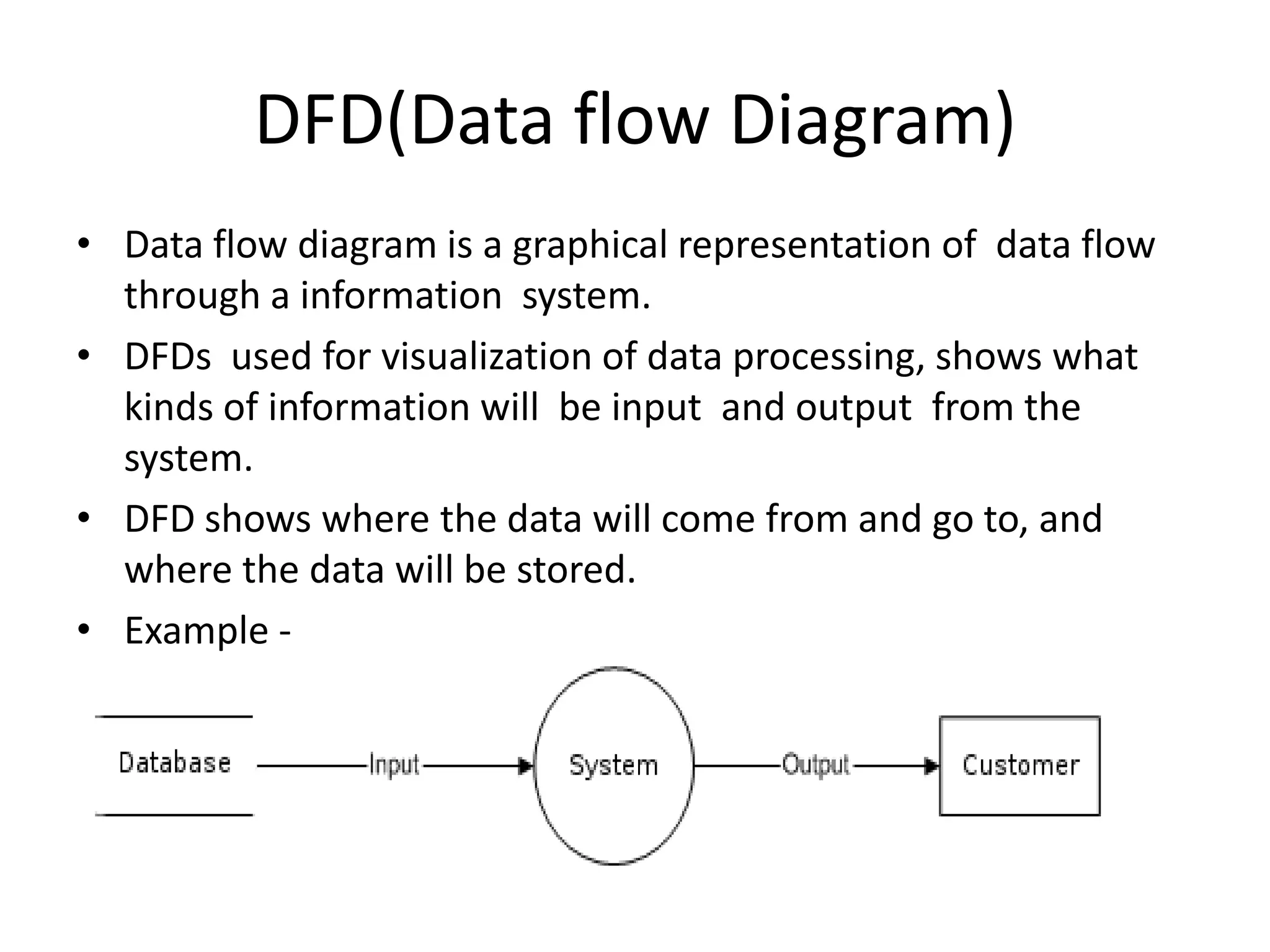
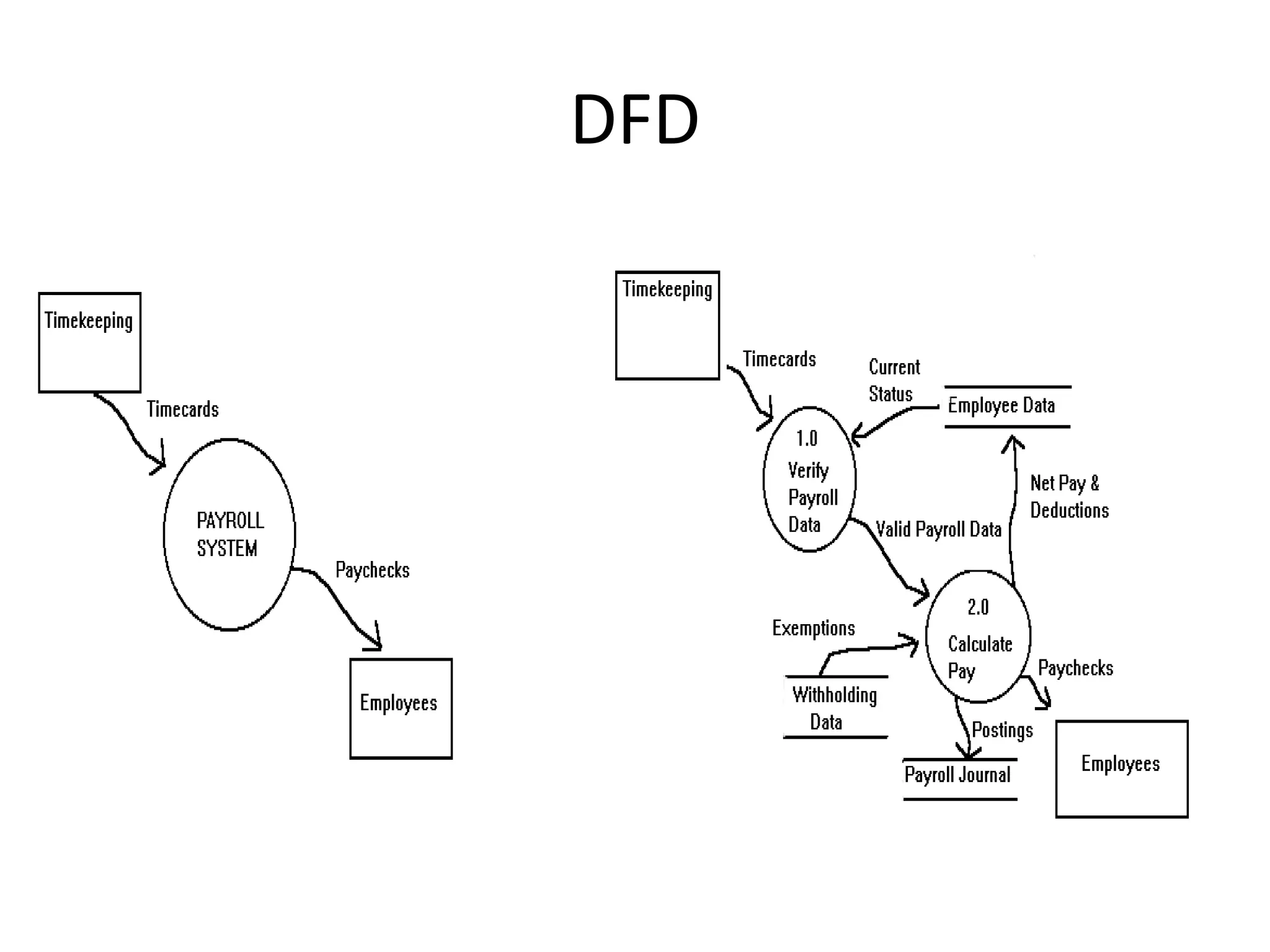
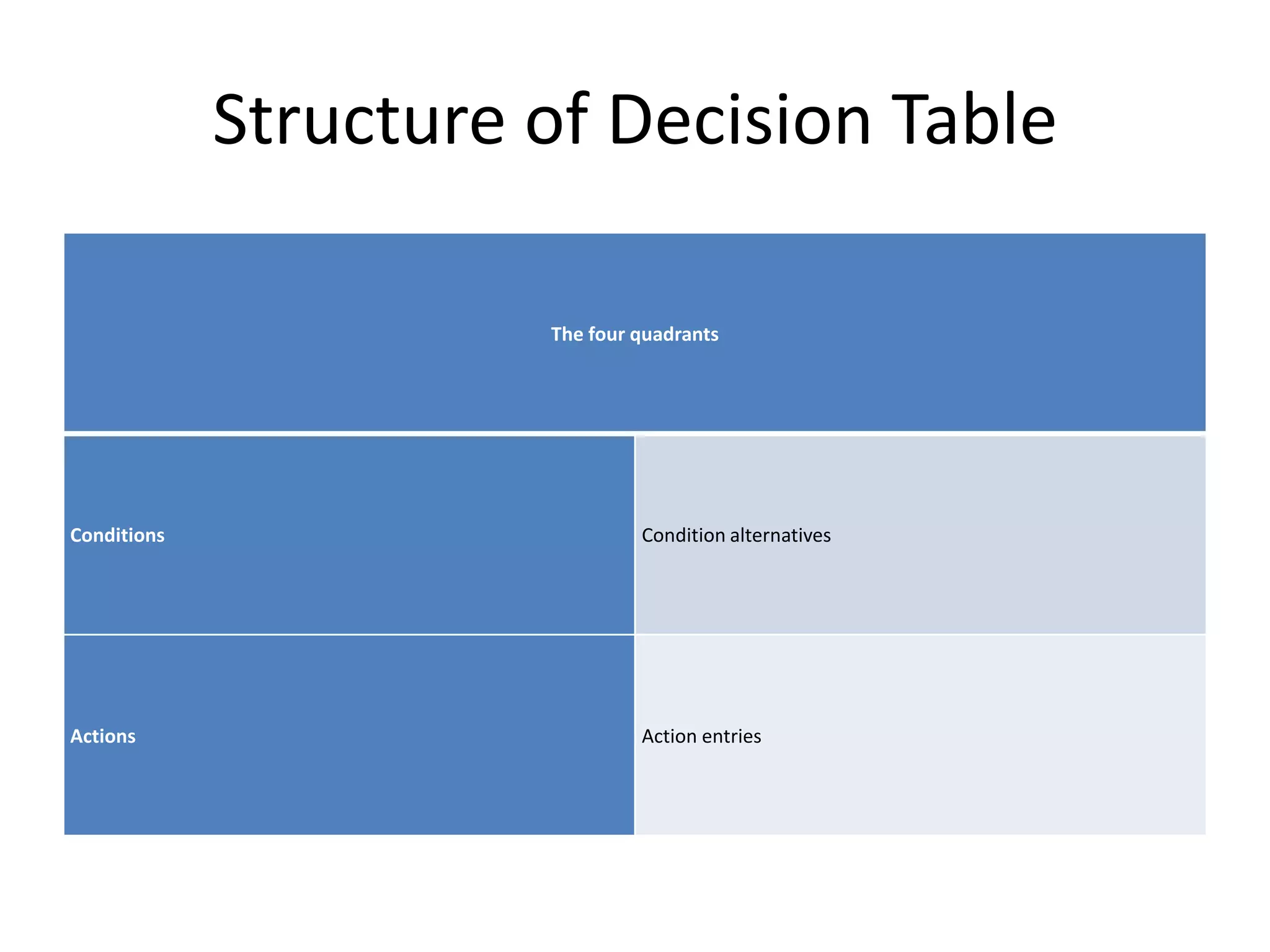
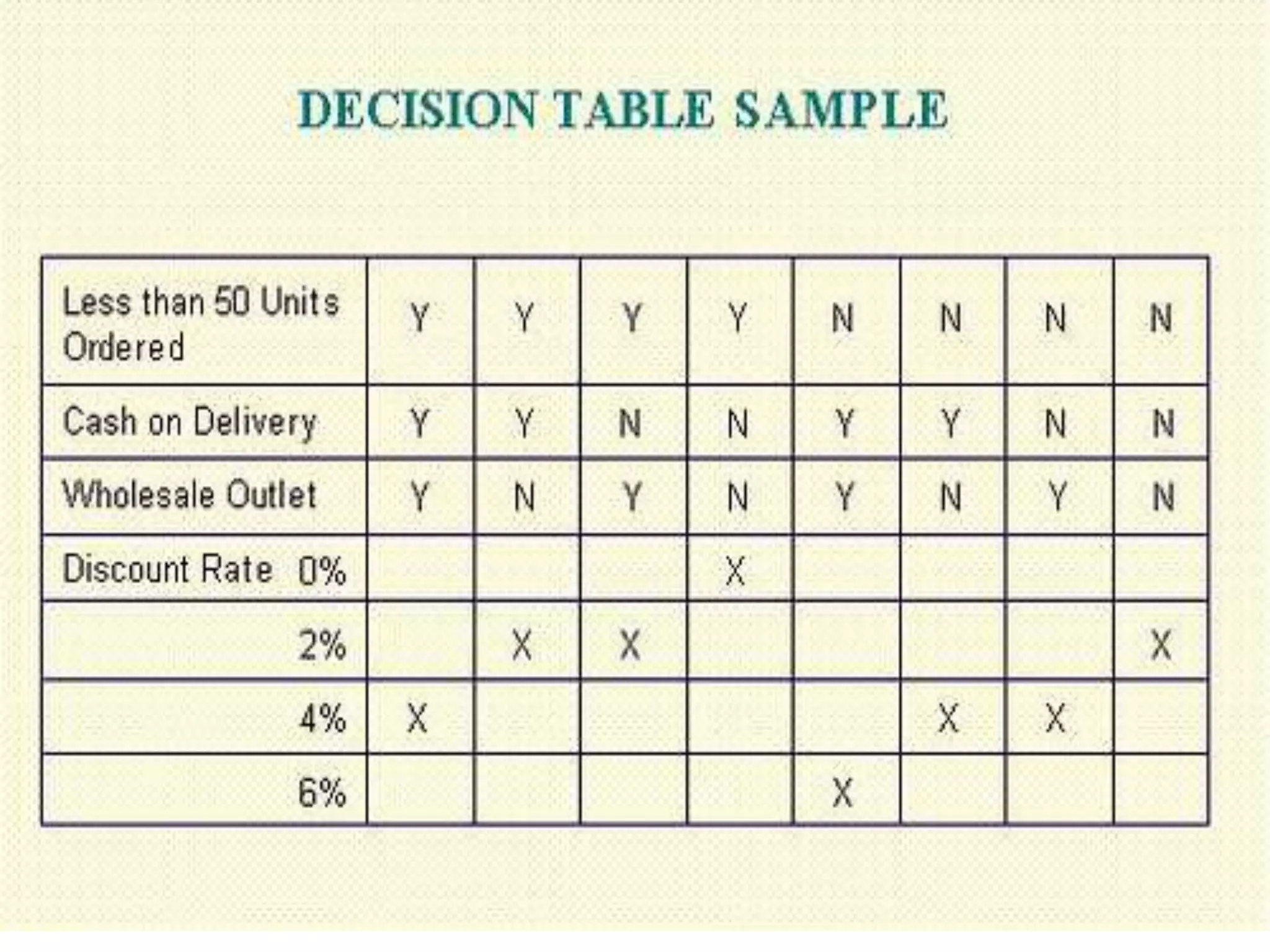
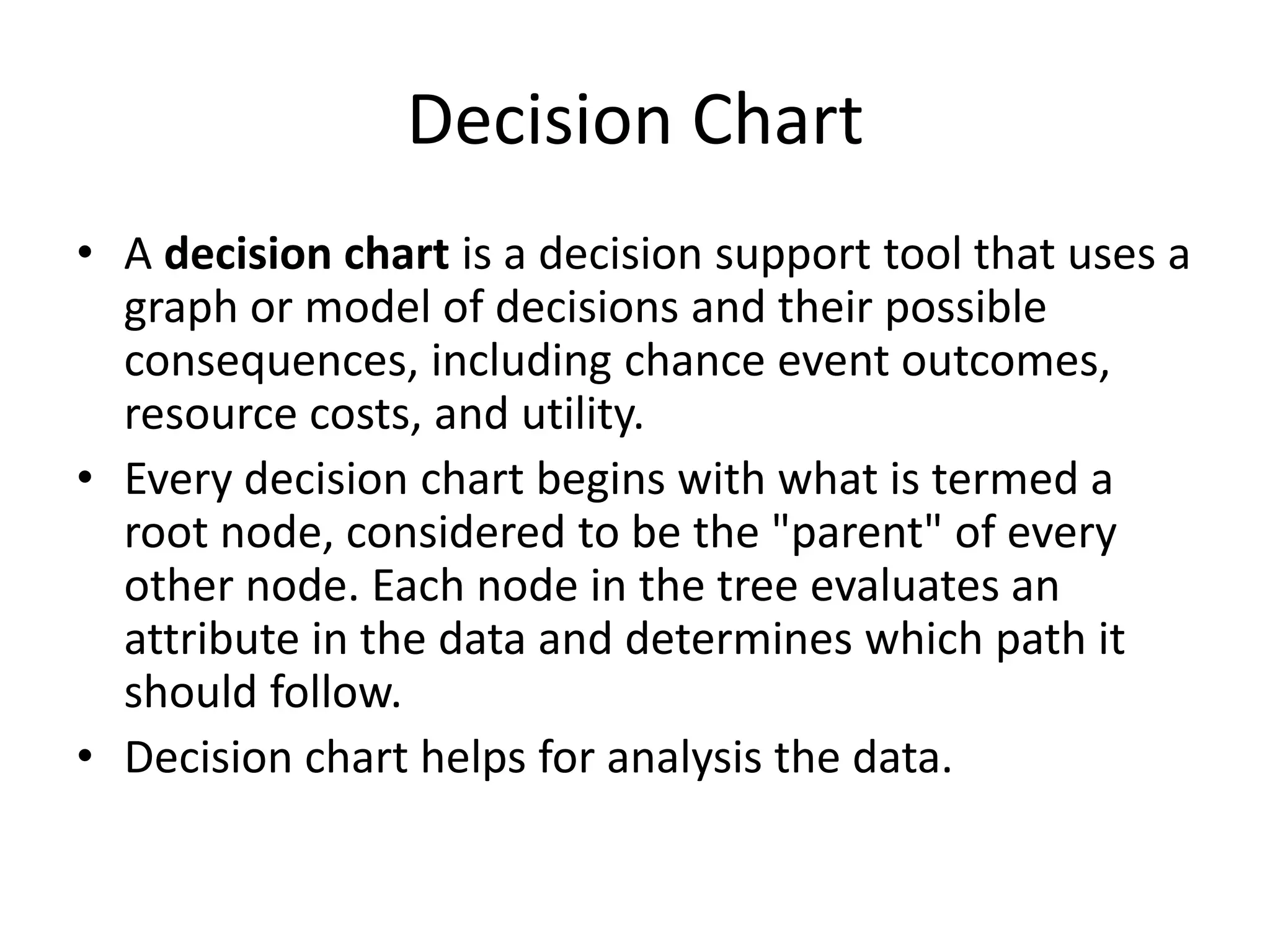
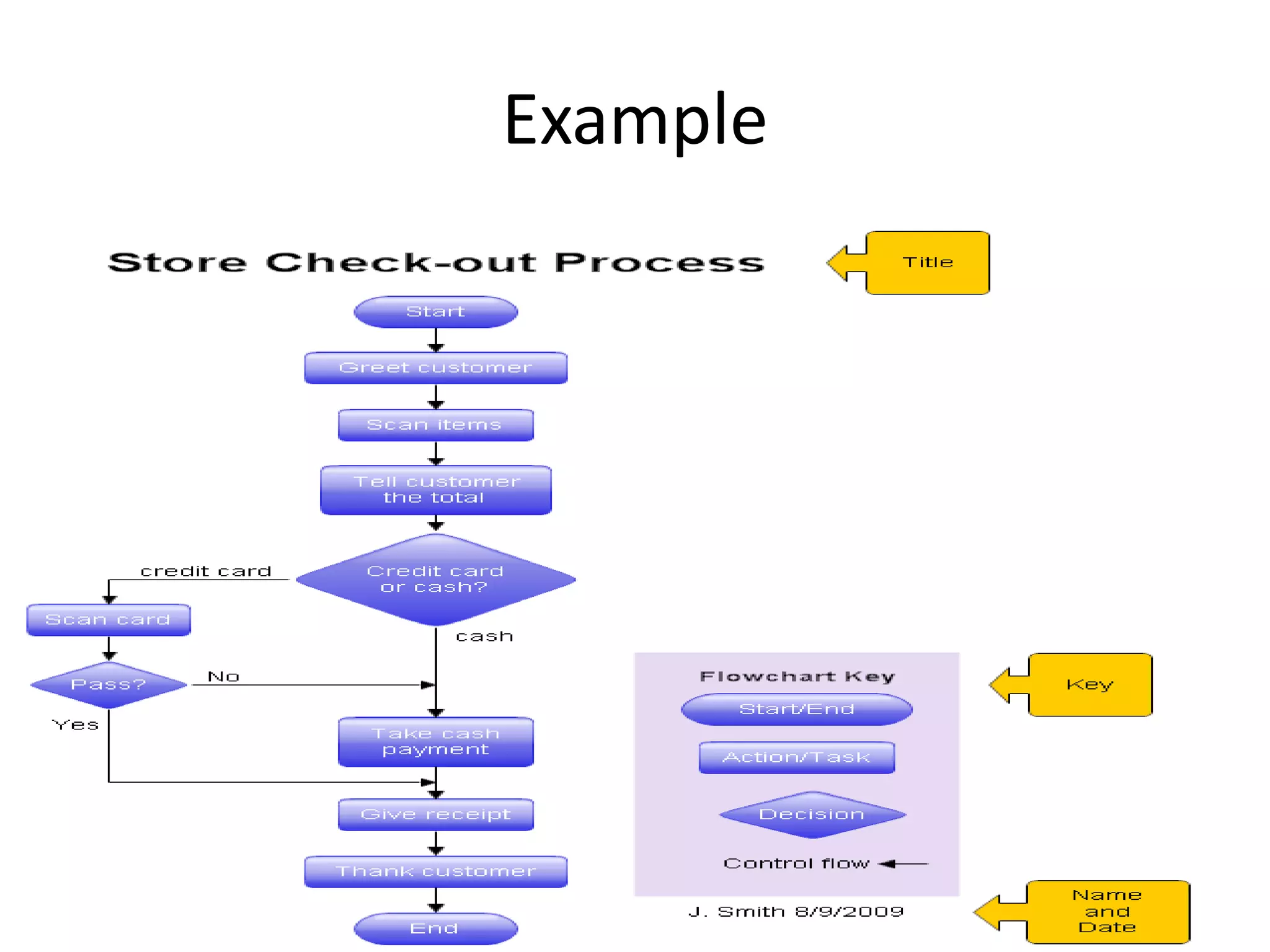
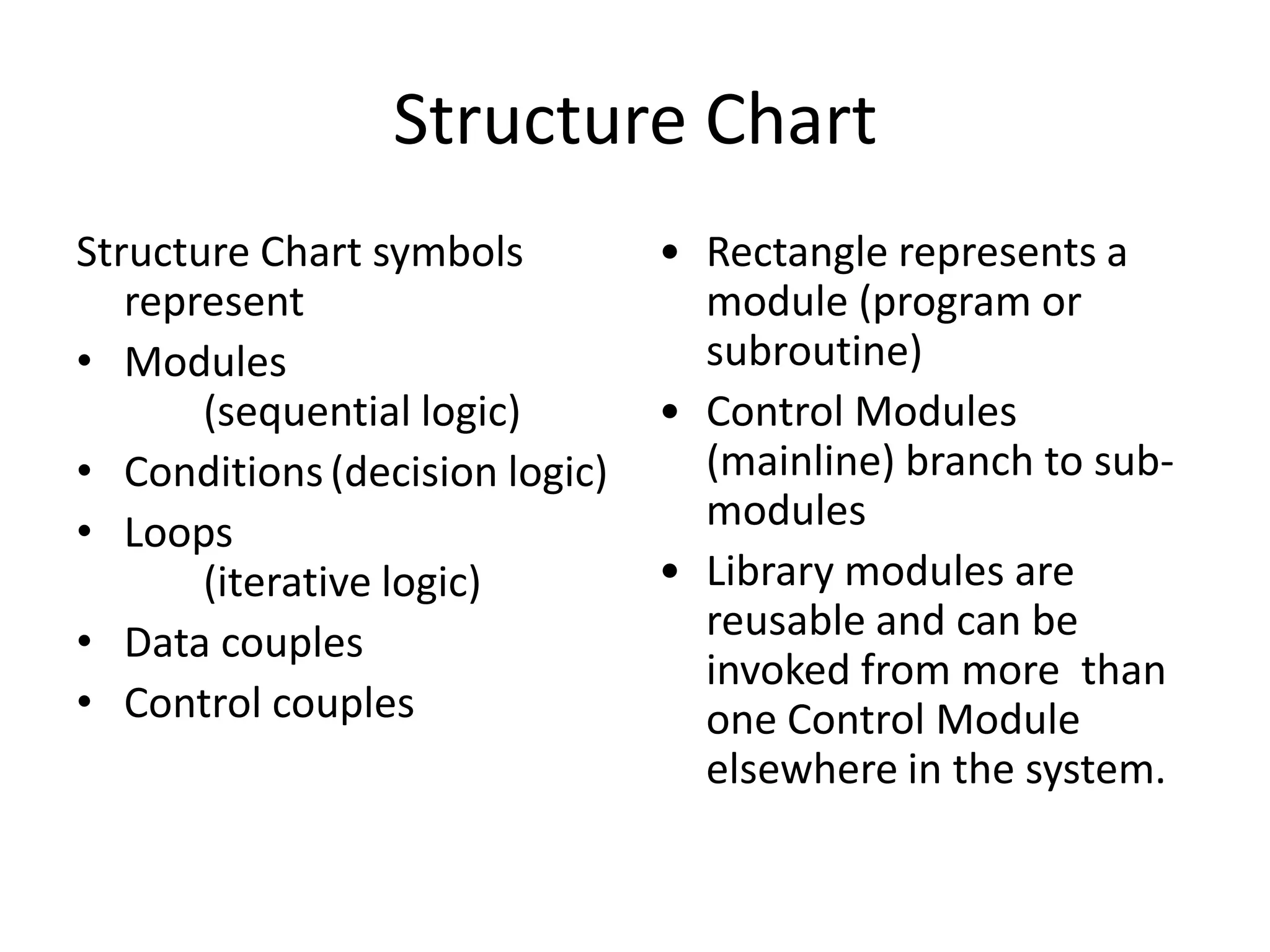
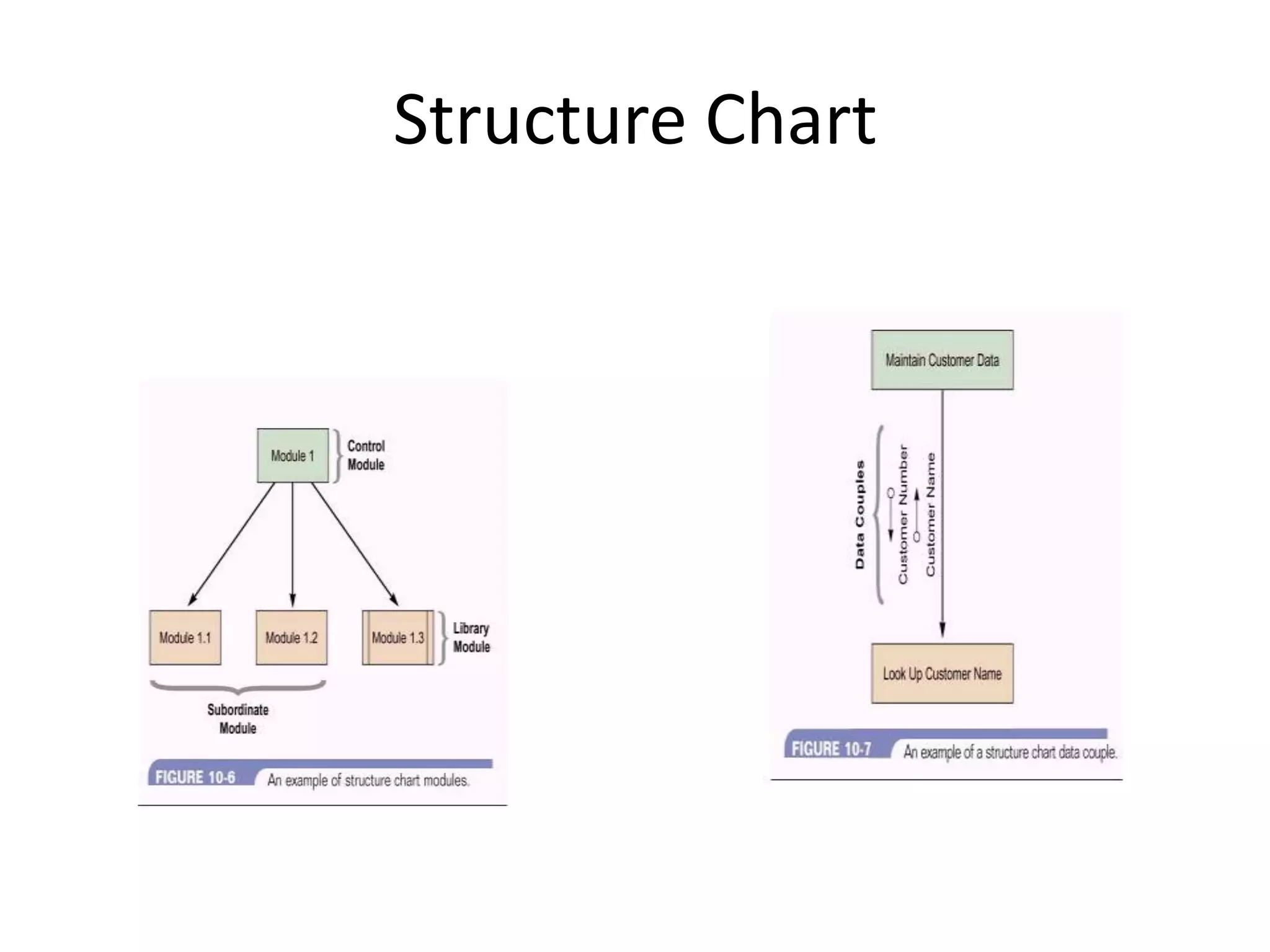
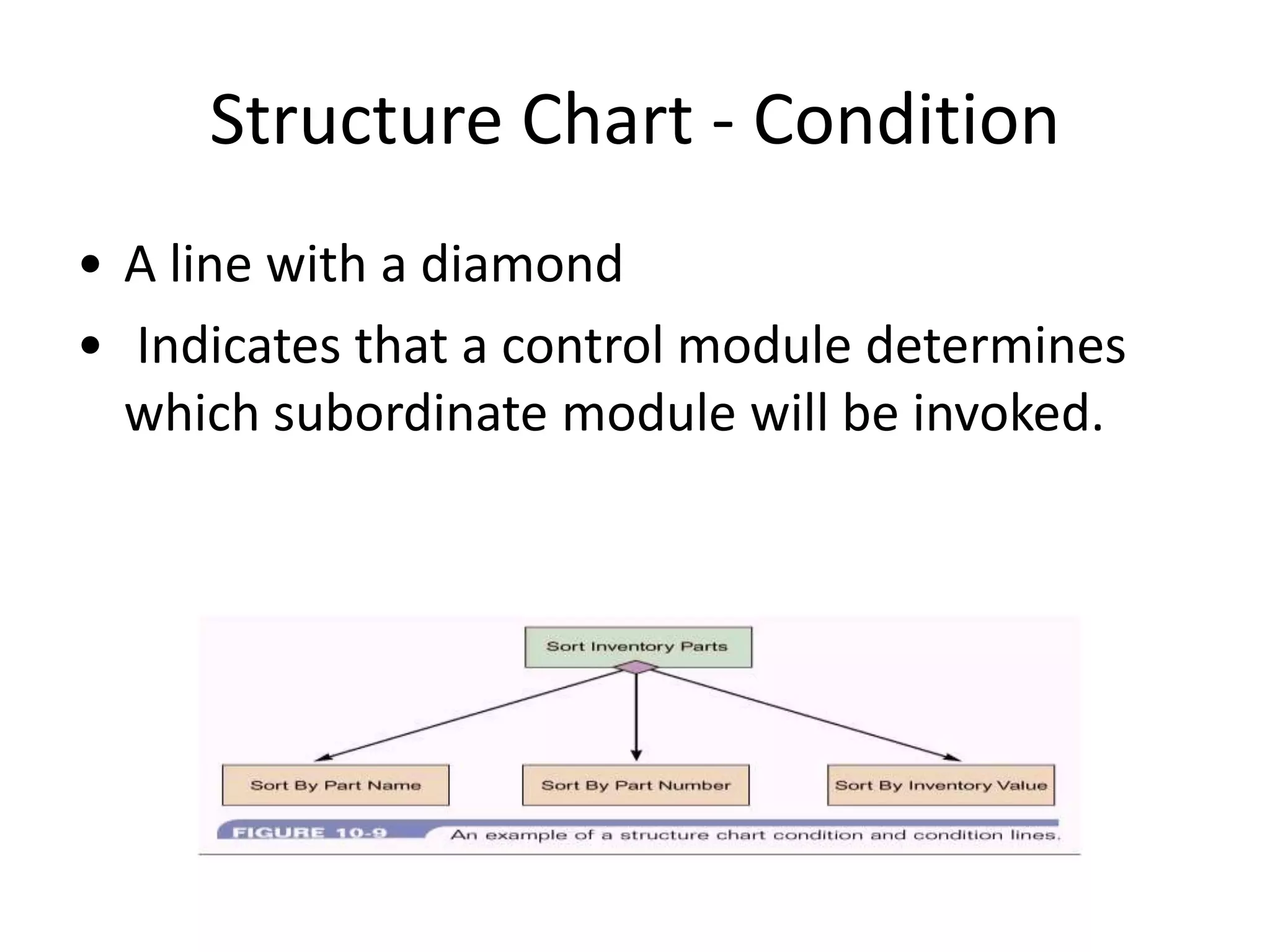
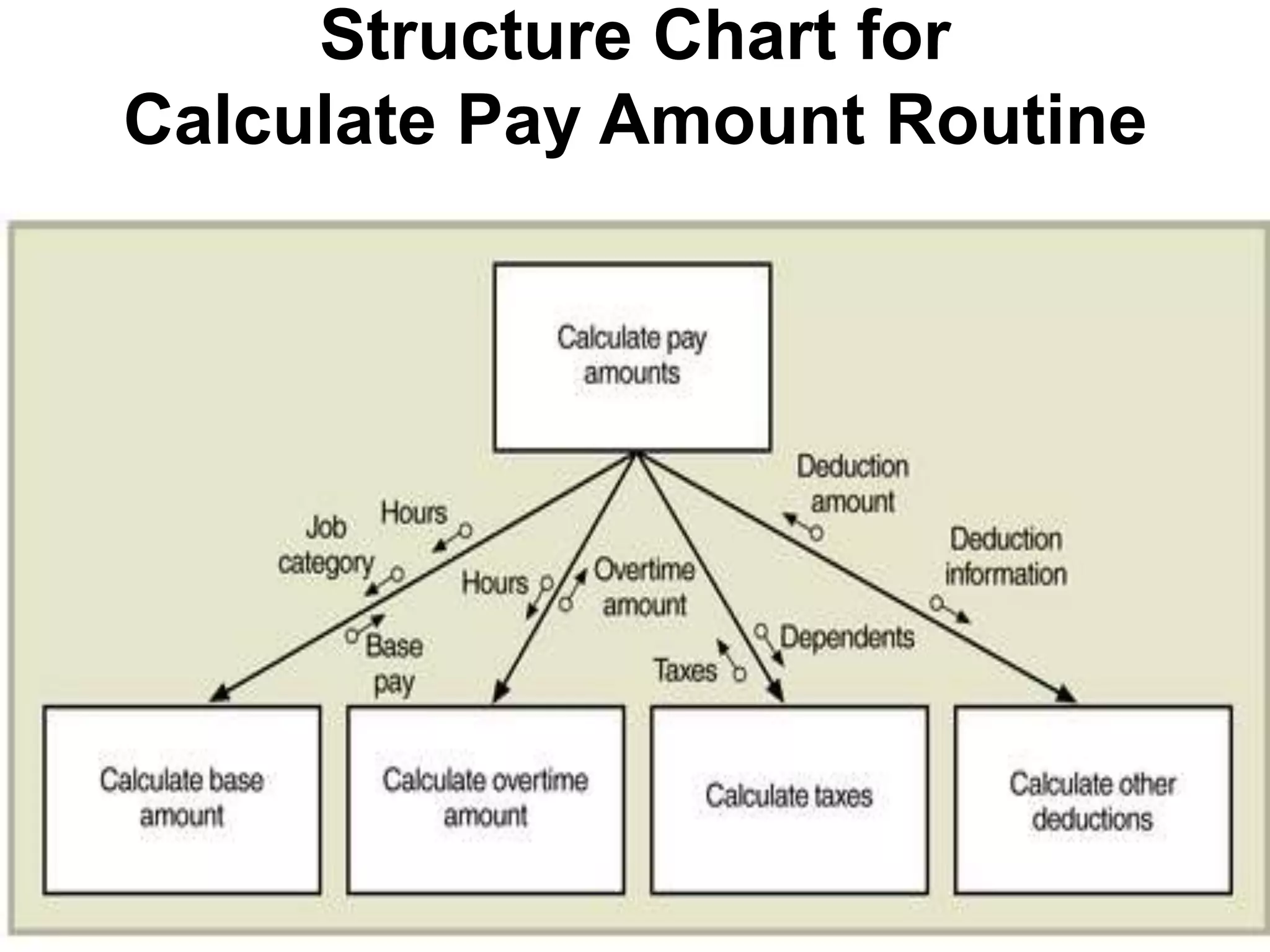
This document discusses and provides examples of various modeling techniques including data flow diagrams (DFDs), decision tables, decision charts, and structure charts. DFDs show the flow of data through a system and can be partitioned into multiple levels. Decision tables organize conditions and effects in a matrix. Decision charts model decision paths and outcomes. Structure charts depict the hierarchical modular structure of a program, showing relationships between modules, data and control couplings, conditions, and loops.