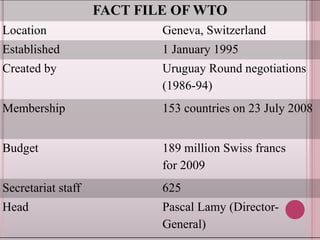
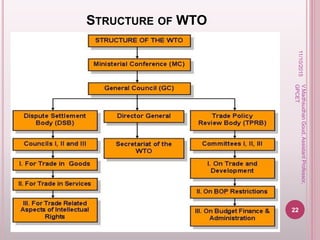
The World Trade Organization (WTO) came into being on January 1, 1995 replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT). The WTO oversees international trade and resolves trade disputes between member nations. It aims to ensure free and fair trade globally through agreements covering trade in goods, services and intellectual property. The WTO currently has 153 member countries and works to lower trade barriers through negotiations while providing a framework for implementing trade agreements and monitoring national trade policies.