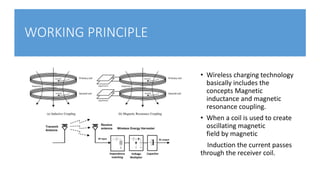
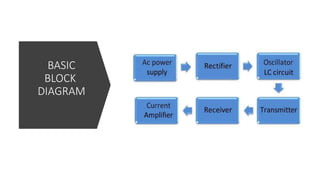
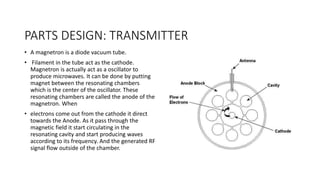
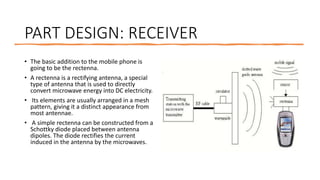
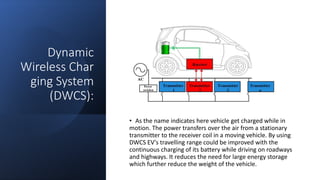
This document provides an overview of wireless charging technology. It discusses the need for wireless charging to overcome issues with wired charging standards and clutter. It then describes the basic working principles of magnetic induction and magnetic resonance coupling. The document outlines the main components involved in wireless charging systems, including transmitters, receivers, and antennas. It also explains different wireless charging techniques such as inductive, radio, and resonant charging and their applications for powering devices like mobile phones and electric vehicles.