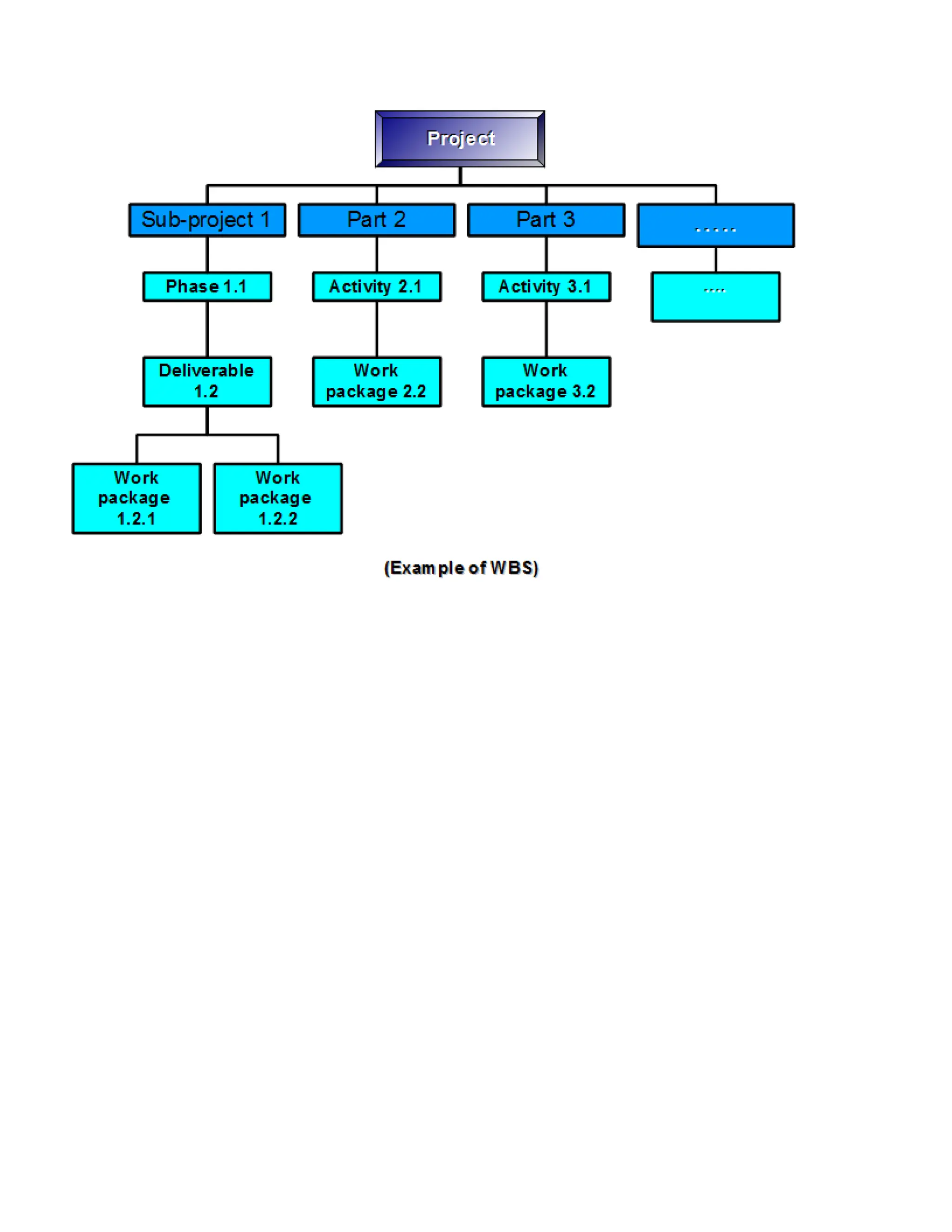
The document explains the concept of Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), a project management methodology that simplifies complex projects into manageable tasks for better supervision and estimation. It outlines the importance of WBS in organizing projects, assigning responsibilities, and estimating costs and risks, while also discussing various rules for task breakdown and its representation in diagrams. Additionally, the document highlights the relationship between WBS and Organizational Breakdown Structure (OBS), emphasizing their roles in project accountability, resource allocation, and management efficiency.