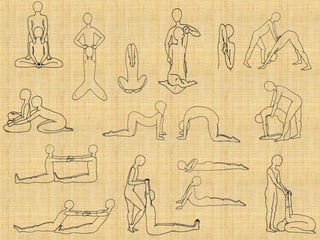
This document discusses arthritis, its types, symptoms, causes, and treatment options. It covers the following types of arthritis: osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, lupus arthritis, and spondyloarthropathies. Exercise, diet, weight management, and yoga are recommended for arthritis prevention and management. Specific gentle yoga poses, breathing techniques, relaxation practices, and meditation are outlined for their arthritis relief benefits.