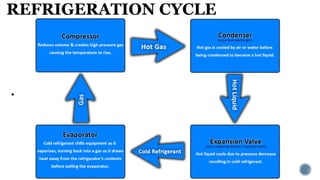
The document explains heat transfer and energy transformation, detailing how thermal energy moves from hotter to cooler objects and the mechanisms for non-spontaneous heat transfer through devices like heat pumps. It outlines the first and second laws of thermodynamics, emphasizing that heat cannot flow naturally from cold to hot without work being done. Additionally, it describes the refrigeration cycle, including the stages of compression, condensation, expansion, and evaporation, which are crucial for cooling processes.