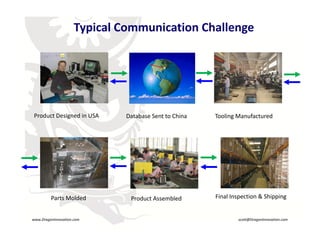
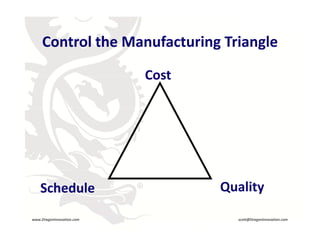
This document provides an overview of manufacturing in China and considerations for companies looking to manufacture products there. It discusses reasons for manufacturing in China including lower costs, available labor, and existing manufacturing technology. It also covers selecting the right manufacturing partner, controlling costs, schedule, quality and protecting intellectual property. Upcoming challenges with the Chinese market like increasing labor costs and currency exchange rates are also mentioned.