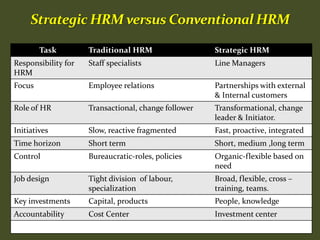
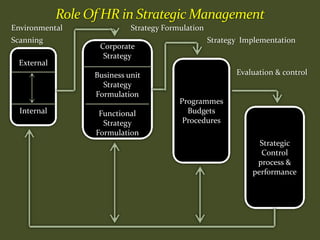
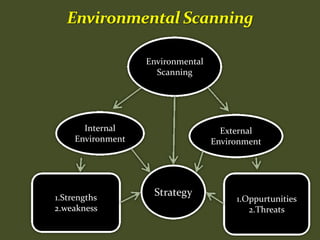
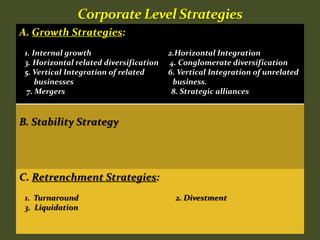
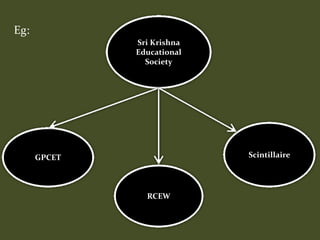
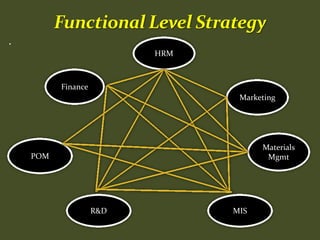
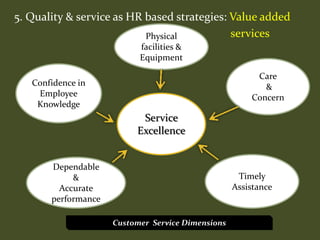
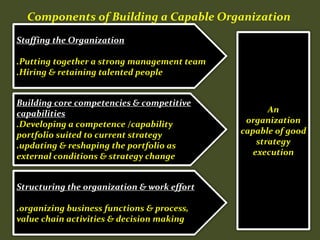
HR plays an important role in mergers and acquisitions by defining the new organizational architecture and identifying parts that need restructuring. The HR department must conduct an audit to assess what needs to change, and identify methods to renovate architectural components. HR also needs to set clear priorities like promoting teamwork and implementing pay-for-performance programs. During strategic evaluations, HR should provide data on its return on investment and be rated by customers to assess how its initiatives support business strategy goals.