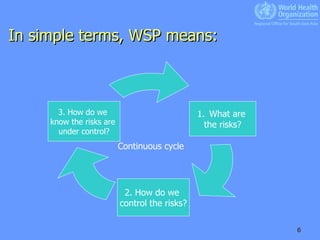
Water Safety Plans (WSPs) are being implemented in various countries in South-East Asia to improve access to safe drinking water and reduce waterborne diseases. WSPs involve identifying hazards and risks from catchment to consumer, prioritizing the highest risks, and mitigating risks through control measures. The key drivers for WSPs are the WHO guidelines emphasizing risk assessment and management, and the need to prevent the majority of diarrheal diseases through safe water and hygiene. Countries that have implemented WSPs have seen benefits like improved water quality, reduced waterborne diseases, and more sustainable water supply systems.