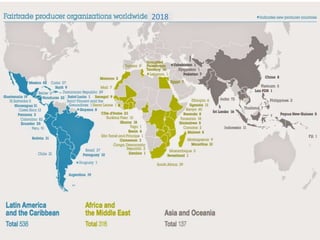
The document outlines the principles, functions, and benefits of fair trade, emphasizing its aim to empower producers in developing countries and promote sustainability through ethical practices. It describes the various fair trade products, the World Fair Trade Organization's code of practice, and statistics highlighting the impact of fair trade on farmers and workers. Additionally, it addresses challenges and criticisms of fair trade, including its ethical basis and selling techniques.