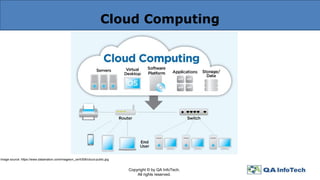
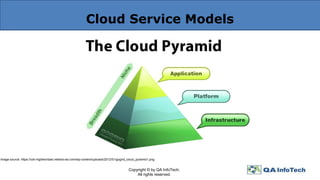
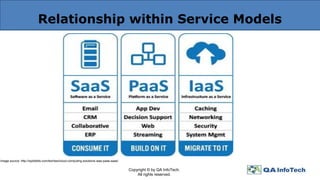
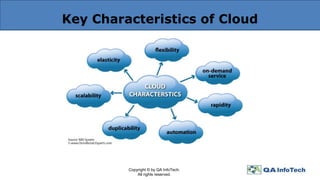
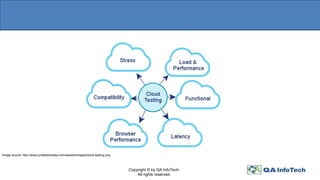
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, defining it as a centralized delivery system for computing services over the internet and detailing the three primary service models: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. It also addresses key characteristics of cloud computing and the importance of thorough cloud testing, including various testing types such as functional, load, performance, network security, and interoperability testing. Finally, it discusses the benefits and challenges of cloud computing, as well as future trends in the field.