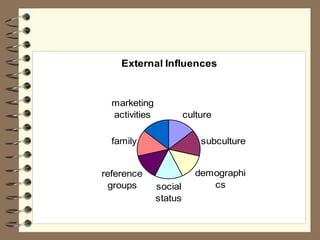
Group influences
- 2. Demographics Describes population in terms of its size, distribution and structure. Population size and distribution occupation Education Income Age Social Stratification
- 3. GROUP INFLUENCES Reference Groups Reference group influences---> a) Informational influence b) Normative influence Roles Role Load Evolving Roles Role Conflicts & Role Overload Group Communication
- 4. Group: two or more individuals who share a set of norms , values or beliefs and have certain implicitly /explicitly defined relationships to one another such that their behaviors are interdependent A reference group is a group whose presumed perspectives or values are being used by an individual as the basis for his or her current behavior.
- 5. Informational Influence : occurs when an individual uses the behaviors and opinions of reference group members as potential useful gbits of information. This influence is based on either the similarity of the group members to the individual or the expertise of the influencing group member. Normative Influence :(utilitarian influence) occurs when an individual fulfills group expectation s to gain a direct reward or avoid sanctions. Normative influence is strongest when individuals have strong ties to the group and the product involved is socially conspicuous.
- 6. GROUP INFLUENCES Opinion Leadership: Moderate Low High Moderate Product Knowledge High Low High low Product/ Purchase Involvement
- 7. Group Influence » OPINION Leader Characteristics » Diffusion of Innovation. Time Fast Diffusion % of total group adopting innovation 100%
- 8. Factors Affecting Spread Of Innovation Type Of group Fulfillment of felt need compatibility complexity observability trialability Perceived risks
- 9. Factors Affecting The Spread of Innovations. Type of group : Some groups are more accepting of change than others. Young affluent and highly educated groups accept change , including new products , readily. Marketing effort:The rate of diffusion is heavily influenced by the extent of marketing effort involved. Type of decision : refer to an individual v/s a group decision . The fewer individuals involved in the purchase decision , the more rapidly an innovation will spread.. Fulfillment of felt need: The more obvious the need that the innovation satisfies , the faster the diffusion. Compatibility: The more the purchase and use of innovation is consistent with the groups’ values and beliefs, the faster the diffusion Complexity : more difficult is the innovation to understand and use , the slower the diffusion.
- 10. Observability : The more easily the consumers can see the positive effects of adopting an innovation , the more rapid the diffusion. Relative advantage : an innovation either must have a performance advantage or cost advantage . - Cassettes- CDs- VCDs- DVDs. Trialability : The easier to have a low cost or low risk trial of the innovation , the more rapid its diffusion --- > 14 days trial or money back , test drive for cars. Perceived risk : The more risk associated with trying an innovation , the slower the diffusion. Risks can be social, financial or physical.
- 11. Diffusion of Innovation Characteristics of individuals who adopt an innovation at varying points in time. Innovators : venturesome risk takers. Capable of absorbing the financial and social costs of adopting an unsuccessful product.. They tend to be younger, better educated and more socially forward. Early adopters : tend to be opinion leaders in local reference groups. They are willing to take a calculated risk on an innovation but are concerned with failure. Early majority :tend to be cautious with respect to innovations. Adopt innovation after the innovation has proven successful with others.. Tend to be older, less well educated . Late Majority : skeptical about innovations. They often adopt more to social pressures or a decreased availability of previous product than because of a positive evaluation of the innovation. Laggards :hate change and are oriented towards the past.
- 12. Households Husband-dominant decisions : automobiles, liquor, cigarettes , life insurance and consumer electronic products. Wife -dominant decisions : furniture, jewelry,food and home appliances Joint- decisions : House, vacation How household menebers interact== Function (Role specialization of different household members, degree of involvement each member has in the product area) Wives specialized role --- in certain aspects of child rearing --- hence have a more specialized role in buying children clothing. Involvement: A spouse interested in electronics as a hobby /profession probably would greatly influence the purchase of a stereo , television or PC.
- 13. Household Decision Making process for children’s products Consumer (children) Purchaser (Parents) Influencer (Children) Information gatherer (Parents) Decision maker (Parents, Children) Comm. Targetted at children (Taste) Comm. Targeted at parents ( nutirtion)
- 15. Internal Influence- Personality DEFN : is an individual’s characteristic response/tendencies across similar situations. Major theories of personality A)) Freudian Theory : Id, Ego, Superego B) Non- Freudian Theory : Karen Horney : Individuals classified into 3 personality groups : 1) Compliant -- Individuals who move towards others -- They want to be appreciated , loved--- peace loving , sober guys. 2) Aggressive : Who move against others--- desire to win /excel and win admiration. 3) Detached : Who move away from others --- desire independence , self- sufficiency and freedom from obligation.
- 16. Internal Influence- Personality C) Jungian Theory : Jungian inspired psychological dimensions 1) Sensing-Intuiting 2) Thinking- Feeling 3) extrovert -introvert 4) Judging-Perceiving D) Trait theory : Any distinguishing relatively enduring way in which one individual differs from another.--- CATELL’s Trait Theory. E.g : 1) Reserved v/s Outgoing 2) Shy v/s Venturesome 3) Conservative v/s experimenting 4) Relaxed v/s tense 5) Sober v/s happy-go-lucky
- 17. Internal Influence-Perception Defn:- The process by which an individual selects , organizes, interprets stimuli into a meaningful coherent picture of the world. Stimuli : unit of input to any of the senses (eyes,ears etc.)e.g of stimuli are ----> product, packaging, Brand name, Advt. Etc. The study of perception is largely the study of what we subconsciously add to or subtract from the sensory input to produce our own private picture of the world. ABSOLUTE THRESHOLD : The lowest level at which an individual can experience a sensation is called the absolute threshold. In simple terms the point at which a person can detect a difference between “SOMETHING” and “ NOTHING” is that person’s absolute threshold for that stimuli
- 18. Internal Influence-Perception Under conditions of constant stimulation such as “seeing” the same ad or the same set of hoarding the A.T increases. Companies change ads or have a series of ads or use different media to overcome this --- bus shelter, inside trains , on top of auto etc. DIFFERENTIAL THRESHOLD : The minimal difference that can be detected between two stimuli. This also called as J.N.D. (Just Noticeable Difference ) WEBER’S LAW : J.N.D between two stimuli was not an absolute amount but an amount relative to the intensity of the first stimulus. The law states : “Stronger the initial stimulus , the greater the additional intensity needed for the second stimulus to be perceived as different.”
- 19. Internal Influence-Perception E.g ALTO -- cost is 2,50,000 1) Cost goes up by 5000. 2) Cost goes up by 30000. PETROL PRICE = Rs. 80/litre 1) price goes up by 50 paise 2) price goes up by 5 Rs. Relevance to Marketing : companies try to find J.N.D for their products for the following reasons- – Reduction in product size , increase in product price or reduction in quality are not discernible to the public. – Product Improvements/sales promotional schemes which are discernible.
- 20. Internal Influence-Learning Defn : Process by which individuals acquire the purchase and consumption knowledge and experience they apply to future related behavior. Learning Intentional (Acquired as a result of a careful search for information) Incidental (Acquired without effort)
- 21. Learning Basic elements required for learning 1) Motivation : Acts as a spur to learning with needs and goals serving as stimuli. E.g : Person wants to be like Sachin ---> will learn about cricket , quality of bat, pitch etc. 2) Cues : Stimuli that give direction to motives e.g -- An ad for a cricket camp will serve as cue for cricket buffs wanting to improve their game . Ad ---- CUE
- 22. Learning – 3) Response : How individuals respond to a cue. 4) Reinforcement : Increases the likelihood that a specific response will occur in the future as the result of particular cue. e.g A student has cold . He takes Levocet tablets. Within a day he becomes okay. “Levocet” tablets has enabled the student to get through the exam week.-----> He is more likely to buy “Levocet” in advance for the next exam.----> The tablets have lived up to expectation.
- 23. LEARNING Learning Theories- 1) Behavioral -- a) Classical b) Instrumental 2) Cognitive CLASSICAL CONDITIONING :All organisms are relatively passive entities that could be taught certain behavior through repetition (conditioning) Three basic concepts derived from Classical theory : 1) Repetition: works by increasing the strength of association and by slowing the process of forgetting. 2) Stimulus Generalization : Making the same response to slightly different stimuli. The practice of Marketing a whole line of company products under the same brand name , capitalizes on the consumer's ability to generalize favorable brand association from one product to other. E.g : TATA
- 24. LEARNING Stimulus Discrimination : Opposite of stimulus generalization , wherein consumer selects a specific stimulus from among similar stimuli. The consumer’s ability to discriminate among stimuli is the basis of Positioning Strategy---> unique image in consumer’s mind.
- 25. Classical Conditioning IVAN PAVLOV Unconditional Stimulus (US) Meat Paste Conditional Stimulus (CS) Bell Conditional Stimulus (CS) Bell Unconditional Response (UR) Salivation Conditioned Response (CR) Salivation E.g : CS--Brands , Products, Retail stores , CR- Purchases or store patronage. US---> Celebrity endorsers
- 26. Instrumental Conditioning B.F.SKINNER Stimulus Situation (Need clothes want a good full shirt) Louis Philippe Arrow Van Huesen Park Avenue Response Arm length short Uncomfortable at shoulder Perfect Fit Too Tight Reward
- 27. Instrumental Conditioning Consumers learn by means of a trial and error process in which some purchase behaviors result in more favorable outcomes than other purchase behavior. A favorable experience is instrumental in teaching the individual to repeat a specific consumption behavior. Positive Reinforcement : Consists of events that strengthen the likelihood of a specific response e.g “CLEAR” helps in reducing dandruff----> will result in repetition of shampoo purchase. Negative Reinforcement : unpleasant outcome that serves to encourage a specific behaviour. E.g ---1) Fear ads---> 1) Cease fire 2) National Insurance. In each of these cases the consumer is encouraged to avoid negative consequences by buying the advertised product.
- 28. Cognitive Learning theory A considerable amount of learning takes place as a result of consumer thinking and problem solving Learning involves complex mental processing of information . Key point of this theory is---> Information Processing : Consumers process product information by attributes, brands, comparison between brands on key features etc.
- 29. ATTITUDE DEFN: A learned predisposition to behave in a consistently favorable or unfavorable way with respect to a given object. brand Packaging retailer advertising Object
- 30. Attitude Learned Predisposition : attitudes relevant to purchase behavior are formed as a result of direct experience with the product , information acquired form others and exposure to mass media. Consistency : e.g If you like Japanese cars, when you want to buy a car--- it will be Japanese. Does situation have an influence on consumer attitudes? A specific situation can cause consumers to behave in ways seemingly inconsistent with their attitudes. E.g ---> Rohit uses Gillette shaving cream regularly --- Next time he chooses the super saver offer of Palmolive ---->Buy 1- Get 1 free ---> overall price is lower then Gillette.
- 31. Structural Model Of Attitudes A) The tricomponent attitude model: 1) Cognitive 2) Affective 3) Conative component 1) Cognitive Component: consists of a consumer’s belief about an object. E.g ---> A consumer believes that DIET COKE has a) No Calories b) contains caffeine c) is competitively priced. The total configuration of beliefs about this brand represents the cognitive component of an attitude towards DIET COKE. BELIEFS MAY BE CORRECT OR INCORRECT----> BUT THEY ALWAYS EXIST.
- 32. 2) Affective Component :Feelings or emotional reactions to an object represent the affective component of an attitude. e.g A consumer who states “ I like Diet coke “ or “ Diet coke is terrible” is expressing the results of an emotional or affective evaluation of the product. 3) Conative or Behavioral component : Tendency to respond in a certain manner towards an object. E.g a series of decisions to purchase /not purchase DIET COKE or to recommend it to friends would reflect the Conative component of an attitude.
