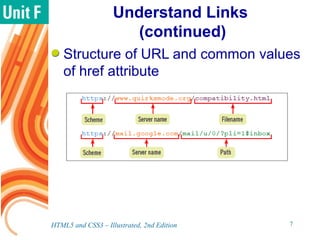
Hyperlinks provide links within and between documents. Links are defined using the <a> element and the href attribute specifies the target document location. Navigation bars contain sets of links for moving between web pages. Pseudo-classes allow formatting of link states like hover and active. Target documents can open in new tabs using the target attribute. Hash links create internal document links using element IDs. Accessibility is improved by allowing users to skip navigation bars.