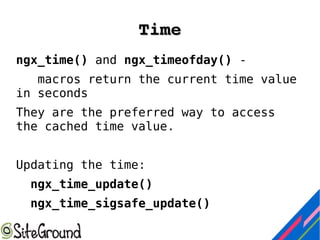
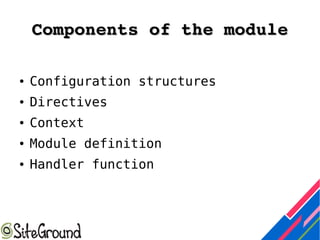
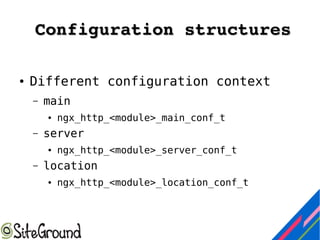
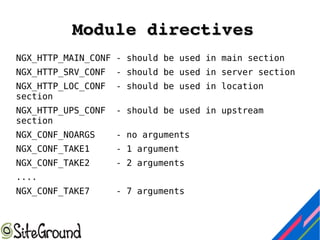
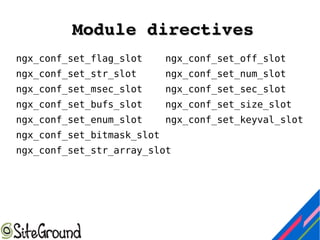
This document discusses Nginx module development. It covers the differences between static and dynamic modules, how to enable third-party modules, and an overview of Nginx request handling. It also provides details on module components like configuration structures, directives, context, and handler functions. Examples are given for common return codes, module definition, and developing a sample "hello world" module.











![Module directivesModule directives
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_hello_commands[] =
{
{ ngx_string("hello"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_conf_set_str_slot,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_hello_loc_conf_t, name),
&ngx_http_hello_p },
ngx_null_command
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nginx-module-development-180316064724/85/Writing-Nginx-Modules-17-320.jpg)

![Module directivesModule directives
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_hello_commands[] =
{
{ ngx_string("hello"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_conf_set_str_slot,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_hello_loc_conf_t, name),
&ngx_http_hello_p },
ngx_null_command
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nginx-module-development-180316064724/85/Writing-Nginx-Modules-20-320.jpg)
![Module directivesModule directives
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_hello_commands[] =
{
{ ngx_string("hello"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_conf_set_str_slot,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_hello_loc_conf_t, name),
&ngx_http_hello_p },
ngx_null_command
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nginx-module-development-180316064724/85/Writing-Nginx-Modules-22-320.jpg)
![Module directivesModule directives
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_hello_commands[] =
{
{ ngx_string("hello"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_conf_set_str_slot,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_hello_loc_conf_t, name),
&ngx_http_hello_p },
ngx_null_command
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nginx-module-development-180316064724/85/Writing-Nginx-Modules-23-320.jpg)
![Module directivesModule directives
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_hello_commands[] =
{
{ ngx_string("hello"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_conf_set_str_slot,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_hello_loc_conf_t, name),
&ngx_http_hello_p },
ngx_null_command
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nginx-module-development-180316064724/85/Writing-Nginx-Modules-24-320.jpg)
![Module directivesModule directives
ngx_http_hello_commands[] = {
...
&ngx_http_hello_p },
...
static ngx_conf_post_handler_pt
ngx_http_hello_p = ngx_http_hello;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nginx-module-development-180316064724/85/Writing-Nginx-Modules-25-320.jpg)