The x-iscker platform is designed to emulate both RISC and CISC architectures using FPGA technology, providing a configurable environment for educational purposes. It allows users to monitor processor behavior during execution and is intended for programmers familiar with processor organization. The platform promotes hands-on learning and development of custom embedded processor solutions through its emulation, application, and reconfiguration capabilities.
![X-ISCKER
Reconfigurable Platform for the Emulation of RISC and CISC Architectures
Jose Pablo Pinilla Alfredo Gualdrón
Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana
Bucaramanga, Colombia Bucaramanga, Colombia
jose.pinilla@upb.edu.co alfredo.gualdron@upb.edu.co
Abstract—This is a project planned to illustrate the structure debugging functionalities for the two processors, called
and operational foundations of Central Processing Units, through RISCKER and CISCKER. A stand-alone application of the
the implementation of a configurable system with two processors, processors is also available, without the IDE-FPGA
one RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing) and one CISC communication. The final stage of development for the
(Complex Instruction Set Computing), on an FPGA (Field platform is “Reconfiguration”. The availability of all source
Programmable Gate Array), along with a programming and code is an invitation to modify the provided architectures.
monitoring user interface software.
Figure 1 is a diagram of the X-ISCKER platform including
Index Terms—Computer Architecture, RISC, CISC, FPGA, the communication module.
Embedded Processors.
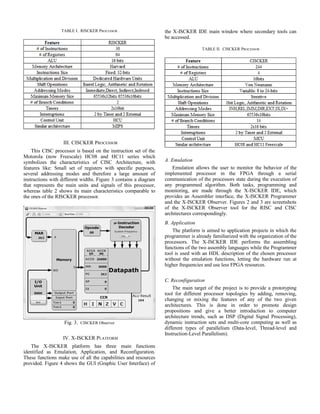
II. RISCKER PROCESSOR
I. INTRODUCTION A RISC processor instruction set and organization is
designed so that it represents this architecture’s characteristics,
Computer organization and computer architecture design such as: A large amount of registers, few Instructions of the
courses rely mostly on commercial microcontrollers that can be same width and logical-arithmetic operations only between
used in application projects. But being commercial implies that registers.
those are closed designs, meaning their documentation leaves This processor’s structure is similar to the Multi-cycle
organization details unmentioned. Another educational option MIPS described by Patterson and Hennessy [1] in order to
is the use of simulation programs, which can be very detailed facilitate the change between this system and a commercial
but lack the applicability of an Integrated Circuit (IC). MIPS-based processor in terms of code compatibility and
X-ISCKER or Reduced/Complex Instruction Set structural behavior. An approximation of the design is shown
Computing Key Educational Resource is a software-hardware in figure 2, highlighting the main units and signals, while an
platform that combines the applicability of a microcontroller IC overview of the main characteristics for its operation can be
with the detailed functionality and monitoring capabilities of a seen on table 1.
processor simulator. It is based on the development of two
basic architectures, one RISC and one CISC, in Verilog HDL
for any FPGA, an IDE (Integrated Development Environment)
software and a thorough documentation of their functionality.
Fig. 1. X-ISCKER Platform.
The user is able to emulate any of the two architectures in
an FPGA while monitoring its state during the execution of any
program written in its corresponding assembly language. The Fig. 2. RISCKER Observer.
IDE is capable of “assembling and linking”, programming, and](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paperxisckeren-121108080618-phpapp02/75/X-ISCKER-1-2048.jpg)
![development is posted on the Computer Architecture course
web page for Informatics Engineers[2], and all finished and
tested results are linked to the X-ISCKER site.
This experience shows that the X-ISCKER platform is not
only useful for digital circuit designers but also for software
designers, covering a wide range of research areas where
students can start developing their ideas.
VI. SUMMARY
Today’s architectures have grown to be more complex due
to compatibility-guided development and the addition of
necessary advanced features, making them “difficult to explain
and impossible to love” [1]. This demands a very solid
introduction of computer architecture trends and evolution, by
empirically studying the principles from which modern
processors are ruled and allowing the designer to test its models
according to their knowledge and application requirements.
Fig. 4. X-ISCKER IDE. The X-ISCKER platform delivers the Verilog HDL
description of two processors, an IDE software and the
documentation that will allow new learners to familiarize with
V. STUDENTES EXPERIENCE computer architecture foundations, and computer designers to
come up with custom embedded processor solutions to their
Throughout the days following the presentation of the X- applications.
ISCKER platform to the academic evaluators and the
The source files for the X-ISCKER platform and related
engineering community at the UPB (Universidad Pontificia
further development will be kept available at the ADT
Bolivariana), there was positive feedback and more
(Advanced Digital Technologies) students’ research group of
importantly the students showed interest on the further
the UPB website [3]..
development of this platform. According to previous definition
of future projects related to the X-ISCKER platform, the REFERENCES
development of a multi-platform assembler is proposed as a
[1] D. Patterson and J. Hennessy, “Computer Organization and Design”,
course project for the Informatics Engineering students taking Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 2005.
the Computer Architecture course at the UPB. This is a [2] H. A. Becerra (2012, Oct 1), “Proyecto ENSAMBLADOR X-ISCKER”,
development guided by the developers of the platform where Available: https://sites.google.com/site/22012archcompupb/proyecto-
information voids were filled with further documentation and ensamblador-x-iscker
where students were required to understand the operation of the [3] A. Gualdrón and J. P. Pinilla (2012, Jul 2), “Semillero ADT -
RISCKER processor in order to develop a fully operational XISCKER”, Available: http://semilleroadt.upbbga.edu.co/xiscker
assembler using Java. A step by step description of this [4] S. G. Shiva, “Computer Organization Design and Architecture”, 4th
Edition, CRC Press, 2008.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paperxisckeren-121108080618-phpapp02/85/X-ISCKER-3-320.jpg)