The document is a solutions worksheet for theory of probability, focusing on sample spaces, events, and their intersections. It illustrates various probability events related to a taxicab company, evaluates probabilities from claims by government officials, and calculates examination results for students. Key problems involve identifying event pairs, mutual exclusivity, and summarizing probabilities for different outcomes.
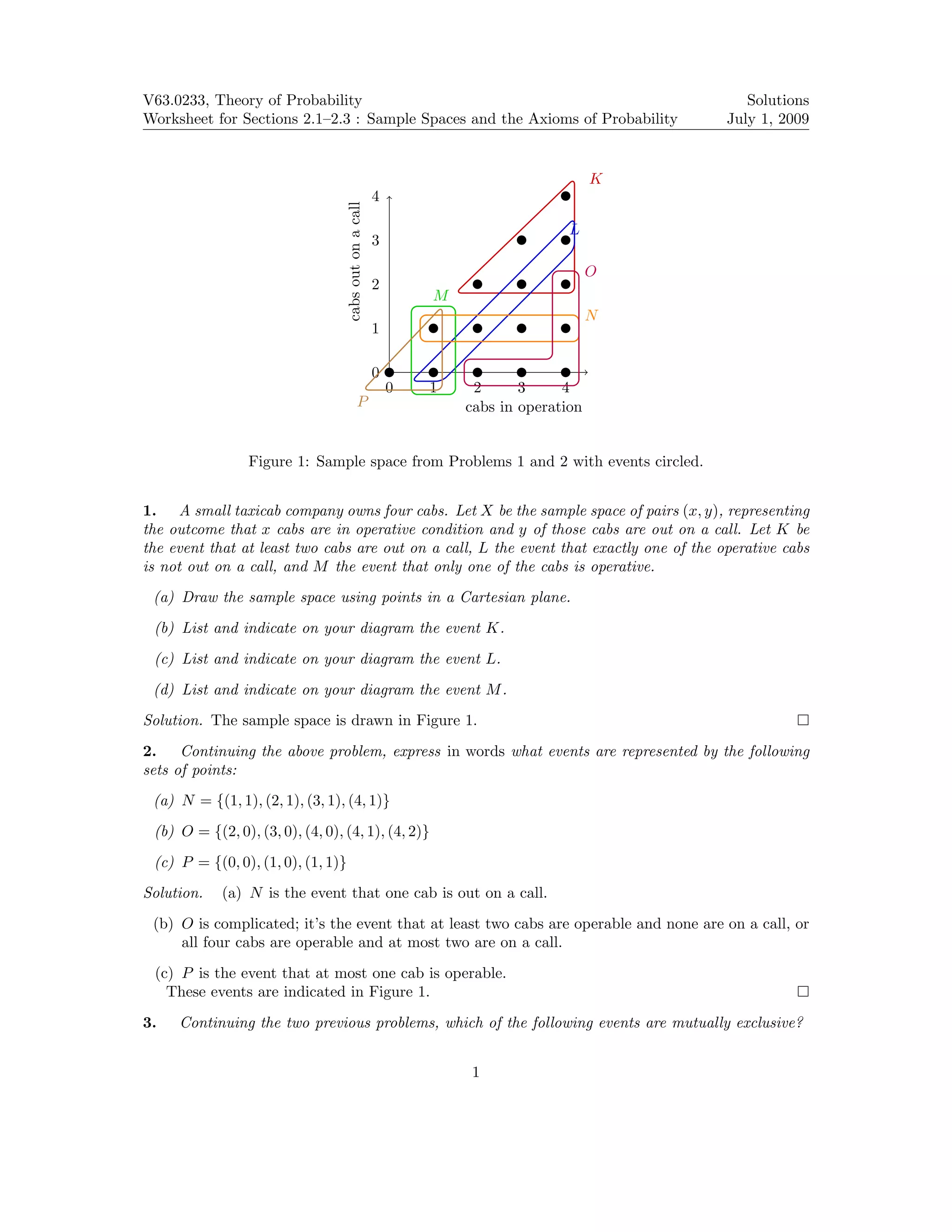
![(a) K and M (d) L and P
(b) K and O (e) O and P
(c) M and N (f ) K and N
Solution. Referring again to Figure 1, we can see which of them are and are not mutually exclusive:
(a) mutually exclusive (d) not mutually exclusive; they share the out-
come (1, 0)
(b) not mutually exclusive; they share the out-
come (4, 2)
(e) mutually exclusive
(c) not mutually exclusive; they share the out-
come (1, 1) (f) mutually exclusive
4. Referring to the sample space of Problems 1 and 2, list the points which constitute the following
events, and express them in words:
(i) K (iv) M ∩ P (vii) O ∩ P
(ii) O (v) K ∪ N (viii) M ∪ P
(iii) L ∪ N (vi) L ∩ M (ix) O ∩ L
Solution. (i) K is the event that at most one cab is out on a call.
K = {(0, 0), (1, 0), (2, 0), (3, 0), (4, 0), (1, 1), (2, 1), (3, 1), (4, 1)}
(ii) As a list,
{ }
O = (0, 0), (1, 0), (1, 1), (2, 1), (3, 1), (2, 2), (3, 2), (3, 3), (4, 3), (4, 4)
O is worse than O. Looking ahead, we could use DeMorgan’s laws and the distributive laws
to get a better description of O in words. Notice
O = ((x ≥ 2) ∩ (y = 0)) ∪ ((x = 4) ∩ (y ≤ 2))
So
O = [((x ≥ 2) ∩ (y = 0)) ∪ ((x = 4) ∩ (y ≤ 2))]
= ((x ≥ 2) ∩ (y = 0)) ∩ ((x = 4) ∩ (y ≤ 2))
( ) ( )
= (x ≥ 2) ∪ (y = 0) ∩ (x = 4) ∪ (y ≤ 2)
= ((x < 2) ∪ (y > 0)) ∩ ((x < 4) ∪ (y > 2))
( ) ( )
= (x < 2) ∩ (x < 4) ∪ (x < 2) ∩ (y > 2)
( ) ( )
∪ (y > 0) ∩ (x < 4) ∪ (y > 0) ∩ (y > 2)
( ) ( )
= (x < 2) ∪ (x < 2) ∩ (y > 2) ∪ (y > 0) ∩ (x < 4) ∪ (y > 2)
( )
= (x < 2) ∪ (y > 0) ∩ (x < 4) ∪ (y > 2)
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson03-samplespacesaxiomsofprobabilityws-sol-090703063825-phpapp02/75/Worksheet-Sample-Spaces-the-Axioms-of-Probability-solutions-2-2048.jpg)
![So O is the event that either
1) fewer than two cabs are operative,
2) more than two cabs are out on a call, or
3) not all cabs are operative and some are out on calls
(iii) L ∪ N is the event that exactly one of the cabs is not out on a call or exactly one of the cabs
is out on a call.
L ∪ N = {(1, 0), (2, 1), (3, 2), (4, 3), (1, 1), (2, 1), (3, 1), (4, 1)}
(iv) M ∩ P is the event that only one of the cabs is operative, and at most one of the cabs is
operable. The first is stricter than the second, so the intersection is M , the event that only
one cab is operative:
M ∩ P = P = {(1, 0), (1, 1)}
(v) K ∪ N is the event that at least two cabs are out on a call, or exactly one cab is out on a call.
To simplify, at least one cab is out on a call:
K ∪ N = {(1, 1), (2, 1), (3, 1), (4, 1), (2, 2), (3, 2), (4, 2), (3, 3), (4, 3), (4, 4)}
(vi) L ∩ M is the event that one cab is operable, and it is not out on a call.
L ∩ M = {(1, 0)}
(vii) By looking at Figure 1, we can see that O ∩ P = O.
(viii) M ∪ P is the event that exactly one cab is operable, or that at least two cabs are operable.
In other words, at least one cab is operable.
{
K ∪ P = (1, 0), (2, 0), (3, 0), (4, 0), (1, 1), (2, 1), (3, 1),
}
(4, 1)(2, 2), (3, 2), (4, 2), (3, 3), (4, 3), (4, 4)
(ix) Since O and L are mutually exclusive, O ∩ L = O.
5. Analyzing business conditions in general, four government officials make the following claims:
The first claims that the probabilities for unemployment to go up, remain unchanged, or go down
are, respectively, 0.51, 0.33, and 0.12, the second claims that the respective probabilities are 0.55,
0.49, and −0.04, the third claims that the respective probabilities are 0.52, 0.38, and 0.10, and the
fourth claims the respective probabilities are 0.48, 0.34, and 0.21. Comment on these claims.
Solution. [Rachel] We can arrange the purported probabilities in a table.
Analyst 1 2 3 4
P (up) 0.51 0.55 0.52 0.48
P (unchg) 0.33 0.49 0.38 0.34
P (down) 0.12 -0.04 0.10 0.21
Total 0.96 1.00 1.00 1.03
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson03-samplespacesaxiomsofprobabilityws-sol-090703063825-phpapp02/75/Worksheet-Sample-Spaces-the-Axioms-of-Probability-solutions-3-2048.jpg)
