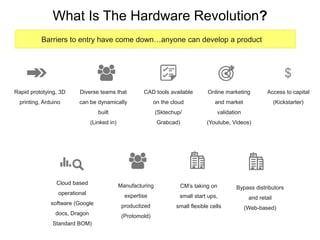
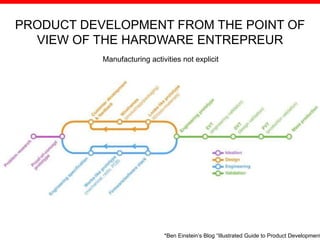
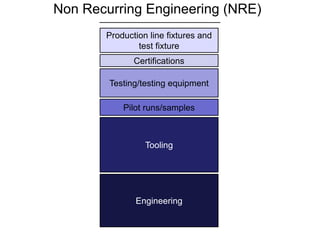
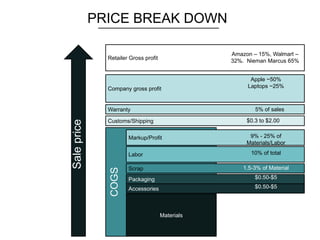
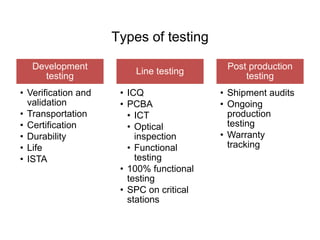
The document discusses the complexities of transitioning from prototypes to saleable consumer electronics, focusing on challenges in cost, quality, and scheduling. It highlights the hardware revolution's impact on small companies, allowing them to operate like larger firms and emphasizes the importance of thorough manufacturing planning and quality control throughout the product development process. Additionally, it addresses common pitfalls, the significance of selecting the right contract manufacturers, and the need for rigorous testing and certifications to meet market expectations.