Embed presentation
Downloaded 69 times




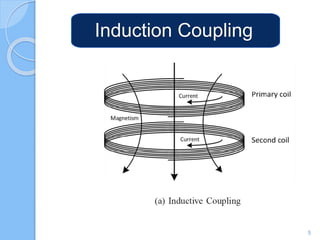
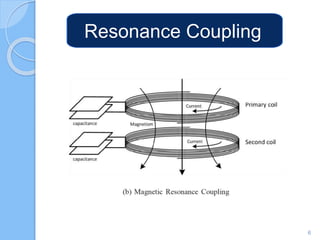
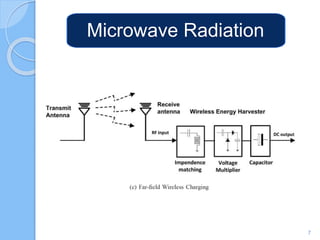

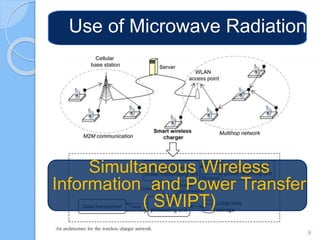


Wireless charging transmits power through an air gap to devices for energy replenishment. It offers benefits such as reduced cost, improved usability, enhanced durability, and compatibility across different brands and models. Key techniques for wireless charging include inductive coupling, resonance coupling, and microwave radiation.










