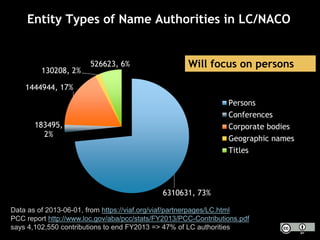
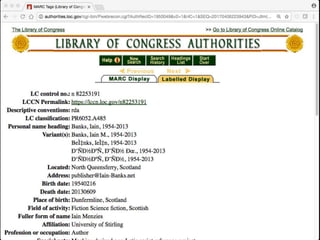
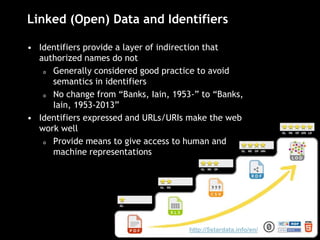
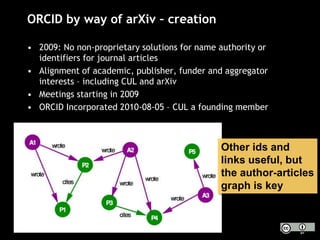
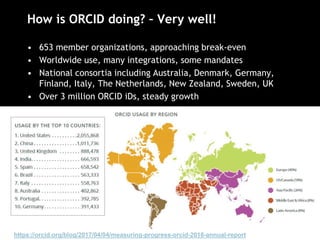
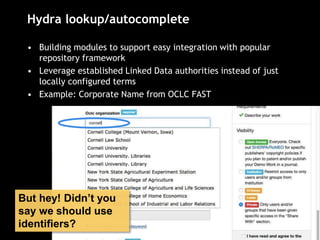
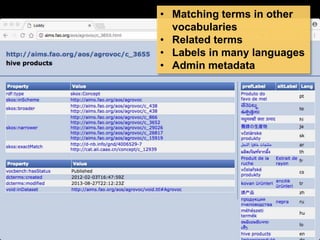
The document discusses the increasing role of various identifiers, such as ORCID, ISNI, NACO, and VIAF, in library authority work and cataloging practices. It highlights the significance of these identifiers in improving the accessibility and accuracy of names associated with researchers and their works, particularly in the context of linked data initiatives for libraries. Additionally, the document provides an overview of the benefits and goals of implementing these identifiers, including better discovery and maintenance in library systems.