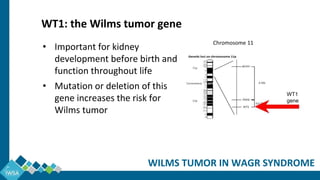
WAGR syndrome is a rare genetic condition characterized by Wilms tumor (a form of kidney cancer that occurs mostly in children), aniridia (eye condition), genital abnormalities, and developmental delays. Children with WAGR syndrome have a very high risk (1 in 2) of developing Wilms tumor due to immature cells in the kidneys called nephrogenic rests that have the potential to develop into cancer. Treatment for Wilms tumor in WAGR syndrome may include surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy tailored to each individual case. Long term surveillance is important given the risks.