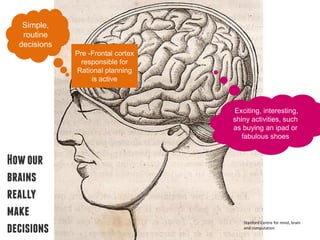
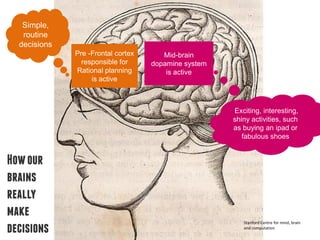
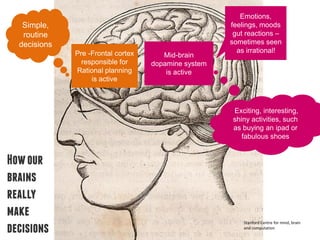
Our brains are wired to make most decisions automatically through emotional and social influences rather than rational deliberation. Priming, social norms, sensory language and who communicates messages can all subtly shape behaviors. A study found that telling hotel guests 75% of others reused towels was more effective at encouraging reuse than messages about saving the environment. Understanding how the unconscious mind works allows for better influencing behaviors.