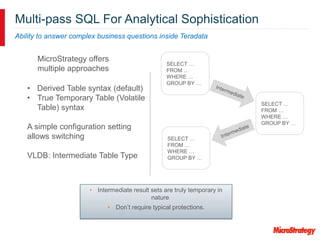
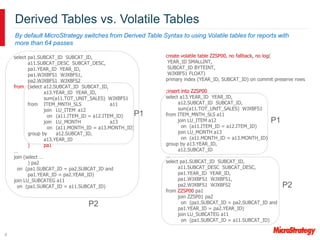
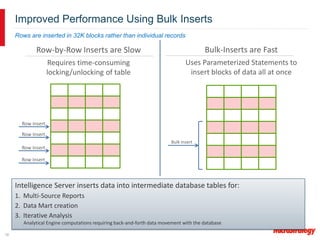
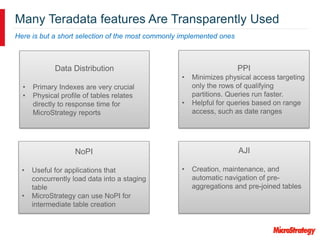
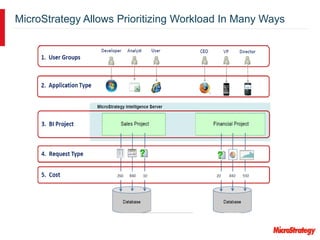
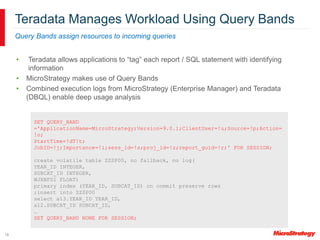
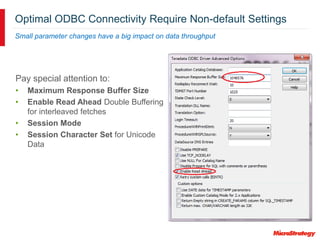
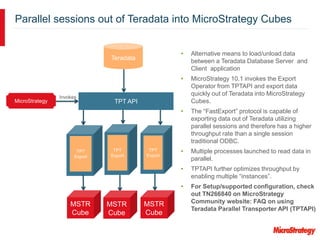
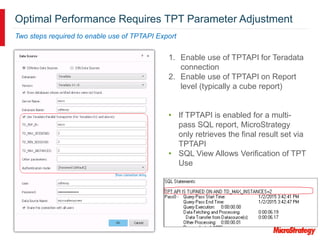
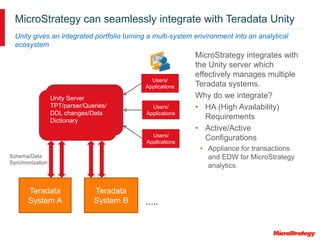
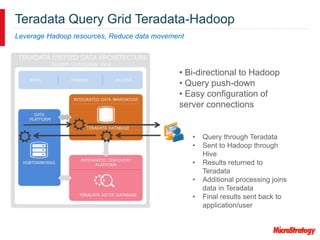
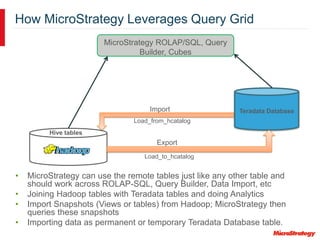
MicroStrategy and Teradata have a long partnership in providing business intelligence capabilities. MicroStrategy is optimized to run on Teradata and leverages many Teradata features and extensions for performance and scalability. These include multi-pass SQL, bulk inserts, Teradata indexing, functions, and syntax. MicroStrategy also integrates with Teradata tools and provides additional functionality like middle-tier computations and caching.