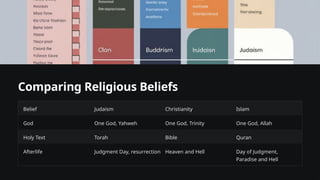
Welcome, esteemed students. Today marks the beginning of our exploration into the vibrant, complex, and often enigmatic world of religion. In this introductory lecture, I want to lay a foundation that underscores why the study of religion is not merely an academic pursuit, but a critical endeavor for anyone seeking to understand the human condition.
https://leshley.ca