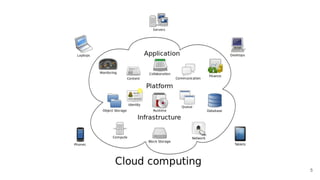
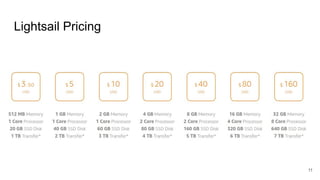
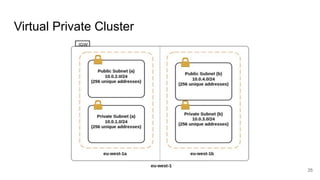
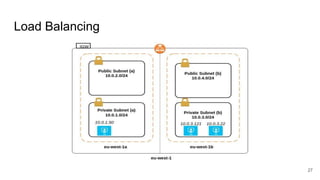
The document provides a comprehensive guide on deploying WordPress applications using AWS, specifically focusing on Amazon Lightsail and Linux servers. It covers cloud computing fundamentals, the advantages and disadvantages of different deployment methods, and highlights important architectural considerations including security, availability, scalability, and visibility. The text also includes technical configurations for setting up WordPress on both platforms, along with cost implications.