Recommended
PPTX
Zinc in nutrition by nikhil
PPT
ZINC IMPORTANCE LECTURE.ppt
PDF
PPTX
PPTX
Nutritional disorders of Skin
PPTX
PPTX
Zn & Cu, Biochemistry minerals
PPTX
Zinc and Nutritional Problems
PPTX
ZINC DEFISIENSI - ANASTASYA HANNIE -gizi.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
Micro Minerals 27.420 (1).pptx
PPTX
MANGANESE, COPPER AND ZINC
PPTX
ZINC DEFISIENSI - ANASTASYA HANNIE.pptx
PPTX
Diseases resulting from deficiency of elements
PPT
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
Zinc,PSM,Community Medicine,DR NARENDRA KUMAR YADAV
PPTX
ODP
Zinc deficiency: causes, treatment and prevention
PPT
3.MICRONUTRIENT DEFICIENCIES.ppt
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PHN - zinc deficiency.pptx
PDF
presentamjgfj hgydtrg gffdf gftion1-.pdf
PPTX
PPTX
PDF
Dr. David Ford Wilson - Provides Holistic Mental Health Care
PPTX
DNS deviated nasal septum ent ward s.pptx
More Related Content
PPTX
Zinc in nutrition by nikhil
PPT
ZINC IMPORTANCE LECTURE.ppt
PDF
PPTX
PPTX
Nutritional disorders of Skin
PPTX
PPTX
Zn & Cu, Biochemistry minerals
PPTX
Zinc and Nutritional Problems
Similar to ZINC DEFICIENCY MANIFESTATIONS effects.pptx
PPTX
ZINC DEFISIENSI - ANASTASYA HANNIE -gizi.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
Micro Minerals 27.420 (1).pptx
PPTX
MANGANESE, COPPER AND ZINC
PPTX
ZINC DEFISIENSI - ANASTASYA HANNIE.pptx
PPTX
Diseases resulting from deficiency of elements
PPT
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
Zinc,PSM,Community Medicine,DR NARENDRA KUMAR YADAV
PPTX
ODP
Zinc deficiency: causes, treatment and prevention
PPT
3.MICRONUTRIENT DEFICIENCIES.ppt
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PHN - zinc deficiency.pptx
PDF
presentamjgfj hgydtrg gffdf gftion1-.pdf
PPTX
PPTX
Recently uploaded
PDF
Dr. David Ford Wilson - Provides Holistic Mental Health Care
PPTX
DNS deviated nasal septum ent ward s.pptx
PPTX
PERI-PROSTHETIC FRACTURE NAIL-PLATE CONSTRUCT [NPC].pptx
PPTX
HYPERTENSION III SEMESTER ADULT HEALTH NURSING-I
PPTX
Atrial Fibrillation and difference with Atrial flutter
PPTX
Fracture, Cleavage , Lustre examples.pptx
PPTX
ICU setup Admission & discharge criteria.pptx
PDF
Seminario biología molecula - EBV-miR-BART5-3p
PPTX
Preformulation Studies for new Pharmaceutical substances
PPTX
Left Ventricular Assist Devices.(New Gen)
PPTX
History and Evolution of Microbiology.pptx
PPTX
SAPIENT3.0 Medi-trivia Quiz (FINALS) | F.A.Q. 2025
PPTX
The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Reflexes
PPT
Managemant of Mutilated Vital Teeth presentation
PPTX
Template for presentation of patients at the MDT Meeting
PPTX
FEBRUARY 2026 ONCOLOGY CARTOONS BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATRO
PPTX
OXFORD TECHNIQUE ,Zinovieff OXFORD TECHNIQUE
PPTX
Stress_Management_ICU_Nurses_with_Notes_Visuals.pptx
PPTX
Cardiovascular Disease ppt. S.Y D-Pharm.
PPTX
LOW DOSE RADIATHERAPY (LDRT) IN OSTEOARTHRITIS
ZINC DEFICIENCY MANIFESTATIONS effects.pptx 1. 2. INTRODUCTION
• Zinc is an essential trace element
• Second most abundant trace element (next to iron) in the human body,
containing approximately 2–4 g
• Zinc is present in all body tissues
60% is in skeletal muscle
30% in bone
4–6% in the skin
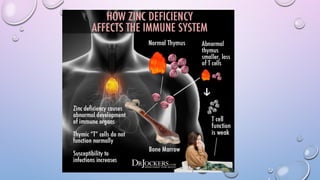
3. 4. 5. 7. CAUSES OF ZINC DEFICIENCY
HEREDITARY
• Defect in Zn transporter- Impaired absorption (Acrodermatitis Enteropathica)
ACQUIRED
• Lack of nutrition
• Excessive alcohol intake
• Long term exposure to environmental toxins
• Malabsorption syndrome
• Chronic diseases e.G. Sickle cell anemia, wilson's disease, renal and liver diseases
• Tpn
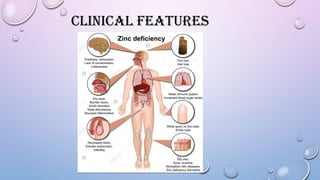
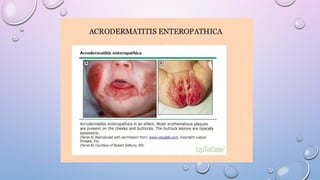
9. 11. ACRODERMATITIS ENTEROPATHICA
• Autosomal recessive
• Inherited defect in Zinc transporter
• Impaired intestinal absorption of Zinc
• Erythematous lesions - Vesiculobullous/ Pustular
lesions – Erythamatous plaques
• Nail changes : Brittle nails, Paronychia, Beau’s lines,
Leukonychia
Acral dermatitis
Alopecia Diarrhoea
13. TREATMENT
• Zinc supplementation – Zinc Sulphate
• Infants and children-0.5 to 1 mg/kg/day 1-3 divided doses
• Adults :- Malabsorption, diarrhoea, burns : 1-2mg/kg
• Acrodermatitis enteropathica / Wilson’s disease : 3 mg/kg/day
• Acrodermatitis Enteropathica : Lifelong zinc supplementation
• Acquired deficiency : Treat the underlying cause