This document provides an overview of Pascal programming including:
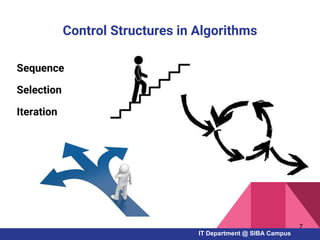
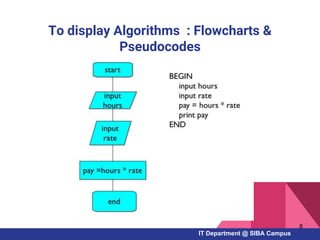
- The basics of algorithms, flowcharts, and pseudocode for representing problems
- An introduction to the Pascal programming language, its history, popularity, and the Turbo Pascal integrated development environment
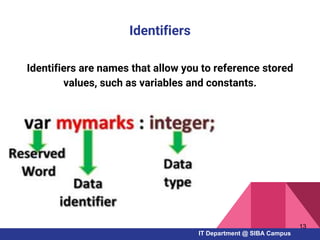
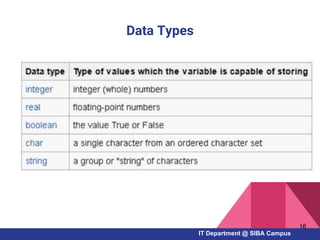
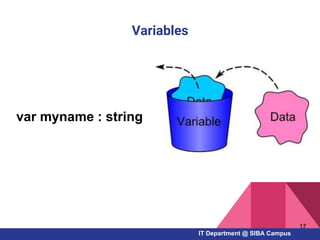
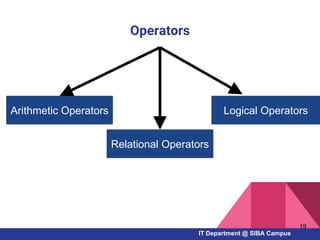
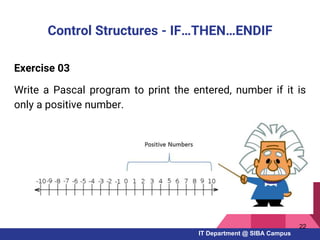
- Key Pascal concepts like identifiers, reserved words, data types, variables, constants, and control structures
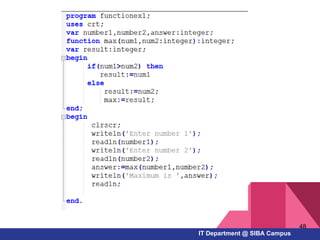
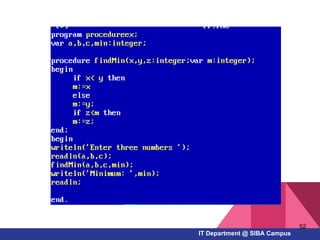
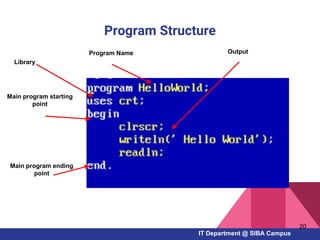
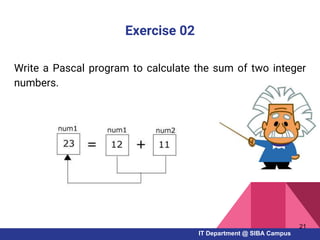
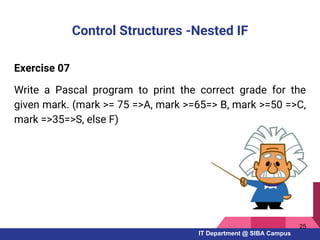
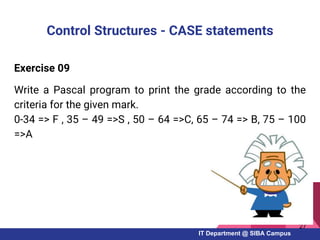
- Examples of Pascal programs for calculating sums, checking conditions, and using selection and repetition structures
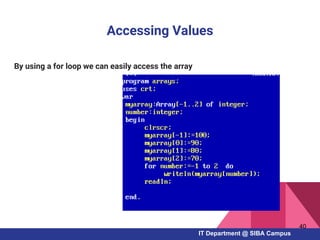
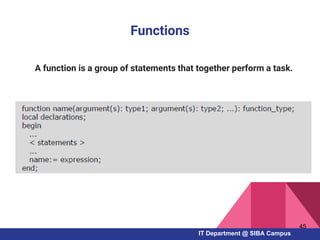
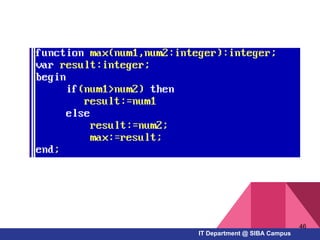
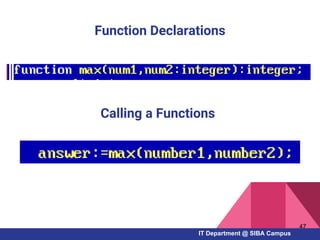
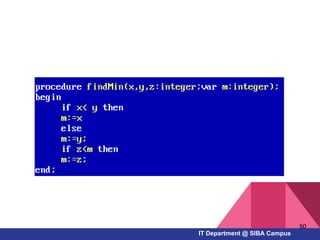
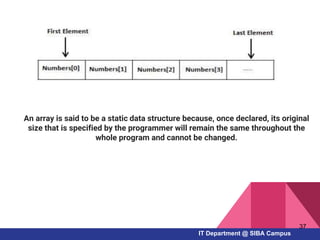
- How to work with arrays, functions, and procedures as fundamental programming structures in Pascal
The document contains explanations, syntax examples, and exercises to help learn and practice Pascal programming.



















![IT Department @ SIBA Campus
Declaring Arrays
Syntax
Var
<arrayName> : Array[n..m] of <Data Type>;
38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/writeprogramstosolveproblems-pascalprogramming-180312103433/85/Write-programs-to-solve-problems-pascal-programming-38-320.jpg)
![IT Department @ SIBA Campus
Assigning Values
Syntax
<arrayName>[index] := <relevant data>
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/writeprogramstosolveproblems-pascalprogramming-180312103433/85/Write-programs-to-solve-problems-pascal-programming-39-320.jpg)