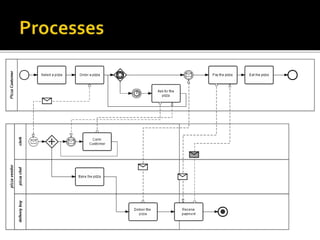
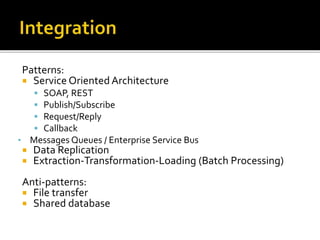
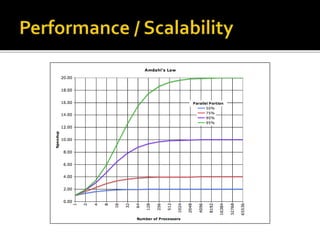
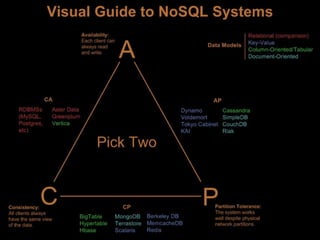
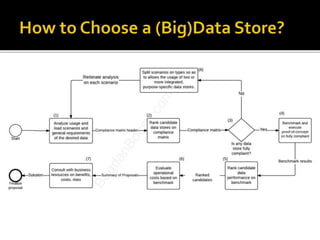
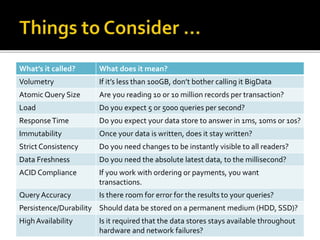
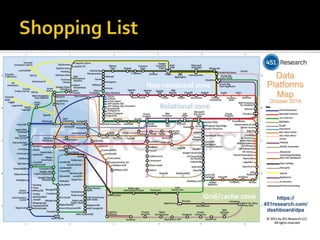
The document outlines the essentials of information technology architecture, including definitions, processes, concerns, and case study considerations for selecting a big data store. It emphasizes the importance of addressing performance, scalability, cost, and various architectural patterns while avoiding common anti-patterns. Key factors in choosing a data store are discussed, such as volumetry, query response times, consistency, and high availability.