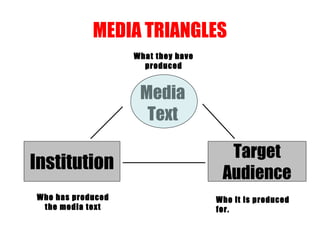
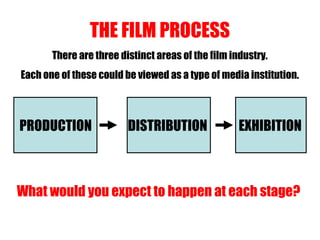
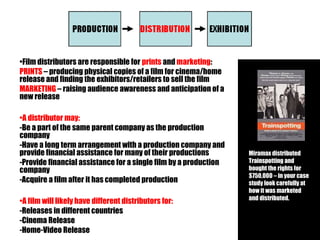
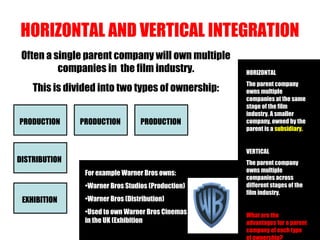
The document provides an overview of the film industry for an exam, including the key areas of production, distribution, and exhibition. It discusses how a film moves through these three stages, from being produced by a production company, to being distributed nationally and internationally by distributors in theaters and home markets, to finally being exhibited in theaters or bought for home viewing. It also explains the concepts of horizontal and vertical integration, where large parent companies own subsidiaries across different stages of the film industry.