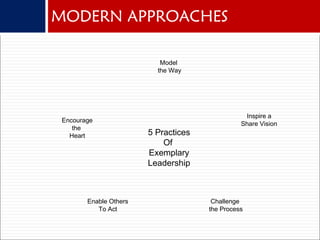
The document discusses the difference between managing and leading projects, emphasizing both the complexity of management and the need for leadership to drive change. It outlines five practices of exemplary leadership identified by Kouzes & Posner, focusing on modeling the way, inspiring a shared vision, challenging processes, enabling others to act, and encouraging the heart. Additionally, it highlights the importance of emotional intelligence in effective leadership, including self-awareness, social awareness, and social skills.